Chemistry:Joro toxin
From HandWiki
Revision as of 00:18, 15 November 2021 by imported>LinuxGuru (update)
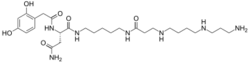
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2S)-N1-{5-[3-({4-[(3-Aminopropyl)amino]butyl}amino)propanamido]pentyl}-2-[2-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)acetamido]butanediamide | |
| Other names
Joro Spider toxin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H47N7O6 | |
| Molar mass | 565.716 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White-grey powder |
| Density | 1.196 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 979.883 °C (1,795.789 °F; 1,253.033 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.53 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 10.573 |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 546.414 °C (1,015.545 °F; 819.564 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
This article includes a list of references, related reading or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (November 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Joro spider toxin (joro toxin, JSTX) - a toxin which was originally extracted from the spider Nephila clavata venom. The compound has demonstrated the ability to selectively block postsynaptic glutamate potentials, AMPA glutamate receptors, and to antagonise the effect of NMDA receptors in the CNS of vertebrates. However, it does not affect aspartate-induced neural depolarization, resting membrane potential, nerve terminal spontaneous signalling, or inhibitory postsynaptic potentials.
Literature
- Kawai, Nobufumi; Niwa, Akiko; Abe, Takashi (1982). "Spider venom contains specific receptor blocker of glutaminergic synapses". Brain Research 247 (1): 169–71. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(82)91044-7. PMID 6127145.
- Shudo, Koichi; Endo, Yasuyuki; Hashimoto, Yuichi; Aramaki, Yoshio; Nakajima, Terumi; Kawai, Nobufumi (1987). "Newly synthesized analogues of the spider toxin block the crustacean glutamate receptor". Neuroscience Research 5 (1): 82–5. doi:10.1016/0168-0102(87)90026-5. PMID 2829068.
- Jackson, Jaewan; Lee, P.N.R. (1988). "Spider toxins as tools for dissecting elements of excitatory amino acid transmission". Trends in Neurosciences 11 (6): 278–83. doi:10.1016/0166-2236(88)90112-9. PMID 2465627.
- Saito, Mitsuyoshi; Sahara, Yoshinori; Miwa, Akiko; Shimazaki, Kuniko; Nakajima, Terumi; Kawai, Nobufumi (1989). "Effects of a spider toxin (JSTX) on hippocampal CA1 neurons in vitro". Brain Research 481 (1): 16–24. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(89)90480-0. PMID 2565131.
- Sahara, Yoshinori; Robinson, Hugh P.C.; Miwa, Akiko; Kawai, Nobufumi (1991). "A voltage-clamp study of the effects of Joro spider toxin and zinc on excitatory synaptic transmission in CA1 pyramidal cells of the guinea pig hippocampal slice". Neuroscience Research 10 (3): 200–10. doi:10.1016/0168-0102(91)90057-6. PMID 1677747.
- Kawai, Nobufumi (1991). "Spider toxin and pertussis toxin differentiate post- and presynaptic glutamate receptors". Neuroscience Research 12 (1): 3–12. doi:10.1016/0168-0102(91)90095-G. PMID 1660989.
- Mueller, Alan L.; Albensi, Benedict C.; Ganong, Alan H.; Reynolds, Linda S.; Jackson, Hunter (1991). "Arylamine spider toxins antagonize NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission in rat hippocampal slices". Synapse 9 (4): 244–50. doi:10.1002/syn.890090403. PMID 1662833.

