Biology:Large mole
| Large mole | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Eulipotyphla |
| Family: | Talpidae |
| Genus: | Mogera |
| Species: | M. robusta
|
| Binomial name | |
| Mogera robusta Nehring, 1891
| |
| |
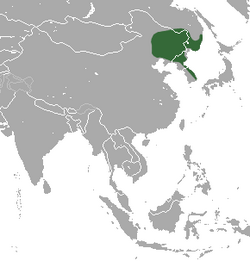
| Large mole range | |
The large mole[1] or Ussuri mole[2] (Mogera robusta), is a species of mammal in the family Talpidae (treated as a subspecies of the Japanese mole by some authorities[3]). It is found in China , North Korea, South Korea , and Russia and lives in a long burrow, seldom emerging on the surface of the ground during the day.
Description
This mole grows to a total length of 154 to 172 mm (6 to 7 in) with a tail of about 20 mm (0.8 in). It is adapted for underground life; the body is cylindrical, the fore-feet are spade-like, the nails are flattened and the eyes are small.[2] The short, dense, dorsal pelage is brownish-grey with a metallic sheen and the underparts are silvery-yellow, with a grey patch on the chest. The bare skin on the muzzle and the feet is yellowish. The short tail is well-covered with hair.[4]
Distribution and habitat
The large mole occurs in northeastern China, the Korean peninsula and southeastern Russia. Its typical habitat is montane forest and woodland, pasture and agricultural land but it is seldom found on steep rocky slopes.[1]
Ecology
This mole is solitary and mainly nocturnal, but is sometimes active on cloudy or rainy days. It feeds mainly on earthworms, insects, spiders, slugs and snails. It excavates feeding passages about 10 cm (4 in) below the surface of the soil, periodically throwing up a "mole hill", a pile of soil on the surface. Main passages may have a total length of 450 m (1,500 ft) and be at least 30 cm (12 in) below the surface; they connect feeding areas with drinking places and the nest. The breeding chamber contains a globular nest of leaves and grasses. The litter size is from 2 to 6 young with a gestation period of 28 days. Large moles live for up to four years, but sometimes fall prey to owls, snakes and weasels.[1][2]
Conservation status
Mogera robusta has a wide range and is said to be abundant in some areas and common in others. Although it used to be hunted for its pelt, this is no longer the case and it now faces no particular threats. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated its conservation status as being of "least concern" because, although its population may be in slow decline, this is not at a fast enough rate to warrant listing it in a more threatened category.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Tsytsulina, K. (2017). "Mogera robusta". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017: e.T41466A22323489. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T41466A22323489.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/41466/22323489.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Jo, Yeong-Seok; Baccus, John T.; Koprowski, John L. (2018). Mammals of Korea. National Institute of Biological Resources. pp. 92–94. ISBN 978-89-6811-369-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=71yHDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA92.
- ↑ Hutterer, R. (2005). "Mogera wogura robusta". in Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 306–304. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494. http://www.departments.bucknell.edu/biology/resources/msw3/browse.asp?id=13700714.
- ↑ Smith, Andrew T.; Xie, Yan (2013). Mammals of China. Princeton University Press. p. 214. ISBN 1-4008-4688-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=sgQsHR-WnTUC&pg=PA214.
- Insectivore Specialist Group 1996. Mogera robusta. 2006 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Downloaded on 30 July 2007.
Wikidata ☰ Q2661249 entry


