Software:wxWidgets
 | |
| Original author(s) | Julian Smart[1][2][3] |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Various developers and contributors[4] |
| Initial release | 1992[5] |
| Stable release | 3.2.4 (11 November 2023 [6]) [±] |
| Written in | C++ |
| Operating system | Cross-platform |
| Type | Development library |
| License | wxWidgets Licence |
| Website | wxwidgets |
wxWidgets (formerly wxWindows) is a widget toolkit and tools library for creating graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for cross-platform applications. wxWidgets enables a program's GUI code to compile and run on several computer platforms with minimal or no code changes. A wide choice of compilers and other tools to use with wxWidgets facilitates development of sophisticated applications.[7] wxWidgets supports a comprehensive range of popular operating systems and graphical libraries, both proprietary and free, and is widely deployed in prominent organizations (see text).
The project was started under the name wxWindows in 1992 by Julian Smart at the University of Edinburgh.[1] The project was renamed wxWidgets in 2004 in response to a trademark claim by Microsoft United Kingdom .
It is free and open source software, distributed under the terms of the wxWidgets Licence, which satisfies those who wish to produce for GPL and proprietary software.[8]
Portability and deployment
wxWidgets covers systems such as Microsoft Windows, Mac OS (Carbon and Cocoa), iOS (Cocoa Touch), Linux/Unix (X11, Motif, and GTK), OpenVMS, OS/2 and AmigaOS. A version for embedded systems is under development.[9]
wxWidgets is used across many industry sectors, most notably by Xerox, Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), Lockheed Martin, NASA and the Center for Naval Analyses. It is also used in the public sector and education by, for example, Dartmouth Medical School, National Human Genome Research Institute, National Center for Biotechnology Information, and many others.[7] wxWidgets is used in many open source projects,[10] and by individual developers.
History
wxWidgets (initially wxWindows; "w" is for Windows, and "x" is for X Window System)[11] was started in 1992 by Julian Smart at the University of Edinburgh.[1] He attained an honours degree in Computational science from the University of St Andrews in 1986, and is still a core developer.[2]
On 20 February 2004, the developers of wxWindows announced that the project was changing its name to wxWidgets, as a result of Microsoft requesting Julian Smart to respect Microsoft's United Kingdom trademark of the term Windows.[12]
Major release versions were 2.4 on 6 January 2003, 2.6 on 21 April 2005 and 2.8.0 on 14 December 2006. Version 3.0 was released on 11 November 2013.
wxWidgets has participated in the Google Summer of Code since 2006.[13][14]
The following table contains the release history of wxWidgets, showing all of its major release versions.
| Version number | Date | Notable changes |
|---|---|---|
| Project started by Julian Smart | 1992[15] | |
| wxWindows 1 | ||
| Alpha 1 | 5 April 1997[16] | |
| Beta 1 | 24 December 1998[16] | |
| wxWidgets 2 | ||
| 2.0.1 | 1 March 1999[16] | |
| 2.2.0 | 9 July 2000[17] | |
| 2.4.0 | 6 January 2003[17] | |
| 2.6.0 | 21 April 2005[17] | |
| 2.8.0 | 14 December 2006[18] |
|
| 2.8.11 | 23 April 2010 | |
| 2.8.12 | 28 March 2011 | |
| 2.9.0 | 8 September 2009 | |
| 2.9.1 | 19 July 2010 | |
| 2.9.2 | 5 July 2011 | |
| 2.9.3 | 14 December 2011 | |
| 2.9.4 | 9 July 2012 | |
| 2.9.5 | 16 July 2013 | |
| wxWidgets 3 | ||
| 3.0.0 | 11 November 2013[16] |
|
| 3.0.1 | 15 June 2014 | |
| 3.0.2 | 6 October 2014 | |
| 3.0.3 | 2 May 2017 | |
| 3.0.4 | 8 March 2018 | |
| 3.0.5 | 27 April 2020 | |
| 3.1.0 | 29 February 2016 |
|
| 3.1.1 | 19 February 2018[19] |
|
| 3.1.2 | 10 December 2018 |
|
| 3.1.3 | 28 October 2019 |
|
| 3.1.4 | 22 July 2020 |
|
| 3.1.5 | 14 April 2021 |
|
| 3.1.6 | 4 April 2022 |
|
| 3.1.7 | 6 June 2022 |
|
| 3.2.0 | 7 July 2022 |
|
| 3.2.1 | 9 September 2022 |
|
| 3.2.2 | 9 February 2023 |
|
| 3.2.2.1 | 13 February 2023 |
|
| 3.2.3 | 10 October 2023 |
|
| 3.2.4 | 11 November 2023 |
|
| Future versions | ||
License
| DFSG compatible | Yes |
|---|---|
| FSF approved | Yes |
| OSI approved | Yes |
| GPL compatible | Yes |
| Copyleft | Yes |
| Linking from code with a different license | Yes |
wxWidgets is distributed under a custom made wxWindows Licence, similar to the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL), with an exception stating that derived works in binary form may be distributed on the user's own terms.[8] This license is a free software license approved by the FSF,[20] making wxWidgets free software. It has been approved by the Open Source Initiative (OSI).[21]
Official support
Supported platforms
wxWidgets is supported on the following platforms:[22][23]
- Windows – (32/64-bits Windows XP up to Windows 11)
- Linux/Unix – wxGTK, wxX11, wxMotif
- Mac OS – wxMac (Mac OS X 10.3 using Carbon, Mac OS X 10.5 using Cocoa), wxOSX/Cocoa (32/64-bits Mac OS X 10.7 or later)
- OS/2 – wxOS2, wxPM, wxWidgets for GTK or Motif can be compiled on OS/2
- Embedded platforms – wxEmbedded[9]
External ports
- Amiga – wxWidgets-AOS: AmigaOS port (Work In Progress)[24]
Supported compilers
wxWidgets is officially confirmed to work properly with the following compilers:[25][26]
| Toolkit | Compiler | Version |
|---|---|---|
| wxMSW | Microsoft Visual Studio – Visual C++ | 5.0+ |
| Borland C++ (dropped in 3.1.5) | 5.5+ | |
| C++Builder | 2006+ | |
| Watcom C++, OpenWatcom | 10.6+ | |
| CodeWarrior | 7+ | |
| Cygwin | 1.5+ | |
| MinGW | 2.0+ | |
| Digital Mars C/C++ compiler | 8.40+ | |
| wxGTK | g++ | 2.95+ |
| Clang++ | 3.3+ | |
| Intel C++ Compiler | 9.1+ | |
| Sun Studio C/C++ | 5.9 | |
| HP aC++ | 3.8 | |
| IBM XL C/C++ | 8.0 |
Programming language bindings

The wxWidgets library is implemented in C++, with bindings available for many commonly used programming languages.[27]
wxWidgets is best described as a native mode toolkit as it provides a thin abstraction to a platform's native widgets, contrary to emulating the display of widgets using graphic primitives. Calling a native widget on the target platform results in a more native looking interface than toolkits such as Swing (for Java), as well as offering performance and other benefits.[28]
The toolkit is also not restricted to GUI development, having an inter-process communication layer, socket networking functionality, and more.
RAD tools and IDEs for wxWidgets
There are many Rapid Application Development (RAD) and Integrated Development Environment (IDE) tools available. Notable tools include:[29][30]
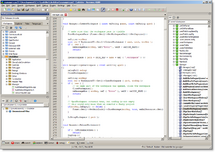
- Code (via wxSmith plugin)
- CodeLite (via wxCrafter plugin)
- wxFormBuilder
Applications built using wxWidgets
Notable applications that use wxWidgets:
- 0 A.D. – a FOSS video game similar to Age of Empires
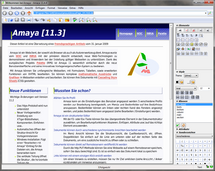
- Amaya – web authoring tool
- aMule – peer-to-peer file sharing application
- ActivePresenter – screen recorder, video editor & e-learning application
- Audacity – cross-platform sound editor
- BitTorrent – peer-to-peer file sharing application
- Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing – an open-source middleware system
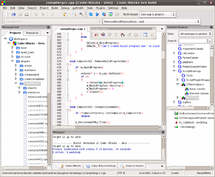
- Code – C/C++ IDE
- CodeLite – simple C++ Editor (Collection of free Tools, implemented by plugins)
- FileZilla – FTP client
- FreeFileSync – a free and open-source file synchronization software
- GrandOrgue – virtual pipe organ simulator
- Guayadeque Music Player – a music player with database
- Hollywood – uses wxWidgets in its RapaGUI plugin
- KiCad – a free software suite for electronic design automation (EDA)
- RapidSVN – Subversion client
- RocketCake – WYSIWYG responsive website builder
- TortoiseCVS – CVS client
See also
- FLTK – a light, cross platform, non-native widget toolkit
- FOX toolkit – a fast, open source, cross-platform widget toolkit
- GTK – the GIMP toolkit, a widget toolkit used by GNOME applications
- gtkmm – C++ version of GTK
- Juce – an extensive cross-platform widget toolkit
- IUP – a multi-platform toolkit for building native graphical user interfaces
- Qt (toolkit) – an application framework used by KDE applications
- U++ – a C++ cross-platform development framework
- Widget toolkit
- List of widget toolkits
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "About the wxWidgets Project". wxwidgets.org. https://wxwidgets.org/about/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "About Julian Smart, www.anthemion.co.uk". anthemion.co.uk. http://www.anthemion.co.uk/julian.htm.
- ↑ "Julian Smart". bookfayre.cz. http://www.bookfayre.cz/books/name/julian_smart.2247651.html.cs.
- ↑ "The Team - wxWidgets". https://wxwidgets.org/about/team/.
- ↑ "History - wxWidgets". https://www.wxwidgets.org/about/history/.
- ↑ "wxWidgets: 3.2.4 Released". 2023-11-11. https://www.wxwidgets.org/news/2023/11/wxwidgets-3.2.4-released/.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "About Who uses wxWidgets?". wxwidgets.org. https://www.wxwidgets.org/about/whouses.htm.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 ""License" page on website". https://www.wxwidgets.org/about/licence/. "The wxWindows Licence is essentially the LGPL, with an exception stating that derived works in binary form may be distributed on the user's own terms."
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "wxEmbedded | embedded cross platform GUI library homepage". http://www.wxembedded.com/.
- ↑ "List of open source applications that uses wxWidgets". SourceForge.net. http://sourceforge.net/softwaremap/?&fq%5B%5D=trove%3A481.
- ↑ "History - wxWidgets". https://www.wxwidgets.org/about/history/.
- ↑ Smart, Julian; Dunn, Robin (August 2004). "Name change". Sourceforge.net. https://wxwidgets.org/about/name.htm.
- ↑ Smart, Julian (2006-10-10). "Google Summer of Code 2006: wxWidgets projects summary". wxwidgets.org. https://wxwidgets.blogspot.com/2006/10/google-summer-of-code-2006-wxwidgets.html.
- ↑ "Google Summer of Code 2006". https://code.google.com/intl/pl/soc/2006/wxwidgets/about.html.
- ↑ "History of wxWidgets". wxwidgets.org. https://www.wxwidgets.org/about/history.htm.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 "wxWidgets Change Log". wxwidgets.org. https://svn.wxwidgets.org/svn/wx/wxWidgets/trunk/docs/changes.txt.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 "News". wxwidgets.org. https://www.wxwidgets.org/about/news/news.htm.
- ↑ Sudiarto Raharjo, Willy (2006-12-14). "WxWidgets 2.8.0". https://slackblogs.blogspot.com/2006/12/wxwidgets-280.html.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 "wxWidgets/wxWidgets Releases". GitHub. https://github.com/wxWidgets/wxWidgets/releases.
- ↑ "Various Licenses and Comments about Them – GNU Project - Free Software Foundation". https://www.gnu.org/licenses/license-list.html#Wx.
- ↑ "Open Source Initiative OSI – The wxWindows Library Licence:Licensing". Open Source Initiative. http://www.opensource.org/licenses/wxwindows.php.
- ↑ "wxWidgets: Introduction". https://docs.wxwidgets.org/trunk/page_introduction.html.
- ↑ "wxWidgets: Platform Details". https://docs.wxwidgets.org/trunk/page_port.html.
- ↑ "wxWidgets-AOS: AmigaOS port". https://sourceforge.net/projects/wxwidget-aos/.
- ↑ "Supported Platforms". wxwidgets.org. https://wiki.wxwidgets.org/Supported_Platforms.
- ↑ "Development: Supported Classes - WxWiki". https://wiki.wxwidgets.org/Development:_Supported_Classes.
- ↑ "wxWidgets General Information". https://wiki.wxwidgets.org/General_Information.
- ↑ "WxWidgets Compared To Other Toolkits". https://wiki.wxwidgets.org/WxWidgets_Compared_To_Other_Toolkits.
- ↑ "Tools for wxWidgets". wxwidgets.org. https://wiki.wxwidgets.org/Tools.
- ↑ "List of Integrated Development Environments". wxwidgets.org. https://wiki.wxwidgets.org/List_of_Integrated_Development_Environments.
Further reading
- Smart, Julian; Hock, Kevin; Csomor, Stefan (5 August 2005), Cross-Platform GUI Programming with wxWidgets, Prentice Hall, ISBN 978-0-13-147381-2, http://www.pearsoned.co.uk/bookshop/detail.asp?item=100000000072372
External links
 |