Astronomy:MHW-RTG
The Multihundred-Watt radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MHW RTG) is a type of US radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) developed for the Voyager spacecraft, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2.[1]
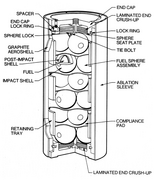
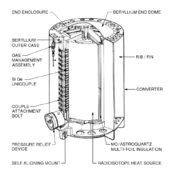
Each RTG has a total weight of 37.7 kg including about 4.5 kg of Pu-238[2] and uses 24 pressed plutonium-238 oxide spheres to provide enough heat to generate approximately 157 Watts of electrical power initially – halving every 87.7 years.[3]
Each RTG initially generated about 2400 Watts of thermal power.[4] Conversion of the decay heat of the plutonium to electrical power uses 312 silicon-germanium (SiGe) thermoelectric couples. The initial thermoelectric couple hot junction temperature was 1273 K (1000 °C, 1832 °F) with a cold junction temperature of 573 K (300 °C, 572 °F).[5]
Each Voyager spacecraft has 3 RTGs. Collectively, the RTGs supply each Voyager spacecraft with 470 Watts at launch.[6][7]
MHW-RTGs were used on the Lincoln Experimental Satellites 8 and 9.
Subsequent US spacecraft used the GPHS-RTG which used similar SiGe thermoelectric devices but a different packaging of the fuel.
The MMRTG is a newer RTG type, used on the Curiosity rover.
-
RTG heat source unit
-
RTG diagram 1
-
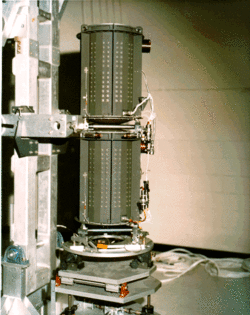
RTG unit
References
- ↑ Heacock (1980). "The Voyager Space Craft". Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers 194: 267–270. doi:10.1243/PIME_PROC_1980_194_026_02. http://www.stickings90.webspace.virginmedia.com/voyager.htm.
- ↑ "Space Nuclear Power" G.L.Bennett 2006
- ↑ "NASA Celebrates 45 Years of Voyager 1, Enabled by Radioisotope Power". NASA. September 5, 2022. https://rps.nasa.gov/news/63/nasa-celebrates-45-years-of-voyager-1-enabled-by-radioisotope-power/.
- ↑ "Totse.com | Nuclear Power in Space". Archived from the original on 2008-06-19. https://web.archive.org/web/20080619143130/http://www.totse.com/en/technology/space_astronomy_nasa/spacnuke.html. Retrieved 2012-10-19.
- ↑ Furlong, Richard R.; Wahlquist, Earl J. (1999). "U.S. space missions using radioisotope power systems". Nuclear News 42 (4): 26–34. http://www2.ans.org/pubs/magazines/nn/pdfs/1999-4-2.pdf. Retrieved January 2, 2011.
- ↑ "VOYAGER 2:Host Information". NASA. 1989. Archived from the original on July 21, 2011. https://web.archive.org/web/20110721050912/http://starbrite.jpl.nasa.gov/pds/viewHostProfile.jsp?INSTRUMENT_HOST_ID=VG2. Retrieved January 2, 2011.
- ↑ "Voyager 2 Craft Details". NASA-NSSDC-Spacecraft-Details. NASA. https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/display.action?id=1977-076A. Retrieved March 9, 2011.
See also
 |