Biology:Ctenotus strauchii
| Ctenotus strauchii | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Family: | Scincidae |
| Genus: | Ctenotus |
| Species: | C. strauchii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Ctenotus strauchii (Boulenger, 1887)
| |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
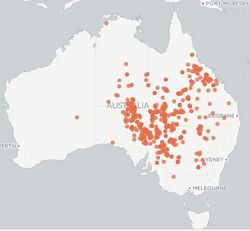
Ctenotus strauchii, also known commonly as the eastern barred wedge-snout ctenotus or Strauch's ctenotus, is a small species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Australia and is found throughout semi-arid and arid regions in most of Australia's mainland states except Western Australia, although one record does exist for Western Australia in 1975.[3]
Etymology
The specific name, strauchii, is in honour of Russian herpetologist Alexander Strauch.[4]
Description
C. strauchii is a small skink, that has an average snout-to-vent length (SVL) of 5.5 cm (2.2 in), and varies in colour from chocolate brown to reddish-brown.[5] A series of pale spots are enclosed by a black laterodorsal stripe, which is edged by a white dorsolateral stripe.[6] This stripe is bordered above by a line of small black blotches.[5] The upper flanks are black with a series of between 1 and 3 pale mostly vertical dots.[5] A narrow white stripe may run from below the eye right through the mid body, where it passes through the groin and continues as a lower lateral stripe until it breaks up into spots of flecks of white along the side of the tail.[5]
Reproduction
C. strauchii is oviparous, which means it lays eggs.[7] This contrasts with other skink species which are live bearers (viviparous). Egg clutch size is unknown.[8]
Conservation status
The conservation status of Ctenotus strauchii is listed as Least Concern (IUCN 3.1) risk.[7] It does not qualify for a more at-risk category. Widespread and abundant taxa are included in this category.
Threats
Although listed as common C. strauchii is not immune to environmental threats such as:
- Climate change
- Habitat destruction
- Habitat degradation
- Feral predators such as foxes, dogs and cats
- Disease
- Cane toads[9]
Habitat and Ecology
C. strauchii inhabits areas with hard stony soils with minimal vegetation cover in woodland and scrubland areas, within the semi-arid and dry regions of Eastern Australia.[6] It is found amongst debris such as fallen timber, leaf litter and other debris within mallee, savannah woodland and grassland areas[5] C. strauchii was given its scientific name by George Albert Boulenger a Belgian-United Kingdom zoologist who described and gave scientific names to over 2,000 new animal species, chiefly fish, reptiles, and amphibians. Skinks of the genus Ctenotus are often called comb-eared skinks, a reference to the scales aligned near the ear. They are active, diurnal lizards found in a variety of habitats.
Geographic range
Ctenotus strauchii has been recorded in New South Wales, Victoria, South Australia, Queensland and Northern Territory[3]
References
- ↑ Wilson S, Shea G, Amey A, Hobson R (2018). "Ctenotus strauchii ". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018: e.T109464651A109464660. https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T109464651A109464660.en. Downloaded on 06 June 2020.
- ↑ Ctenotus strauchii at the Reptarium.cz Reptile Database. Accessed 4 June 2016.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Atlas of Living Australia". http://bie.ala.org.au/species/urn:lsid:biodiversity.org.au:afd.taxon:78171eb5-db5b-44d6-a4f2-58bea3356283#overview.
- ↑ Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. ISBN:978-1-4214-0135-5. (Ctenotus strauchii, p. 256).
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Cogger, Harold (2000). Reptiles and Amphibians of Australia. Sydney: New Holland Publishers. ISBN 187633433-9.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Wilson, Steve; Swan, Gerry (2003). A Complete Guide to Reptiles of Australia. Sydney: New Holland Publishers. ISBN 187633472X. https://archive.org/details/completeguidetor0000wils.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Eastern barred wedgesnout ctenotus (Ctenotus strauchii )". http://bie.ala.org.au/species/urn:lsid:biodiversity.org.au:afd.taxon:78171eb5-db5b-44d6-a4f2-58bea3356283. Retrieved 10 June 2017.
- ↑ "Clutch size". http://www.arod.com.au/arod/reptilia/Squamata/Scincidae/Ctenotus/strauchii.
- ↑ "Threats to Ctenotus strauchii ". http://www.arod.com.au/arod/reptilia/Squamata/Scincidae/Ctenotus/strauchii.
Further reading
- Boulenger GA (1887). Catalogue of the Lizards in the British Museum (Natural History). Second Edition. Volume III. ... Scincidæ ... London: Trustees of the British Museum (Natural History). (Taylor and Francis, printers). xii + 575 pp. + Plates I–XL. (Lygosoma strauchii, new species, p. 229 + Plate XII, figures 3, 3a).
- Cogger HG (2014). Reptiles and Amphibians of Australia, Seventh Edition. Clayton, Victoria, Australia. CSIRO Publishing. xxx + 1,033 pp. ISBN:978-0643100350.
- Wilson, Steve; Swan, Gerry (2013). A Complete Guide to Reptiles of Australia, Fourth Edition. Sydney: New Holland Publishers. 522 pp. ISBN:978-1921517280.
Wikidata ☰ Q5129415 entry
 |