Biology:Oxalis stricta
| Oxalis stricta | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Oxalidales |
| Family: | Oxalidaceae |
| Genus: | Oxalis |
| Species: | O. stricta
|
| Binomial name | |
| Oxalis stricta | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Oxalis europaea Jord. | |
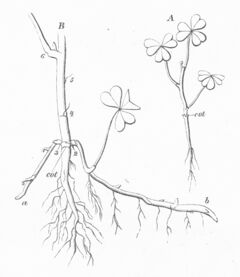
Oxalis stricta, called the common yellow woodsorrel (or simply yellow woodsorrel), common yellow oxalis, upright yellow-sorrel, lemon clover, or more ambiguously and informally "sourgrass", "sheep weed",[2] or "pickle plant", is a herbaceous plant[3] native to North America, parts of Eurasia, and a rare introduction in Britain.[4] It tends to grow in woodlands, meadows, and in disturbed areas as both a perennial and annual.[5] Erect when young, this plant later becomes decumbent as it lies down, and branches regularly. It is not to be confused with similar plants in the same genus which are also often referred to as "yellow woodsorrel".
Growth
Commonly considered a weed of gardens, fields, and lawns, it grows in full sun or shade. The alternate leaves of this plant are divided into three heart-shaped leaflets (a typical trait of other species of Oxalis) that can grow up to 2 cm wide. These leaves curl up at night (exhibiting nyctinasty), and open in the day to perform photosynthesis. The mature seed capsules open explosively when disturbed (a very similar trait to that of the mature seed capsules or fruits of plants found in the genus Impatiens) and can disperse seeds up to 4 meters (about 13 feet) away. The flowers of the plant are hermaphroditic, blooming from July to October.
O. stricta generally requires dry or moist, alkaline soils, preferring sandy and loamy dirt to grow in. It requires well-drained soil and can grow in nutritionally poor grounds.
Cultivation
Culinary uses
All parts of the plant are edible,[4] with a distinct tangy flavor (common to all plants in the genus Oxalis). However, it should only be eaten in small quantities, since oxalic acid is an antinutrient and can inhibit the body's absorption supply of calcium.[6]
The leaves and flowers of the plant are sometimes added to salads for decoration and flavoring. These can also be chewed raw (along with other parts of the plant, but not the root) as a thirst-quencher.[4] The green pods are pleasant raw, having a juicy crisp texture and a tartness similar to rhubarb in flavor.
The leaves can be used to make a flavored drink that is similar in taste to lemonade,[4] and the whole plant can be brewed as herbal tea that has an aroma somewhat like that of cooked green beans.
The juices of the plant have been extracted from its greens as a substitute to common vinegar.
Oxalis stricta contains large amounts of vitamin C.[citation needed]
Practical uses
An orange dye can be obtained by boiling the whole plant.[4]
Medicinal uses
A poultice of the plant has been used to treat swellings.[4]
References
- ↑ {{citation | mode = cs1 | title = Oxalis stricta L. | work = Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN) | url = https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?26216 | publisher = [[Organization:Agricultural Research ServAgricultural Research Service (ARS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) | access-date = 10 March 2011 }}
- ↑ Common Yellow Oxalis (Oxalis stricta)
- ↑ Oxalis stricta
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Oxalis stricta - Plants For A Future. Retrieved 2016-08-02.
- ↑ http://www.kingdomplantae.net/yellowWoodSorrel.php Yellow Wood Sorrel |access-date=2018-08-05
- ↑ "Oxalis stricta (Yellow Wood Sorrel) - Practical Plants". http://practicalplants.org/wiki/Oxalis_stricta.
External links
- Oxalis stricta - Plants For A Future
- United States Department of Agriculture: Profile For Oxalis Stricta
Wikidata ☰ Q158332 entry
 |