Astronomy:Modern Maximum
This article possibly contains inappropriate or misinterpreted citations that do not verify the text. (October 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
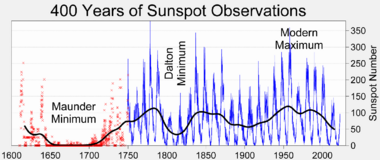
The Modern Maximum was found by Sami Solanki, Ilya G. Usoskin and colleagues[1] as the period of unusually high solar activity[2] which began with solar cycle 15 in 1914. It reached a maximum in solar cycle 19 during the late 1950s and may have ended with the peak of solar cycle 23 in 2000, as solar cycle 24 is recording, at best, very muted solar activity.[3] [needs update] Another proposed end date for the maximum is 2007, with the decline phase of Cycle 23. In any case the low solar activity of solar cycle 24 in the 2010s marked a new period of reduced solar activity. However the on-going (as of 2025) solar cycle 25 significantly exceeded its predicted low maximum.[4]
This maximum period is a natural example of solar variation, and one of many that are known from proxy records of past solar variability. The Modern Maximum reached a double peak once in the 1950s and again during the 1990s.
See also
- Maunder minimum
References
- ↑ Solanki, Sami K.; Usoskin, Ilya G.; Kromer, Bernd; Schüssler, Manfred; Beer, Jürg (2004). "Unusual activity of the Sun during recent decades compared to the previous 11,000 years". Nature 431 (7012): 1084–7. doi:10.1038/nature02995. PMID 15510145. Bibcode: 2004Natur.431.1084S. http://cc.oulu.fi/%7Eusoskin/personal/nature02995.pdf. Retrieved 17 April 2007., "11,000 Year Sunspot Number Reconstruction". Global Change Master Directory. http://gcmd.nasa.gov/KeywordSearch/Metadata.do?Portal=GCMD&KeywordPath=%5BParameters%3ACategory%3D%27EARTH+SCIENCE%27%2CTopic%3D%27SUN-EARTH+INTERACTIONS%27%2CTerm%3D%27SOLAR+ACTIVITY%27%2CVariable%3D%27SUNSPOTS%27%5D&OrigMetadataNode=GCMD&EntryId=NOAA_NCDC_PALEO_2005-015&MetadataView=Brief&MetadataType=0&lbnode=gcmd3b. Retrieved 2005-03-11.
- ↑ Usoskin I.G. (2017). "A History of Solar Activity over Millennia". Living Reviews in Solar Physics 14 (3): 3. doi:10.1007/s41116-017-0006-9. Bibcode: 2017LRSP...14....3U. PDF Copy
- ↑ Rigozo, N. R.; Echer, E.; Vieira, L. E. A.; Nordemann, D. J. R. (2001). "Reconstruction of Wolf Sunspot Numbers on the Basis of Spectral Characteristics and Estimates of Associated Radio Flux and Solar Wind Parameters for the Last Millennium". Solar Physics 203 (1): 179–191. doi:10.1023/A:1012745612022. Bibcode: 2001SoPh..203..179R.
- ↑ Solar Cycle 25 Continues to Strengthen Rapidly
 |
