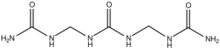
Chemistry:Dimethylene triurea
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
5-Oxa-2,4,6,8-tetraazanonane-1,9-diamide | |
| Other names
methylenebis(urea), 5-oxo-2,4,6,8-Tetraazanonanediamide, 1,3-bis[(carbamoylamino)methyl]urea
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H12N6O3 | |
| Molar mass | 204.190 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dimethylene triurea (DMTU) is the organic compound with the formula (H2NC(O)NHCH2NH)2CO. It is a white water-soluble solid. The compound is formed by the condensation of formaldehyde with urea. Both branched and linear isomers exist.
Applications
DMTU is an intermediate in the production of urea-formaldehyde resins.[1]
Together with methylene diurea, DMTU is a component of some controlled-release fertilizers.[2]
References
- ↑ Steinhof, Oliver; Kibrik, Éléonore J.; Scherr, Günter; Hasse, Hans (2014). "Quantitative and qualitative1H, 13C, and15N NMR spectroscopic investigation of the urea-formaldehyde resin synthesis". Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry 52 (4): 138–162. doi:10.1002/mrc.4044. PMID 24496721.
- ↑ Dittmar, Heinrich; Drach, Manfred; Vosskamp, Ralf; Trenkel, Martin E.; Gutser, Reinhold; Steffens, Günter (2009). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.n10_n01.
 |

