Chemistry:Trimethylenetetrathiafulvalenedithiolate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(5,6-dihydro-4H-cyclopenta[d][1,3]dithiol-2-ylidene)-1,3-dithiole-4,5-dithiolate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H6S6−2 | |
| Molar mass | 306.51 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Trimethylenetetrathiafulvalenedithiolate (tmdt) is a ligand used in the making of metal organic electric conductors. It normally has a charge of −2.[1] Known compounds include Ni(tmdt)2,[2] Pt(tmdt)2,[3] Pd(tmdt)2,[2] Au(tmdt)2,[4]
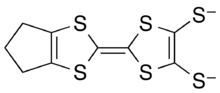
The tmdt2− ion is based on fulvalene, but with the four atoms adjacent to the bridging double bond replaced with sulfur yielding tetrathiafulvalene, at one end of the pair of rings is another five-member ring attached by adding three carbon atoms (the trimethylene part), and the other side of the fulvalene has two sulfur atoms, that bond to the metal ion.[5]
The gold compound has an antiferromagnetic transition at 100 K (−173 °C).[6]
Some of the sulfur atoms can be replaced by selenium to yield similar conducting compounds.[6]
List
| formula | comment | CAS | ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni(tmdt)2 | [2] | ||
| Pd(tmdt)2 | [2] | ||
| Pt(tmdt)2 | 1196461-89-8 | [3] | |
| Au(tmdt)2 | 852955-03-4 | [6] |
References
- ↑ Devillanova, Francesco A.; Mont, Woolf-Walther Du (2013) (in en). Handbook of Chalcogen Chemistry: New Perspectives in Sulfur, Selenium and Tellurium. Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 155. ISBN 9781849736244. https://books.google.com/books?id=EEnuwFun-4QC&pg=PA155.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Tanaka, Hisashi; Kobayashi, Hayao; Kobayashi, Akiko (January 2002). "Syntheses and physical properties of metal complex conductors with extended ttf ligands". Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals 380 (1): 197–202. doi:10.1080/713738705. Bibcode: 2002MCLC..380..197T.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Zhou, Biao; Kobayashi, Akiko; Okano, Yoshinori; Nakashima, Takeshi; Aoyagi, Shinobu; Nishibori, Eiji; Sakata, Makoto; Tokumoto, Madoka et al. (18 September 2009). "Single-Component Molecular Conductor [Pt(tmdt)2] (tmdt = trimethylenetetrathiafulvalenedithiolate) - An Advanced Molecular Metal Exhibiting High Metallicity". Advanced Materials 21 (35): 3596–3600. doi:10.1002/adma.200803116. Bibcode: 2009AdM....21.3596Z.
- ↑ Suzuki, Wakako; Fujiwara, Emiko; Kobayashi, Akiko; Fujishiro, Yuichi; Nishibori, Eiji; Takata, Masaki; Sakata, Makoto; Fujiwara, Hideki et al. (February 2003). "Highly Conducting Crystals Based on Single-Component Gold Complexes with Extended-TTF Dithiolate Ligands". Journal of the American Chemical Society 125 (6): 1486–1487. doi:10.1021/ja0292243. PMID 12568602.
- ↑ Bruce, Duncan W.; O'Hare, Dermot; Walton, Richard I. (2011) (in en). Molecular Materials. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781119972952. https://books.google.com/books?id=hft0i1x2e0oC&pg=PT251.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Saito, Gunzi; Enoki, Toshiaki; Wudl, Fred; Haddon, Robert C.; Tanigaki, Katsumi (2007) (in en). Multifunctional Conducting Molecular Materials. Royal Society of Chemistry. ISBN 9780854044962. https://books.google.com/books?id=VgCrMqOlCh4C&pg=PA45.
 |

