Astronomy:Moonlet
From HandWiki
Short description: Small natural satellite orbiting a planet

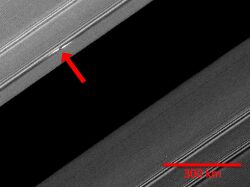



A moonlet, minor moon, minor natural satellite, or minor satellite is a particularly small natural satellite orbiting a planet, dwarf planet, or other minor planet.
Up until 1995, moonlets were only hypothetical components of Saturn's F-ring structure, but in that year, the Earth passed through Saturn's ring plane. The Hubble Space Telescope and the European Southern Observatory both captured objects orbiting close or near the F-ring. In 2004, Cassini caught an object 4–5 kilometers in diameter on the outer ring of the F-ring and then 5 hours later on the inner F-ring, showing that the object had orbited.[1]
Several different types of small moons have been called moonlets:
- A belt of objects embedded in a planetary ring, especially around Saturn, such as those in the A Ring, S/2009 S 1 in the B Ring ("propeller" moonlets),[2][3] and those in the F Ring[4]
- Occasionally asteroid moons, such as those of 87 Sylvia[5]
- Flashes seen near Jupiter's moon Amalthea that is likely debris ejected from its surface[6]
- Subsatellites[7]
See also
- Minor-planet moon
- Natural satellite
- Ring system
References
- ↑ Winter, Othon C. et al. (2007). "Moonlets wandering on a leash-ring". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters 380 (1): L54–L57. doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2007.00347.x. Bibcode: 2007MNRAS.380L..54W.
- ↑ Tiscareno, Matthew S. et al. (2006). "100-metre-diameter moonlets in Saturn's A ring from observations of 'propeller' structures". Nature 440 (7084): 648–650. doi:10.1038/nature04581. PMID 16572165. Bibcode: 2006Natur.440..648T.
- ↑ Sremčević, Miodrag et al. (2007). "A belt of moonlets in Saturn's A ring". Nature 449 (7165): 1019–1021. doi:10.1038/nature06224. PMID 17960236. Bibcode: 2007Natur.449.1019S.
- ↑ Murray, Carl D. et al. (June 5, 2008). "The determination of the structure of Saturn's F ring by nearby moonlets". Nature (The Science and Technology Facilities Council) 453 (7196): 739–44. doi:10.1038/nature06999. PMID 18528389. Bibcode: 2008Natur.453..739M. https://hal-cea.archives-ouvertes.fr/cea-00930885/file/mur.pdf.
- ↑ Marchis, Franck et al. (2005). "Discovery of the triple asteroidal system 87 Sylvia". Nature 436 (7052): 822–24. doi:10.1038/nature04018. PMID 16094362. Bibcode: 2005Natur.436..822M. https://escholarship.org/uc/item/7nb376hk.
- ↑ Fieseler P. D.; Adams O. W.; Vandermey N.; Theilig E. E.; Schimmels K. A.; Lewis G. D.; Ardalan S. M.; Alexander C. J. (2004). "The Galileo star scanner observations at Amalthea". Icarus 169 (2): 390–401. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2004.01.012. Bibcode: 2004Icar..169..390F.
- ↑ Walker, Robert (17 April 2015). "Can Moons Have Moonlets? Or Rings? Moonlets Of Pluto's Moons?". Science 2.0. http://www.science20.com/robert_inventor/can_moons_have_moonlets_or_rings_moonlets_of_plutos_moons-154917.
Further reading
Links
 |
