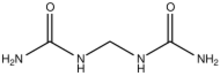
Chemistry:Methylene diurea
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N′′-Methylenediurea | |
| Other names
methylenebis(urea), (carbamoylamino)methylurea
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1812254 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| 694187 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H8N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 132.123 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 203 °C (397 °F; 476 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Methylene diurea (MDU) is the organic compound with the formula CH2(NHC(O)NH2)2. It is a white water-soluble solid. The compound is formed by the condensation of formaldehyde with urea. Methylene diurea is the substrate for the enzyme methylenediurea deaminase.
Applications
MDU is an intermediate in the production of urea-formaldehyde resins.[1]
Together with dimethylene triurea, MDU is a component of some controlled-release fertilizers.[2]
References
- ↑ Steinhof, Oliver; Kibrik, Éléonore J.; Scherr, Günter; Hasse, Hans (2014). "Quantitative and qualitative1H, 13C, and15N NMR spectroscopic investigation of the urea-formaldehyde resin synthesis". Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry 52 (4): 138–162. doi:10.1002/mrc.4044. PMID 24496721. https://osf.io/7u48z/download.
- ↑ Dittmar, Heinrich; Drach, Manfred; Vosskamp, Ralf; Trenkel, Martin E.; Gutser, Reinhold; Steffens, Günter (2009). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.n10_n01.
 |

