Software:FatFs
 Listing files on Micro SD card connected to Arduino Nano using FatFs | |
| Developer(s) | ChaN |
|---|---|
| Initial release | February 26, 2006 |
| Stable release | R0.15
/ 2022 |
| Repository | Releases archive |
| Written in | ANSI C |
| Platform | Intel 8051, PIC, AVR, ARM, Z80 |
| Type | Embedded systems software |
| License | Own license, similar to BSD |
| Website | elm-chan.org |
FatFs is a lightweight software library for microcontrollers and embedded systems that implements FAT/exFAT file system support.[1] Written on pure ANSI C, FatFs is platform-independent and easy to port on many hardware platforms such as 8051, PIC, AVR, ARM, Z80. FatFs is designed as thread-safe and is built into ChibiOS, RT-Thread, ErlendOS,[2] and Zephyr real-time operating systems.[3]
Most often, FatFs is used in low-power Embedded systems where memory is limited, since the library takes up little space in RAM and program code. In the minimum version, the working code takes from 2 to 10 kB of RAM.[4]
Overview
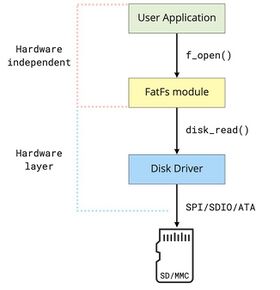
FatFs is designed to be a Filesystem Layer that is agnostic to the platform and storage media it is used with. This is achieved by providing a media access interface that is used to communicate with the storage device control module which is provided by the implementer.[5] This means that FatFs can work with any physical device such as an SD card or a hard disk on any platform that can run plain C code if the implementer provides a control module interface.
Architecture
FatFs library architecture logically separates the abstractions of the user app and the platform-dependent code. The user application and the low level disk I/O layer (driver) must be added by the implementer.[5]:11 Also, the architecture of the library implies that the system can have several storage devices with different drivers and the library can work in a multi-threaded operating system. At the application level it is hidden which physical media is used.
In the minimum implementation, the driver layer must support at least these 3 interfaces:[5]:14
disk_status— return block device status (not initialized, missing, protected, ready)disk_initialize— initialize the physical diskdisk_read— read block from physical disk
This level of abstraction allows implementers to write an application once, and then port it on different platforms, changing only the implementation of the driver.[6]
License
FatFs has its own minimalistic license [7] similar to the BSD license. It allows usage in commercial products without disclosing the source code.[5]:12 The only condition is to keep the copyright notice in case of redistribution of the source code. The conditions of FatFs license are not cover any redistributions in binary form, such as embedded code and hex files.
Projects using FatFs
- Arduino (STM32Duino) — port of Arduino platform for STM32 MCU's[8]
- ChibiOS/RT — open-source real-time operating system (RTOS) for microcontrollers
- Dreamshell — a Unix-like operating system, designed for the Sega Dreamcast video game console
- Flipper Zero — open source portable multi-tool device
- Marlin (firmware) — open source firmware for 3D printers and CNC machines
- ESP-IDF — official IoT Development Framework for the ESP32 series SoC's[9]
- Prusa Mini — open-source firmware for low cost 3D printer
- RT-Thread — open-source real-time operating system for embedded systems[10]
- Zephyr — real-time operating system for embedded systems supporting multiple architectures
- ErlendOS — an open source minimal UNIX-like operating system for embedded systems
References
- ↑ Ivan Cibrario Bertolotti (2016). Embedded Software Development; The Open-Source Approach. Tingting Hu. p. 361. ISBN 9781466593930. OCLC 932464067. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/932464067.
- ↑ "erlends-os / kmod / fatfs" (in en). https://git.erlendjs.no/erlends-os/kmod/fatfs.
- ↑ Yi Qiu (2020). The design and implementation of the RT-thread operating system. Xiong Puxiang, Tianlong Zhu. p. 361. ISBN 9780367554866. OCLC 1197810565. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/1197810565.
- ↑ "FatFs Memory Usage comparison table". http://elm-chan.org/fsw/ff/doc/appnote.html#memory.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "Developing applications on STM32Cube with FatFs". STMicroelectronics. https://www.st.com/resource/en/user_manual/um1721-developing-applications-on-stm32cube-with-fatfs-stmicroelectronics.pdf.
- ↑ Beningo, Jacob (2017). Reusable Firmware Development; A Practical Approach to APIs, HALs and Drivers. p. 255. ISBN 9781484232972. OCLC 1484232976. https://books.google.com/books?id=wzVCDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA255.
- ↑ "FatFs License". http://elm-chan.org/fsw/ff/doc/appnote.html#license.
- ↑ "FatFs Library description on Arduino platform documentation". https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/libraries/fatfs/.
- ↑ "FAT Filesystem Support - ESP32 - — ESP-IDF Programming Guide latest documentation". https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/esp32/api-reference/storage/fatfs.html.
- ↑ "FatFs File System Configuration in rt-thread operating system". https://www.rt-thread.io/document/site/programming-manual/filesystem/filesystem/#elm-fatfs-file-system-configuration-option.
 |