Biology:DicF RNA
From HandWiki
Revision as of 14:57, 25 November 2021 by imported>WikiEd2 (update)
Short description: Non-coding RNA
| DicF RNA | |
|---|---|
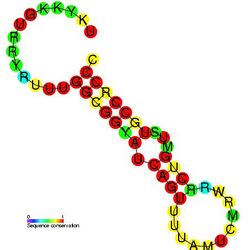 Predicted secondary structure and sequence conservation of DicF | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | DicF |
| Rfam | RF00039 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene; antisense |
| Domain(s) | Bacteria |
| GO | 0003729 |
| SO | 0000644 |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
DicF RNA is a non-coding RNA that is an antisense inhibitor of cell division gene ftsZ.[1] DicF is bound by the Hfq protein which enhances its interaction with its targets. Pathogenic E. coli strains possess multiple copies of sRNA DicF in their genomes, while non-pathogenic strains do not. DicF and Hfq are both necessary to reduce FtsZ protein levels, leading to cell filamentation under anaerobic conditions.[2]
References
- ↑ "Division inhibition gene dicF of Escherichia coli reveals a widespread group of prophage sequences in bacterial genomes". Journal of Bacteriology 176 (4): 1150–1156. February 1994. doi:10.1128/jb.176.4.1150-1156.1994. PMID 7508908.
- ↑ "Escherichia coli responds to environmental changes using enolasic degradosomes and stabilized DicF sRNA to alter cellular morphology". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 114 (38): E8025–E8034. September 2017. doi:10.1073/pnas.1703731114. PMID 28874523.
Further reading
- "Regulation of the expression of the cell-cycle gene ftsZ by DicF antisense RNA. Division does not require a fixed number of FtsZ molecules". Molecular Microbiology 6 (5): 615–620. March 1992. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01508.x. PMID 1372677.
- "Genetic evidence that DicF, a second division inhibitor encoded by the Escherichia coli dicB operon, is probably RNA". Molecular Microbiology 3 (7): 991–994. July 1989. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00249.x. PMID 2477663.
- "Sigma S-dependent overexpression of ftsZ in an Escherichia coli K-12 rpoB mutant that is resistant to the division inhibitors DicB and DicF RNA". Molecular & General Genetics 248 (2): 190–194. July 1995. doi:10.1007/BF02190800. PMID 7651342.
- "Escherichia coli cell division inhibitor DicF-RNA of the dicB operon. Evidence for its generation in vivo by transcription termination and by RNase III and RNase E-dependent processing". Journal of Molecular Biology 212 (3): 461–471. April 1990. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(90)90325-G. PMID 1691299.
External links
 |

