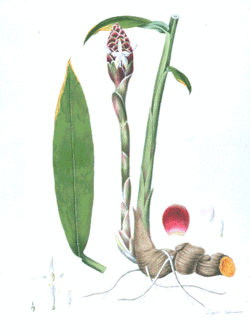
Biology:Zingiber cassumunar
| Zingiber cassumunar | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Clade: | Commelinids |
| Order: | Zingiberales |
| Family: | Zingiberaceae |
| Genus: | Zingiber |
| Species: | Z. cassumunar
|
| Binomial name | |
| Zingiber cassumunar Roxb.
| |
Cassumunar ginger: Zingiber cassumunar, now thought to be a synonym of Zingiber montanum (J.König) Link ex A.Dietr.,[1] is a species of plant in the ginger family and is also a relative of galangal. It is called plai (ไพล) in Thailand, in addition to (ว่านไฟ wan-fai) in Isan language and (ปูเลย bpulai) in northern Thai language. The rhizome of variant 'Roxburgh' is used medicinally in massage and even in food in Thailand, and somewhat resembles ginger root or galangal.[2] In aromatherapy, plai oil is used as an essential oil and is believed to ease pain and inflammation. It is also known as ponlei (ពន្លៃ) in Cambodia.
A Japanese study from 1991 suggests (E)-1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)but-1-ene, an active ingredient of Z. cassumunar rhizomes, has analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties.[3] In addition, an American study found that plai oil exhibits antimicrobial activity against a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, dermatophytes, and yeasts.[4] A study also showed essential oil from Z. cassumunar had anti-microbial activity against XDR Acinetobacter baumannii and synergized with medically useful antibiotics.[5] Finally, a 1992 study discovered the zerumbone contained in the rhizomes of the plant has antifungal properties against pathogenic fungi.[6]
The plant also contains the essential oils sabinene 31–48%, terpineol 4–30%,[2] and apparently unique curcuminoid antioxidants, namely cassumunarin types A, B, and C.[7]
References
- ↑ "Search results — the Plant List". http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl/search?q=zingiber.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "ICS-UNIDO - MAPs". http://portal.ics.trieste.it/MAPs/MedicinalPlants_Plant.aspx?id%3D665. International Center for Science and High Technology Portal
- ↑ Ozaki, Y; Kawahara, N; Harada, M (1991). "Anti-inflammatory effect of Zingiber cassumunar Roxb. And its active principles". Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 39 (9): 2353–6. doi:10.1248/cpb.39.2353. PMID 1804548.
- ↑ Pithayanukul, P.; Tubprasert, J.; Wuthi-Udomlert, M. (2007). "In Vitro antimicrobial activity of Zingiber cassumunar (Plai) oil and a 5% Plai oil gel". Phytotherapy Research 21 (2): 164–9. doi:10.1002/ptr.2048. PMID 17128430.
- ↑ Boonyanugomol, W.; Kraisriwattana, K.; Rukseree, K.; Boonsam, K.; Narachai, P. (2017). "In vitro synergistic antibacterial activity of the essential oil from "Zingiber cassumunar" Roxb against extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strains". Journal of Infection and Public Health 10 (5): 586–592. doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2017.01.008. PMID 28162962.
- ↑ Kishore, N.; Dwivedi, R. S. (1992). "Zerumbone: A potential fungitoxic agent isolated from Zingiber cassumunar Roxb". Mycopathologia 120 (3): 155–9. doi:10.1007/BF00436393.
- ↑ Jitoe, A (1994). "Novel Antioxidants, Cassumunarin A, B, and C, from Zingiber cassumunar". Tetrahedron Letters 35 (7): 981–4. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)79944-8.
External links
- Plai Page (in Thai)
Wikidata ☰ Q3779298 entry
 |

