Biology:Crotalus mitchellii
| Crotalus mitchellii | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Viperidae |
| Genus: | Crotalus |
| Species: | C. mitchellii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Crotalus mitchellii (Cope, 1861)
| |
| |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
Crotalus mitchellii is a venomous pit viper species in the family Viperidae. The species is endemic to the Southwestern United States and adjacent northern Mexico. The species was named in honor of Silas Weir Mitchell (1829–1914), an American medical doctor who also studied rattlesnake venoms.[3][6] Five subspecies are currently recognized, including the nominate subspecies described here.[7]
Description
Generally, C. mitchelli does not exceed 100 cm (39 in) in total length (including tail), with large males measuring between 90 and 100 cm (35 and 39 in). The race on Isla Ángel de la Guarda is known to become larger, the maximum recorded length for a specimen there being 136.7 cm (53.8 in). In contrast, the population on El Muerto Island only reaches a maximum of 63.7 cm (25.1 in) in length.[3]
Geographic range
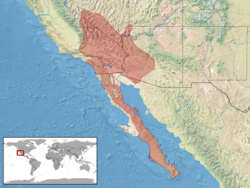
C. mitchelli is found in the southwestern United States and in northwestern Mexico. In the US, its range includes east-central and southern California , southwestern Nevada, extreme southwestern Utah, and western Arizona. In Mexico, it is native in most of Baja California, including Baja California Sur. It also inhabits a number of islands in the Gulf of California, including Angel de la Guarda Island, Carmen, Cerralvo, El Muerto, Espíritu Santo, Monserrate, Piojo, Salsipuedes, and San José, as well as on Santa Margarita Island off the Pacific coast of Baja California Sur.[2]
The type locality is listed as "Cape St. Lucas, Lower California" (Cabo San Lucas, Baja California Sur, Mexico).[2]
Subspecies and taxonomy
| Subspecies[7] | Taxon author[7] | Common name[8] | Geographic range[8] |
|---|---|---|---|
| C. m. mitchellii | (Cope, 1861) | San Lucan speckled rattlesnake | Mexico, in Baja California Sur and on the islands of Santa Margarita, Cerralvo, Espíritu Santo, San José, Monserrate, and Carmen |
| C. m. muertensis | Klauber, 1949 | El Muerto Island speckled rattlesnake | Mexico, on the island of Isla El Muerto |
Grismer (1999) argued that C. m. angelensis and C. m. muertensis should be given species status, mainly due to differences in body size.[3] More recently, Douglas et al. (2007) [9] recognised C.m. stephensi as a full species, and Meik et al. (2015) [10] elevated both the southwestern and the Angel de la Guarda speckled rattlesnakes to the state of full species, C. pyrrhus and C. angelensis, whereas the El Muerto Island speckled rattlesnake was considered part of C. pyrrhus
Conservation status
The nominate subspecies (C. m. mitchellii ) is classified as "Least Concern" on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. The population trend was stable when assessed in 2007.[1] Species are listed as such due to their wide distribution, presumed large population, or because they are unlikely to be declining fast enough to qualify for listing in a more threatened category.[11]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Frost, D.R.; Hammerson, G.A.; Gadsden, H. (2007). "Crotalus mitchellii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2007: e.T64323A12768039. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2007.RLTS.T64323A12768039.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/64323/12768039. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 McDiarmid RW, Campbell JA, Touré TA (1999). Snake Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, Volume 1. Washington, District of Columbia. Herpetologists' League. 511 pp. ISBN:1-893777-00-6 (series). ISBN:1-893777-01-4 (volume).
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Campbell JA, Lamar WW (2004). The Venomous Reptiles of the Western Hemisphere. Ithaca and London: Comstock Publishing Associates. 870 pp. 1500 plates. ISBN:0-8014-4141-2.
- ↑ U.S. Navy (1991). Poisonous Snakes of the World. United States Government. New York: Dover Publications Inc. 203 pp. ISBN:0-486-26629-X.
- ↑ Ditmars RL (1933). Reptiles of the World. Revised Edition. New York: The MacMillan Company. 329 pp. 89 plates.
- ↑ Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. ISBN:978-1-4214-0135-5. ("Mitchell, S.W.", p. 180).
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 "Crotalus mitchellii ". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=174313. Retrieved 25 February 2007.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Klauber LM (1997). Rattlesnakes: Their Habitats, Life Histories, and Influence on Mankind. Second Edition. First published in 1956, 1972. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN:0-520-21056-5.
- ↑ Douglas ME, Douglas MR, Schuett GW, Porras LW, Thomason BL (2007). "Genealogical concordance between mitochondrial and nuclear DNAs supports species recognition of the Panamint rattlesnake (Crotalus mitchellii stephensi )". Copeia 2007: 920–932.
- ↑ Meik JM, Streicher JW, Lawing AM, Flores-Villela O, Fujita MK (2015). "Limitations of Climatic Data for Inferring Species Boundaries: Insights from Speckled Rattlesnakes". PLoS ONE 10 (6): e0131435. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0131435
- ↑ 2001 Categories & Criteria (version 3.1) at the IUCN Red List. Accessed 13 September 2007.
Further reading
- Cope ED (1861). "Contributions to the Ophiology of Lower California, Mexico and Central America". Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia 13: 292-306. (Caudisona mitchellii, new species, pp. 293–294).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Crotalus mitchellii. |
- Crotalus angelensis at San Diego Natural History Museum
- Crotalus mitchelli at San Diego Natural History Museum
- Crotalus mitchellii pyrrhus
Wikidata ☰ Q1498023 entry
 |


