Astronomy:Firmament
In ancient near eastern cosmology, the firmament means a celestial barrier that separates the heavenly waters above from the Earth below.[1] In biblical cosmology, the firmament (Hebrew: רָקִ֫יעַ rāqīaʿ) is the vast solid dome created by God during the Genesis creation narrative to separate the primal sea into upper and lower portions so that the dry land could appear.[2][3]
The concept was adopted into the subsequent Classical and Medieval models of heavenly spheres, but was dropped with advances in astronomy in the 16th and 17th centuries. Today it is known as a synonym for sky or heaven.
Etymology
Firmament
In English, the word "firmament" is recorded as early as 1250, in the Middle English Story of Genesis and Exodus. It later appeared in the King James Bible. The same word is found in French and German Bible translations, all from Latin firmamentum (a firm object), used in the Vulgate (4th century).[4] This in turn is a calque of the Greek στερέωμᾰ (steréōma), also meaning a solid or firm structure (Greek στερεός = rigid), which appears in the Septuagint, the Greek translation made by Jewish scholars around 200 BC.
Raqia
These words all translate the Biblical Hebrew word rāqīaʿ (רָקִ֫יעַ), used for example in Genesis 1.6, where it is contrasted with shamayim (שָׁמַיִם), translated as "heaven(s)" in Genesis 1.1. Rāqīaʿ derives from the root rqʿ (רָקַע), meaning "to beat or spread out thinly".[5][6] The Hebrew lexicographers Brown, Driver and Briggs gloss the noun with "extended surface, (solid) expanse (as if beaten out)" and distinguish two main uses: 1. "(flat) expanse (as if of ice), as base, support", and 2. "the vault of heaven, or 'firmament,' regarded by Hebrews as solid and supporting 'waters' above it."[7] A related noun, riqquaʿ (רִקּוּעַ), found in Numbers 16.38 (Hebrew numbering 17.3), refers to the process of hammering metal into sheets.[7] Gerhard von Rad explains:
Rāqīaʿ means that which is firmly hammered, stamped (a word of the same root in Phoenecian means "tin dish"!). The meaning of the verb rqʿ concerns the hammering of the vault of heaven into firmness (Isa. 42.5; Ps.136.6). The Vulgate translates rāqīaʿ with firmamentum, and that remains the best rendering.
— Gerhard von Rad[8]
History
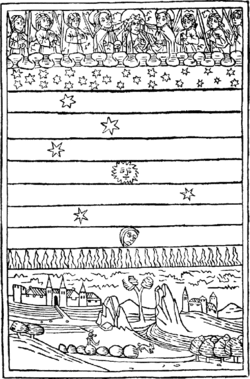
Ancient Near Eastern cosmology
A firmament is created according to the Enūma Eliš Babylonian creation myth.[9] In the Hebrew Bible, it is mentioned in the Genesis creation narrative, the Psalms, and the Book of Isaiah. Between these two main sources, there is a fundamental agreement in the cosmological models pronounced: this included a flat and likely disk-shaped world with a solid firmament.[10][11]
The two prominent representations of the firmament were that it was either flat and hovering over the Earth, or that it was a dome and entirely enclosed the Earth's surface. Beyond the firmament is the upper waters, above which further still is the divine abode.[11] The gap between heaven and Earth was bridged by ziggurats and these supported stairways that allowed gods to descend into the Earth from the heavenly realm. A Babylonian clay tablet from the 6th century BC illustrates a world map.[12]
Egyptian cosmology
In ancient Egyptian texts, and from texts across the near east generally, the firmament was described as having special doors or gateways on the eastern and western horizons to allow for the passage of heavenly bodies during their daily journeys. These were known as the windows of heaven or the gates of heaven.[13][14] In Egyptian texts particularly, these gates also served as conduits between the earthly and heavenly realms for which righteous people could ascend. The gateways could be blocked by gates to prevent entry by the deceased as well. As such, funerary texts included prayers enlisting the help of the gods to enable the safe ascent of the dead.[15] Ascent to the celestial realm could also be done by a celestial ladder made by the gods.[16]
Four different Egyptian models of the firmament and/or the heavenly realm are known. One model was that it was the shape of a bird: the firmament above represented the underside of a flying falcon, with the sun and moon representing its eyes, and its flapping causing the wind that humans experience.[17] The second was a cow, as per the Book of the Heavenly Cow. The cosmos is a giant celestial cow represented by the goddess Nut or Hathor. The cow consumed the sun in the evening and rebirthed it in the next morning.[18] The third is a celestial woman, also represented by Nut. The heavenly bodies would travel across her body from east to west. The midriff of Nut was supported by Shu (the air god) and Geb (the earth god) lay outstretched between the arms and feet of Nut. Nut consumes the celestial bodies from the west and gives birth to them again in the following morning. The stars are inscribed across the belly of Nut and one needs to identify with one of them, or a constellation, in order to join them after death.[19] The fourth model was a flat (or slightly convex) celestial plane which, depending on the text, was thought to be supported in various ways: by pillars, staves, scepters, or mountains at the extreme ends of the Earth. The four supports give rise to the motif of the "four corners of the world".[20]
Early Greek cosmology
Prior to the systematic study of the cosmos by the Ionian School in the city of Miletus in the 6th century BC, the early Greek conception of cosmology was closely related to that of near eastern cosmology and envisioned a flat Earth with a solid firmament above the Earth supported by pillars. However, the work of Anaximander, Anaximenes, and Thales, followed by classical Greek theoreticians like Aristotle and Ptolemy ushered in the notions of a spherical Earth and an Earth floating in the center of the cosmos as opposed to resting on a body of water. This picture was geocentric and represented the cosmos as a whole as spherical.[21]
Patristic cosmology

One problem for Christian interpreters was in understanding the distinction between the heaven created on the first day and the firmament created in the second day. Origen followed the cosmological dualism of the Hellenistic Jewish scholar Philo of Alexandria, who proposed a distinction between the material and eternal creations but does not appear to have associated matter or materiality with evil.[22] Under Origen's influence the waters above became associated with the spiritual plane of Christian contemplative exercise and the waters below with the demonic and infernal.[23] The firmament is the boundary between the physical and spiritual worlds.[24]
Origen's model of two heavens was followed by later writers who kept the concept of a spiritual and immaterial heaven of the first day (caelum) and the corporeal/sidereal firmamentum.[25][26]
Various views on the materiality of the firmament emerged among the Church Fathers, including that it had been made out of air, out of the four elements, or out of a yet-distinct fifth element.[27] In the Hexaemeron of Basil of Caesarea the firmament is depicted as spherical or domed with a flat underside that formed a pocket or membrane in which the waters were held. Not all of the Church fathers followed Origen.[28][29] Manlio Simonetti noted Basil of Caesarea's "strong tone of criticism" of Origen's teaching.[30]
Appealing to a Platonic division between base matter and heavenly or spiritual matter, Augustine of Hippo would distinguish between the waters below the firmament and the waters above the firmament. This involved the spiritual interpretation of the upper waters. In this, he was followed by John Scotus Eriugena. In De Genesi ad litteram (perhaps his least studied work) Augustine wrote: "only God knows how and why [the waters] are there, but we cannot deny the authority of Holy Scripture which is greater than our understanding".[31]
Ambrose struggled with understanding how the waters above the firmament could be held up given the spherical nature of the cosmos: the solution was to be sought in God's dominion over the cosmos, in the same way that God held up the Earth in the middle of the cosmos though it has no support.[32] About this Ambrose wrote: "Wise men of the world say that water cannot be over the heavens".[33]
The debate about the waters being located above the heavens continued into the Middle Ages. It made no sense under the explanations of the natural world proposed by Aristotle, recalling the statement from Augustine's literal commentary on Genesis: "Our business now, after all, is to inquire how God's Scriptures say he established things according to their proper natures." Scholastic theologians engaged in the pursuit of applying natural science to illuminate the sacred included Alexander of Hales, William of Auxerre (who offered that the location of the waters as recorded by Moses could only be explained by a miracle), William of Auvergne, and Philip the Chancellor.[34][35][27]
Whether the firmament was hard/firm or soft/fluid was also up for debate: the notion of a soft or fluid firmament was held until it was challenged in the 13th century by the introduction of the Aristotelian-Ptolemaic cosmos, a trend that would only culminate in the 16th century.[27] Bede reasoned that the waters might be held in place if they were frozen solid: the siderum caelum (heaven of the celestial bodies) was made firm (firmatum) in the midst of the waters so should be interpreted as having the firmness of crystalline stone (cristallini Iapidis).[36]
Jewish cosmology
A distinctive collection of ideas about the cosmos were drawn up and recorded in the rabbinic literature, though the conception is rooted deeply in the tradition of near eastern cosmology recorded in Hebrew, Akkadian, and Sumerian sources, combined with some additional influences in the newer Greek ideas about the structure of the cosmos and the heavens in particular.[37] The rabbis viewed the heavens to be a solid object spread over the Earth, which was described with the biblical Hebrew word for the firmament, raki’a. Two images were used to describe it: either as a tent, or as a dome; the former inspired from biblical references, though the latter is without an evident precedent.[38] As for its composition, just as in cuneiform literature the rabbinic texts describe that the firmament was made out of a solid form of water, not just the conventional liquid water known on the Earth. A different tradition makes an analogy between the creation of the firmament and the curdling of milk into cheese. Another tradition is that a combination of fire and water makes up the heavens. This is somewhat similar to a view attributed to Anaximander, whereby the firmament is made of a mixture of hot and cold (or fire and moisture).[39] Yet another dispute concerned how thick the firmament was. A view attributed to R. Joshua b. R. Nehemiah was that it was extremely thin, no thicker than two or three fingers. Some rabbis compared it to a leaf. On the other hand, some rabbis viewed it as immensely thick. Estimates that it was as thick as a 50 year journey or a 500 year journey were made. Debates on the thickness of the firmament also impacted debates on the path of the sun in its journey as it passes through the firmament through passageways called the "doors" or "windows" of heaven.[40] The number of heavens or firmaments was often given as more than one: sometimes two, but much more commonly, seven. It is unclear whether the notion of the seven heavens is related to earlier near eastern cosmology or the Greek notion of the surrounding of the Earth by seven concentric spheres: one for the sun, one for the moon, and one for each of the five other (known) planets.[41] A range of additional discussions in rabbinic texts surrounding the firmament included those on the upper waters,[42] the movements of the heavenly bodies and the phenomena of precipitation,[43] and more.[44][45]
The firmament also appears in non-rabbinic Jewish literature, such as in the cosmogonic views represented in the apocrypha. A prominent example is in the Book of Enoch composed around 300 BC. In this text, the sun rises from one of six gates from the east. It crosses the sky and sets into a window through the firmament in the west. The sun then travels behind the firmament back to the other end of the Earth, from whence it could rise again.[46] In the Testament of Solomon, the heavens are conceived in a tripartite structure and demons are portrayed as being capable of flying up to and past the firmament in order to eavesdrop on the decisions of God.[47] Another example of Jewish literature describing the firmament can be found in Samaritan poetry.[48]
Quranic cosmology
The Quran describes a concrete[clarification needed] firmament above the Earth, built by God and lifted up:[49][50] the firmament is maintained not by any pillars but by God directly maintaining it, in a description resembling that of the Syriac theologian Jacob of Serugh in his Hexaemeron.[51] Another commonality between the two is in describing the firmament as being decorated by stars.[52] The heavens are analogized to a roof, structure, and edifice without crack or fissure. It is extremely broad and stretched, but it is also constantly broadening.[50] Though there has been some dispute over the exact shape of the Quranic firmament (primarily over whether it is flat or domed), the most recent study by Tabatabaʾi and Mirsadri favors a flat firmament.[53] In addition, there are seven heavens or firmaments[54][55] and they were made from smoke during the creation week, resembling the view of Basil of Caesarea.[56]
Modern cosmology
The model established by Aristotle became the dominant model in the Classical and Medieval world-view, and even when Copernicus placed the Sun at the center of the system he included an outer sphere that held the stars (and by having the earth rotate daily on its axis it allowed the firmament to be completely stationary). Tycho Brahe's studies of the nova of 1572 and the Comet of 1577 were the first major challenges to the idea that orbs existed as solid, incorruptible, material objects,[57] and in 1584 Giordano Bruno proposed a cosmology without a firmament: an infinite universe in which the stars are actually suns with their own planetary systems.[58] After Galileo began using a telescope to examine the sky it became harder to argue that the heavens were perfect, as Aristotelian philosophy suggested, and by 1630 the concept of solid orbs was no longer dominant.[57]
See also
- Religion:Abzu – Primeval sea in Mesopotamian mythology
- Religion:Chinese theology – Chinese theological conception of Heaven
- Religion:Cosmic ocean – Mythological motif
- Unsolved:Flood geology – Pseudoscientific attempt to reconcile geology with the Genesis flood narrative
- Religion:Heaven in Judaism – Dwelling place of God and other heavenly beings
- Astronomy:Primum Mobile – Outermost moving sphere in the geocentric model of the universe
- Religion:Sky deity – Deity associated with the sky
References
Citations
- ↑ Rochberg 2010, p. 344.
- ↑ Pennington 2007, p. 42.
- ↑ Ringgren 1990, p. 92.
- ↑ "Online Etymology Dictionary – Firmament". http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=firmament.
- ↑ Brown, Driver & Briggs 1906, p. 955.
- ↑ "Lexicon Results Strong's H7549 – raqiya'". Blue Letter Bible. https://www.blueletterbible.org/lang/lexicon/lexicon.cfm?t=kjv&strongs=h7549.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Brown, Driver & Briggs 1906, p. 956.
- ↑ von Rad 1961, p. 53.
- ↑ Horowitz 1998.
- ↑ Stadelmann 1970.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Simon-Shoshan 2008, p. 70.
- ↑ Hannam 2023, p. 19–20.
- ↑ Kulik 2019, p. 243.
- ↑ Heimpel 1986, p. 132–140.
- ↑ Wright 2000, p. 19, 33–34.
- ↑ Wright 2000, p. 22.
- ↑ Wright 2000, p. 6–7.
- ↑ Wright 2000, p. 7–8.
- ↑ Wright 2000, p. 8–10.
- ↑ Wright 2000, p. 10–16.
- ↑ Simon-Shoshan 2008, p. 70–71.
- ↑ van Groningen 1967, p. 67.
- ↑ Rasmussen 2019, p. 118-9.
- ↑ Rasmussen 2019, p. 121.
- ↑ Rochberg 2010, p. 349.
- ↑ Rasmussen 2019, p. 120.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 27.2 Rochberg 2010, p. 350–353.
- ↑ Scott, Mark S. M. (2012). Journey Back to God: Origen on the Problem of Evil. Oxford Academic. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199841141.003.0004. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199841141.003.0004.
- ↑ The Making of Orthodoxy: Essays in Honour of Henry Chadwick. Cambridge University Press. 2002. pp. 69–70.
- ↑ The Reception and Interpretation of the Bible in Late Antiquity: Proceedings of the Montréal Colloquium in Honour of Charles Kannengiesser. Brill. 2008. p. 512.
- ↑ Lemay, Helen Rodnite (1977). "Science and Theology at Chartres: The Case of the Supracelestial Waters". The British Journal for the History of Science 10 (3): 226–236. doi:10.1017/S0007087400015673.
- ↑ Rochberg 2010, p. 349–350.
- ↑ Boccaletti Dino, The Waters Above the Firmament, p.36 2020
- ↑ Philosophy and Theology in the Late Middle Ages. Brill. 2011. pp. 44–46.
- ↑ Rasmussen 2019, p. 119.
- ↑ Randles, W. G. L. (1999). The Unmaking of the Medieval Christian Cosmos, 1500–1760. Routledge.
- ↑ Simon-Shoshan 2008, p. 69.
- ↑ Simon-Shoshan 2008, p. 72.
- ↑ Simon-Shoshan 2008, p. 72–75.
- ↑ Simon-Shoshan 2008, p. 75–77.
- ↑ Simon-Shoshan 2008, p. 77–80.
- ↑ Simon-Shoshan 2008, p. 80–81.
- ↑ Simon-Shoshan 2008, p. 81–88.
- ↑ Simon-Shoshan 2008, p. 88–96.
- ↑ Hannam 2023, p. 150–151.
- ↑ Hannam 2023, p. 149.
- ↑ Brannon 2011, p. 196.
- ↑ Lieber 2022, p. 137–138.
- ↑ Decharneux 2023, p. 180–185.
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 Tabatabaʾi & Mirsadri 2016, p. 209.
- ↑ Decharneux 2019.
- ↑ Sinai 2023, p. 413–414.
- ↑ Tabatabaʾi & Mirsadri 2016, p. 218–233.
- ↑ Decharneux 2023, p. 185–193.
- ↑ Hannam 2023, p. 184.
- ↑ Decharneux 2023, p. 128–129.
- ↑ 57.0 57.1 Grant 1996, p. 349.
- ↑ Giordano Bruno, De l'infinito universo e mondi (On the Infinite Universe and Worlds), 1584.
Sources
- Brannon, M. Jeff (2011). The Heavenlies in Ephesians: A Lexical, Exegetical, and Conceptual Analysis. Bloomsbury Publishing.
- Brown, Francis; Driver, S.R.; Briggs, Charles A. (1906). A Hebrew and English Lexicon of the Old Testament. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Decharneux, Julien (2019). "Maintenir le ciel en l'air " sans colonnes visibles " et quelques autres motifs de la creatio continua selon le Coran en dialogue avec les homélies de Jacques de Saroug". Oriens Christianus 102: 237–267. https://www.academia.edu/44557376.
- Decharneux, Julien (2023). Creation and Contemplation The Cosmology of the Qur'ān and Its Late Antique Background. De Gruyter.
- Grant, Edward (1996). Planets, Stars, and Orbs: The Medieval Cosmos, 1200-1687. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-56509-7.
- van Groningen, G (1967). First Century Gnosticism: Its Origin and Motifs. Brill.
- Hannam, James (2023). The Globe: How the Earth Became Round. Reaktion Books.
- Heimpel, Wolfgang (1986). "The Sun at Night and the Doors of Heaven in Babylonian Texts". Journal of Cuneiform Studies 38 (2): 127–151. doi:10.2307/1359796. https://www.jstor.org/stable/1359796.
- Horowitz, Wayne (1998). Mesopotamian Cosmic Geography. Eisenbrauns.
- Kulik, Alexander (2019). "The enigma of the five heavens and early Jewish cosmology". Journal for the Study of the Pseudepigrapha 28 (4): 239–266. doi:10.1177/0951820719861900. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/0951820719861900.
- Lieber, Laura Suzanne (2022). Classical Samaritan Poetry. Eisenbrauns.
- Pennington, Jonathan T. (2007). Heaven and earth in the Gospel of Matthew. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-16205-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=EGTaBJDQoD0C&pg=PA42.
- Rasmussen, Adam (2019). Genesis and Cosmos. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-39693-7.
- Ringgren, Helmer (1990). "Yam". in Botterweck, G. Johannes; Ringgren, Helmer. Theological Dictionary of the Old Testament. Eerdmans. ISBN 978-0-8028-2330-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=MCOd-uAEQy0C&q=cosmic+ocean&pg=PA92.
- Rochberg, Francesca (2010). In the Path of the Moon: Babylonian Celestial Divination and Its Legacy. Brill.
- Simon-Shoshan, Moshe (2008). ""The Heavens Proclaim the Glory of God..." A Study in Rabbinic Cosmology". Bekhol Derakhekha Daehu–Journal of Torah and Scholarship 20: 67–96. https://asif.co.il/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/E-067-096.pdf.
- Sinai, Nicolai (2023). Key Terms of the Qur'an: A Critical Dictionary. Princeton University Press.
- Stadelmann, Luis I.J. (1970). The Hebrew Conception of the World. Biblical Institute Press.
- Tabatabaʾi, Mohammad Ali; Mirsadri, Saida (2016). "The Qurʾānic Cosmology, as an Identity in Itself". Arabica 63 (3–4): 201–234. doi:10.1163/15700585-12341398.
- von Rad, Gerhard (1961). Genesis: A Commentary. London: SCM Press.
- Wright, Edward J. (2000). The Early History of Heaven. Oxford University Press.
Further reading
- Blenkinsopp, Joseph (2011). Creation, Un-Creation, Re-Creation: A Discursive Commentary on Genesis 1–11. T&T Clarke International. ISBN 978-0-567-57455-8.
- Clifford, Richard J (2017). "Creatio ex Nihilo in the Old Testament/Hebrew Bible". in Anderson, Gary A.; Bockmuehl, Markus. Creation ex nihilo: Origins, Development, Contemporary Challenges. University of Notre Dame. ISBN 978-0-268-10256-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=vPA-DwAAQBAJ&pg=PT51.
- Couprie, Dirk L. (2011). Heaven and Earth in Ancient Greek Cosmology: From Thales to Heraclides Ponticus. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-1-4419-8116-5.
- James, E.O. (1969). Creation and Cosmology: A Historical and Comparative Inquiry. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-37807-0.
- López-Ruiz, Carolina (2010). When the Gods Were Born: Greek Cosmogonies and the Near East. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-04946-8.
- von Rad, Gerhard (1961). Genesis: A Commentary. London: SCM Press.[ISBN missing]
- Walton, John H. (2006). Ancient Near Eastern Thought and the Old Testament: Introducing the Conceptual World of the Hebrew Bible. Baker Academic. ISBN 0-8010-2750-0.
- Walton, John H. (2015). The Lost World of Adam and Eve: Genesis 2-3 and the Human Origins Debate. InterVarsity Press. ISBN 978-0-8308-9771-1.
- Wasilewska, Ewa (2000). Creation Stories of the Middle East. Jessica Kingsley Publishers. ISBN 978-1-85302-681-2.
External links
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Firmament. |
 |
