Chemistry:Copper(I) thiophene-2-carboxylate
From HandWiki
Revision as of 05:38, 6 May 2022 by imported>OrgMain (over-write)
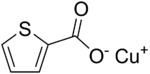
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Copper(I) thiophene-2-carboxylate
| |
| Other names
CuTC
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H3CuO2S | |
| Molar mass | 190.68 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
TWA 100 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
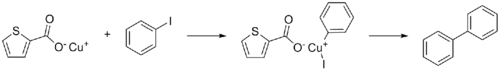
Copper(I) thiophene-2-carboxylate or CuTC is a coordination complex derived from copper and thiophene-2-carboxylic acid. It is used as a reagent to promote the Ullmann reaction between aryl halides.[3]
References
- ↑ Copper(I) thiophene-2-carboxylate at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0150". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0150.html.
- ↑ Shijie Zhang; Dawei Zhang; Lanny S. Liebeskind (1997). "Ambient Temperature, Ullmann-like Reductive Coupling of Aryl, Heteroaryl, and Alkenyl Halides". J. Org. Chem. 62 (8): 2312–2313. doi:10.1021/jo9700078. PMID 11671553.
 |