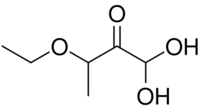
Chemistry:Kethoxal
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-Ethoxy-1,1-dihydroxy-2-butanone
| |
| Other names
3-Ethoxy-2-oxobutyraldehyde hydrate
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | C005135 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12O4 | |
| Molar mass | 148.158 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Pale yellow syrup[1] |
| Boiling point | 145 °C (293 °F; 418 K)[1][2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Kethoxal (3-ethoxy-1,1-dihydroxy-2-butanone) is an organic compound that has antiviral and anaplasmosis properties.[1][3] It also forms a stable covalent adduct with guanine, which makes it useful for nucleic acid structure determination.[4]
Nucleic acid binding
Kethoxal, as with other 1,2-dicarbonyl compounds,[5] reacts with nucleic acids. It has high specificity for guanine over other ribonucleotides. In whole RNA, it reacts preferentially with guanine residues that are not involved in hydrogen-bonding.[6][7] It can thus be used to probe the interactions involved with the secondary structure and other binding interactions of RNA[8] and help with nucleic acid sequence analysis. The binding is reversible, which allows the kethoxal to be removed and the original RNA recovered.[citation needed]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 J. Elks (2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. p. 510. ISBN 9781475720853. https://books.google.com/books?id=0vXTBwAAQBAJ&dq=3-ethoxy-2-butanone&pg=PA510.
- ↑ SciFinder record for CASRN 27762-78-3
- ↑ "Kethoxal". Merriam-Webster. http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/kethoxal.
- ↑ Robert Shapiro; Bertram I. Cohen; Shian-Jan Shiuey; Hans Maurer (1969). "Reaction of guanine with glyoxal, pyruvaldehyde, and kethoxal, and the structure of the acylguanines. Synthesis of N2-alkylguanines". Biochemistry 8 (1): 238–245. doi:10.1021/bi00829a034. PMID 5777326.
- ↑ Shapiro, Robert; Hachmann, John (1966). "The Reaction of Guanine Derivatives with 1,2-Dicarbonyl Compounds". Biochemistry 5 (9): 2799–2807. doi:10.1021/bi00873a004. PMID 5961865.
- ↑ Litt, Michael; Hancock, Virginia (1967). "Kethoxal—A Potentially Useful Reagent for the Determination of Nucleotide Sequences in Single-Stranded Regions of Transfer Ribonucleic Acid". Biochemistry 6 (6): 1848–1854. doi:10.1021/bi00858a036. PMID 6035923.
- ↑ Staehelin, Matthys (1959). "Inactivation of virus nucleic acid with glyoxal derivatives". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 31 (2): 448–454. doi:10.1016/0006-3002(59)90019-8. PMID 13628672.
- ↑ Gopinath, S.C.B. (2009). "Mapping of RNA-protein interactions". Analytica Chimica Acta 636 (2): 117–128. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2009.01.052. PMID 19264161.
 |

