Biology:Proarticulata
| Proarticulata | |
|---|---|

| |
| Fossil of Dickinsonia costata | |

| |
| Fossil of Spriggina | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| (unranked): | Holozoa |
| (unranked): | Filozoa |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | †Proarticulata Fedonkin, 1985 |
| Class / Family | |
For more taxa, see text | |
Proarticulata is a proposed phylum of extinct, bilaterally symmetrical animals known from fossils found in the Ediacaran (Vendian) marine deposits, and dates to approximately 567 to 550 million years ago.[1][2] The name comes from the Greek προ (pro-) = "before" and Articulata, i.e. prior to animals with true segmentation such as annelids and arthropods. This phylum was established by Mikhail A. Fedonkin in 1985 for such animals as Dickinsonia, Vendia, Cephalonega, Praecambridium[3] and currently many other Proarticulata are described (see list).[4][5]
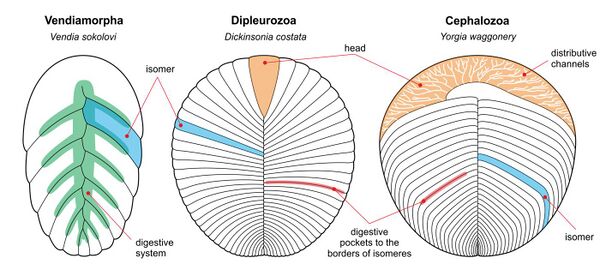
Due to their simplistic morphology, their affinities and mode of life are subject to debate. They are almost universally considered to be metazoans, and due to possessing a clear central axis have been suggested to be stem-bilaterians. In the traditional interpretation, the Proarticulatan body is divided into transverse articulation (division) into isomers as distinct from the transverse articulation segments in annelids and arthropods, as their individual isomers occupy only half the width of their bodies, and are organized in an alternating pattern along the longitudinal axis of their bodies.[5] In other words, one side is not the direct mirror image of its opposite (chirality). Opposite isomers of left and right side are located with displacement of half of their width. This phenomenon is described as the symmetry of gliding reflection.[6][7] Some recent research suggests that some proarticulatans like Dickinsonia have genuine segments, and the isomerism is superficial and due to taphonomic distortion.[8] However, other researchers dispute this.[9][10] Displacement of left-right axis is known in bilaterians, notably lancelets.[11][12]
Morphology
Vendiamorpha
The body is completely segmented, with all isomers curved towards the posterior, and the first isomer is normally much larger than the rest. The first two isomers at the anterior dorsal end are partly fused. (e.g., Vendia, Paravendia and Karakhtia).[6][13][14][15]
Cephalozoa
These proarticulatans are incompletely segmented, as the anterior zone is free of isomers, often making a "hairband" like appearance (example cephalozoans include Yorgia, Praecambridium, Andiva, Archaeaspinus, Ivovicia, Podolimirus, Tamga, Spriggina, Marywadea and Cyanorus).[6][13][15][16] Some cephalozoans from the family Yorgiidae demonstrate pronounced asymmetry of left and right parts of the body. For instance, Yorgia’s initial right isomer is the only one which spreads far towards the left side of the body. Archaeaspinus has an unpaired anterior lobe confined by the furrow to the left side only.[6][7][15]
thumb|right|Artist's reconstruction of Lossinia'' feeding on surface algae. In Cephalonega stepanovi and Tamga hamulifera the zone containing the isomers is encircled by a peripheral, undivided zone.[16] The Cephalonega's isomers are connected to each other, forming a body resembling a rubber raft; the Tamga's isomers are separated from each other, and do not touch.
In Lossinia, the center undivided region has no visible isomers, instead having the lobe-like isomers emanate from the periphery of the undivided region as "transverse articulations."[16]
Dipleurozoa
The dipleurozoan body is subradial, divided by isomers entirely (e.g., Dickinsonia and Phyllozoon). Dickinsonia juveniles show undivided anterior areas but these regions were reduced in the course of ontogeny, and in the adult stages Dickinsonia-like proarticulates changed so radically that they became almost indistinguishable from isomers.[13][16][18]
List of Proarticulata
Body fossils
- Armillifera Fedonkin, 1980[19]
- A. parva Fedonkin, 1980
- A. ivantsovi Fedonkin, 2002
- A. fedonkini Ivantsov, 2001
- Cephalonega Ivantsov et al., 2019[21]
- Chondroplon Wade, 1971 (possible =Dickinsonia)
- C. bilobatum Wade, 1971
- C. singularis Ivantsov, 2004
- Dickinsonia Sprigg, 1947
- D. costata Sprigg, 1947
- D. menneri Keller 1976[16] (=Vendomia menneri Keller 1976[22])
- D. tenuis Glaessner & Wade, 1966
- I. rugulosa Ivantsov, 2007
- Karakhtia Ivantsov, 2004
- K. nessovi Ivantsov, 2004
- L. lissetskii Ivantsov, 2007
- Marywadea Glaessner, 1976
- M. ovata Glaessner & Wade, 1966
- Ovatoscutum Glaessner & Wade, 1966
- O. concentricum Glaessner & Wade, 1966
- Paravendia Ivantsov, 2004[6][13]
- P. janae Ivantsov, 2001 (=Vendia janae Ivantsov, 2001)
- Podolimirus Fedonkin, 1983 (=Valdainia Fedonkin, 1983)[23]
- P. mirus Fedonkin, 1983 (Valdainia plumosa Fedonkin, 1983)
- Praecambridium Glaessner & Wade, 1966
- P. siggilum Glaessner & Wade, 1966
- Spriggina Glaessner, 1958
- S. floundersi Glaessner, 1958
- T. hamulifera Ivantsov, 2007
- V. sokolovi Keller, 1969
- V. rachiata Ivantsov, 2004
- ? Windermeria Narbonne, 1994
- W. aitkeni Narbonne, 1994[24]
- Y. waggoneri Ivantsov, 1999
Trace fossils
- E. axiferus Ivantsov, 2002.
- E. waggoneris Ivantsov, 2011. This is a trace of Yorgia waggoneri
- E. costatus Ivantsov, 2011. This is a trace of Dickinsonia costata
- Phyllozoon Jenkins & Gehling, 1978
- P. hanseni Jenkins & Gehling, 1978
See also
References
- ↑ "Upper Vendian in the east, northeast and north of East European Platform: Depositional processes and biotic evolution". Litosfera 18 (4): 520–542. 2018. doi:10.24930/1681-9004-2018-18-4-520-542. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/327388718.
- ↑ "A reassessment of the problematic Ediacaran genus Orbisiana Sokolov 1976". Precambrian Research 316: 197–205. 2018. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2018.08.011. Bibcode: 2018PreR..316..197K. https://www.repository.cam.ac.uk/handle/1810/285052.
- ↑ "Systematic Description of Vendian Metazoa". Vendian System: Historical–Geological and Paleontological Foundation. 1: Paleontology. Moscow: Nauka. 1985. pp. 70–106.
- ↑ "The origin of the Metazoa in the light of the Proterozoic fossil record". Paleontological Research 7 (1): 9–41. 31 March 2003. doi:10.2517/prpsj.7.9. http://www.bionet.nsc.ru/live/ppt/Fedonkin_2003.pdf.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Cephalonega, a new generic name, and the system of Vendian Proarticulata". Paleontological Journal 53 (5): 447–454. 2019. doi:10.1134/S0031030119050046. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/335988735.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 Ivantsov, A.Yu. (2001). "Vendia and other precambrian "Arthropods"". Paleontological Journal 35 (4): 335–343. https://www.academia.edu/2605872.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Ivantsov, A.Yu. (1999). "A new Dickinsoniid from the upper Vendian of the White Sea Winter Coast (Russia, Arkhangelsk region)". Paleontological Journal 33 (3): 233–241. https://www.academia.edu/2604893.
- ↑ "Ediacaran developmental biology". Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society 93 (2): 914–932. May 2018. doi:10.1111/brv.12379. PMID 29105292.
- ↑ "Morphology of integuments of the Precambrian animals, Proarticulata". Invertebrate Zoology 16 (1): 19–26. June 2019. doi:10.15298/invertzool.16.1.03.
- ↑ "Cephalonega, A New Generic Name, and the System of Vendian Proarticulata". Paleontological Journal 53 (5): 447–454. September 2019. doi:10.1134/s0031030119050046.
- ↑ "The evolution and conservation of left-right patterning mechanisms". Development 141 (8): 1603–13. April 2014. doi:10.1242/dev.100560. PMID 24715452.
- ↑ "Left-right asymmetry specification in amphioxus: review and prospects". The International Journal of Developmental Biology 61 (10–11–12): 611–620. 2017. doi:10.1387/ijdb.170251vs. PMID 29319110.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 13.5 Ivantsov, A.Yu. (2004). "New Proarticulata from the Vendian of the Arkhangel'sk Region". Paleontological Journal 38 (3): 247–253. http://vend.paleo.ru/pub/Ivantsov_2004_eng.pdf.
- ↑ Ivantsov, A.Yu.; Malakhovskaya, Y.E.; Serezhnikova, E.A. (2004). "Some problematic fossils from the Vendian of the south-eastern White Sea region". Paleontological Journal 38 (1): 1–9. http://www.vend.paleo.ru/pub/Ivantsov_et_al_2004_eng.pdf.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Ivantsov, A.Yu. (2004). "Vendian animals in the phylum Proarticulata". The Rise and Fall of the Vendian Biota. Prato, Italy. p. 52. IGSP Project 493. https://www.monash.edu/__data/assets/pdf_file/0010/75655/ivantsov.pdf.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 16.4 16.5 16.6 16.7 16.8 16.9 Ivantsov, A.Yu. (April 2007). "Small Vendian transversely articulated fossils". Paleontological Journal 41 (2): 113–122. doi:10.1134/S0031030107020013. https://www.academia.edu/2352394.
- ↑ illustration (c) Stanton F. Fink
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Ivantsov, A.Yu.; Malakhovskaya, Y.E. (2002). "Giant traces of Vendian animals". Doklady Earth Sciences 385 (6): 618–622. http://vend.paleo.ru/pub/Ivantsov_et_Malakhovskaya_2002-e.pdf.
- ↑ "Paleontological evidence for the supposed precambrian occurrence of mollusks". Paleontological Journal 40 (12): 1552–1559. December 2010. doi:10.1134/S0031030110120105.
- ↑ "Andiva ivantsovi gen. et sp. n. and related carapace‐bearing Ediacaran fossils from the Vendian of the Winter Coast, White Sea, Russia". Italian Journal of Zoology 69 (2): 175–181. 2002. doi:10.1080/11250000209356456.
- ↑ "Cephalonega, a new generic name, and the system of Vendian Proarticulata". Paleontological Journal 53 (5): 447–454. 2019. doi:10.1134/S0031030119050046. https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=39324149.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 "New Records of Fossils in the Valdaian Group of the Precambrian on the Syuz'ma River" (in ru). Izvestiya Akademii Nauk SSR. Seriya Geologicheskaya 3: 38–44. 1976. http://vend.paleo.ru/pub/Keller_Fedonkin_1976.pdf.
- ↑ Dzik, J.; Martyshyn, A. (2015). "Taphonomy of the Ediacaran Podolimirus and associated dipleurozoans from the Vendian of Ukraine". Precambrian Research 269: 139–146. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2015.08.015. https://www.academia.edu/15860379.
- ↑ "New Ediacaran fossils from the Mackenzie Mountains, Northwestern Canada". Journal of Paleontology 63 (3): 411–416. May 1994. doi:10.1017/S0022336000025816.
- ↑ "Feeding traces of Proarticulata — the Vendian metazoa". Paleontological Journal 45 (3): 237–248. May 2011. doi:10.1134/S0031030111030063. https://www.academia.edu/2394670.
External links
- Database of Ediacaran Biota Advent of Complex Life
Wikidata ☰ Q2566978 entry
 |