Astronomy:May 2021 lunar eclipse
| Total eclipse | |||||||||||||||||
 Mountain View, California at 11:23 UTC, end of totality | |||||||||||||||||
| Date | 26 May 2021 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma | 0.4774 | ||||||||||||||||
| Magnitude | 1.0095 | ||||||||||||||||
| Saros cycle | 121 (55 of 82) | ||||||||||||||||
| Totality | 14 minutes, 30 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| Partiality | 187 minutes, 25 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| Penumbral | 302 minutes, 2 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||

A total lunar eclipse occurred on 26 May 2021.[1] A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. This can occur only when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are exactly or very closely aligned (in syzygy) with Earth between the other two, which can only happen at a full moon. The eclipsed moon appeared as a faint red disk in the sky due to a small amount of light being refracted through the Earth's atmosphere; this appearance gives a lunar eclipse its nickname of a Blood Moon.
It was the first total lunar eclipse since the January 2019 lunar eclipse, and the first in a series of an almost tetrad (with four consecutive total or deep partial lunar eclipses).[2] The next total eclipse occurred in May 2022. The event took place near lunar perigee; as a result, this supermoon was referred to in United States media coverage as a "super flower blood moon",[Note 1][3][4] and elsewhere as a "super blood moon".[5][6]
It was followed two weeks later by an annular solar eclipse on 10 June 2021 over the northern polar regions of Earth.
This lunar eclipse was the first of an almost tetrad, the others being 19 Nov 2021 (P), 16 May 2022 (T) and 08 Nov 2022 (T).
Visibility
The total lunar eclipse was visible over the Pacific Ocean, Oceania, and Antarctica in its entirety. Observers located in southern and eastern Asia saw the eclipse at moonrise, whilst observers located in western North America and western South America saw the eclipse at moonset.[7]
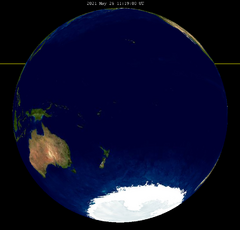 
|
 Visibility map |
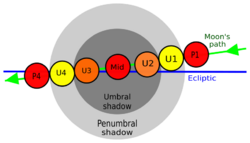
Contact timing
Local times are recomputed here for the time zones of the areas where the eclipse was visible:
| Time Zone adjustments from UTC |
+8h | +10h | +12h | -10h | -8h | -7h | -6h | -5h | -4h | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWST | AEST | NZST | HST | AKDT | PDT | MDT | CDT | EDT | |||||
| Event | Evening 26 May / Morning 27 May | Morning 26 May | |||||||||||
| P1 | Penumbral began | 4:48 pm | 6:48 pm | 8:48 pm | 10:48 pm | 12:48 am | 1:48 am | 2:48 am | 3:48 am | 4:48 am | |||
| U1 | Partial began | 5:45 pm | 7:45 pm | 9:45 pm | 11:45 pm | 1:45 am | 2:45 am | 3:45 am | 4:45 am | 5:16 am | |||
| U2 | Total began | 7:11 pm | 9:11 pm | 11:11 pm | 1:11 am | 3:11 am | 4:11 am | 5:11 am | 6:11 am | Set | |||
| Greatest eclipse | 7:19 pm | 9:19 pm | 11:19 pm | 1:19 am | 3:19 am | 4:19 am | 5:19 am | 6:19 am | Set | ||||
| U3 | Total ended | 7:26 pm | 9:26 pm | 11:26 pm | 1:26 am | 3:26 am | 4:26 am | 5:26 am | Set | Set | |||
| U4 | Partial ended | 8:52 pm | 10:52 pm | 12:52 am | 2:52 am | 4:52 am | Set | Set | Set | Set | |||
| P4 | Penumbral ended | 9:50 pm | 11:50 pm | 1:50 am | 3:50 am | 5:50 am | Set | Set | Set | Set | |||
Observations
-
Garrett County, Maryland, 9:43 UTC
-
Minneapolis, Minnesota, 10:19 UTC
-
Berwick Forest, New Zealand, 10:52 UTC
-
Taoyuan, Taiwan, 11:02 UTC
-
Banyuwangi, Indonesia, 11:03 UTC
-
Canberra, Australia, 11:11 UTC
-
Manila, Philippines, 11:13 UTC
-
Laguna, Philippines, 11:15 UTC
-
Geelong, Victoria, 11:23 UTC
-
Tarlac, Philippines, 11:32 UTC
-
Kediri, Indonesia, 11:32 UTC
-
Magetan, Indonesia, 11:34 UTC
-
New South Wales, Australia, 12:01 UTC
-
New South Wales, Australia, 12:21 UTC
-
Chennai, India, 13:27 UTC
Related eclipses
Eclipses of 2021
- A total lunar eclipse on 26 May
- An annular solar eclipse on 10 June
- A partial lunar eclipse on 19 November
- A total solar eclipse on 4 December
Lunar year series
Saros series
This eclipse was the 55th eclipse and final total eclipse of Saros cycle 121.[8]
Metonic series
First eclipse: May 26, 2002 Second eclipse: May 26, 2021. Third eclipse: May 26, 2040. Fourth eclipse: May 27, 2059.
Tzolkinex
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of April 15, 2014
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of July 6, 2028
Half-Saros cycle
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[9] This lunar eclipse is related to two annular solar eclipses of Solar Saros 128.
| May 20, 2012 | June 1, 2030 |
|---|---|

|

|
See also
- List of lunar eclipses and List of 21st-century lunar eclipses
Notes
- ↑ A full moon occurring in May has been termed a "Flower moon" in the US as recorded in the Old Farmer's Almanac.
References
- ↑ Template:LEplot2001 link
- ↑ "26 May 2021 Total Lunar Eclipse (Blood Moon)" (in en). https://www.timeanddate.com/eclipse/lunar/2021-may-26/.
- ↑ Look up! The Super Flower Blood Moon lunar eclipse is coming 26 May www.space.com
- ↑ "The 'Super Flower Blood Moon' Is About to Light Up Skies! How to Watch This Week's Celestial Event" (in en). https://people.com/human-interest/how-to-watch-super-flower-blood-moon-may-2021/.
- ↑ "Sydney takes 'pole position' in rare super blood moon display" (in en). 26 May 2021. https://www.smh.com.au/sydney-news/sydney-takes-poll-position-in-rare-super-blood-moon-display-20210526-p57vg6.html.
- ↑ "Catch the super flower blood moon last night? It may not have been all it was cracked up to be". 26 May 2021. https://www.abc.net.au/news/2021-05-27/super-moon-blood-flower-lunar-eclipse-name/100153804.
- ↑ "26 May 2021 Total Lunar Eclipse (Blood Moon)" (in en). https://www.timeanddate.com/eclipse/lunar/2021-may-26/.
- ↑ "Total Lunar Eclipse of 26 May, 2021 AD". https://moonblink.info/Eclipse/eclipse/2021_05_26.
- ↑ Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
 |















