Chemistry:Oxyfluorfen
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
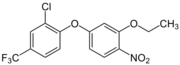
| IUPAC name
2-chloro-1-(3-ethoxy-4-nitrophenoxy)-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzene
| |
| Other names
Oxyfluorfen; Oxyfluorofen; 2-chloro-1-(3-ethoxy-4-nitrophenoxy)-4-trifluoromethylbenzene; 2-chloro-α,α,α-trifluoro-p-tolyl-3-ethoxy-4-nitrophenyl ether; Galigan; Goal; Goldate; Oxyfluorfene; Oxygold; Zoomer
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H11ClF3NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 361.702 g/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
5 g/kg (rat, oral) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Oxyfluorfen is a chemical compound used as an herbicide. It is manufactured by Dow AgroSciences and Adama Agricultural Solutions under the trade names Goal and Galigan.[2] Oxyfluorfen is used to control broadleaf and grassy weeds in a variety of nut, tree fruit, vine, and field crops, especially wine grapes and almonds. It is also used for residential weed control.[2]
Toxicity
Oxyfluorfen has low acute oral, dermal, and inhalation toxicity in humans. The primary toxic effects are in the liver and alterations in blood parameters (anemia).[2] It is classified as a possible human carcinogen.[2]
Environmental impact
Oxyfluorfen is classified as an environmental hazard under the GHS due to being "very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects".[1]
Oxyfluorfen is toxic to plants, invertebrates, and fish. Birds and mammals may also experience subchronic and chronic effects from oxyfluorfen.[2] It is persistent in soil and has been shown to drift from application sites to nearby areas.[2] It can contaminate surface water through spray drift and runoff.[2]
References
 |

