Astronomy:NGC 508
| NGC 508 | |
|---|---|
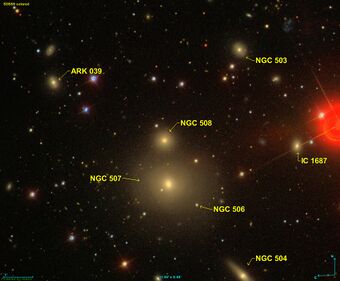 SDSS view of NGC 508 | |
| Observation data (J2000[1] epoch) | |
| Constellation | Pisces[2] |
| Right ascension | 01h 23m 40.6s[3] |
| Declination | +33° 16′ 49″[3] |
| Redshift | 0.01835 ± 0.00007[1] |
| Helio radial velocity | (5451 ± 21) km/s[1] |
| Distance | 247 Mly[4] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 13.1[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (B) | 14.1[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Type | E[2] |
| Apparent size (V) | 1.1' × 1.1'[2] |
| Other designations | |
| PGC 5099, UGC 939, GC 295, MGC +05-04-045, 2MASS J01234058+3316502 [1][5] | |
NGC 508, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5099 or UGC 939, is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Pisces.[2] It is located approximately 247 million light-years from the Solar System[4] and was discovered on 12 September 1784 by British astronomer William Herschel.[5] [6]
Observation history
Herschel discovered NGC 508 along with NGC 507 and described the objects as "Two. Both eF, S, but unequal.". His observed position was catalogued and is accurate.[6] John Louis Emil Dreyer, creator of the New General Catalogue, described the galaxy as "very faint, small, northern of two", with the other object being NGC 507.[5]
Description
The galaxy has an apparent size of 1.1 × 1.1 arcmins and a recessional velocity of 5525 kilometers per second. It is thought to be a group member with NGC 507, but as there is no evidence of interaction between the objects, the two are not necessarily a physical pair. Although NGC 508 is usually treated as part of Arp 229, the description of the Arp-galaxy only applies to the larger NGC 507. Therefore, the term Arp 229 should only be used as an alternative designation for NGC 507.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "NGC 508". http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-id?Ident=NGC+508.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 "Revised NGC Data for NGC 508". http://spider.seds.org/ngc/revngcic.cgi?NGC508.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Your NED Search Results". http://ned.ipac.caltech.edu/cgi-bin/nph-objsearch?objname=NGC+508.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 An object's distance from Earth can be determined using Hubble's law: v=Ho is Hubble's constant (70±5 (km/s)/Mpc). The relative uncertainty Δd/d divided by the distance is equal to the sum of the relative uncertainties of the velocity and v=Ho
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "New General Catalog Objects: NGC 500 - 549" (in en-US). http://cseligman.com/text/atlas/ngc5.htm#508.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "astronomy-mall.com/Adventures.In.Deep.Space/NGC%201-7840%20complete.htm". http://www.astronomy-mall.com/Adventures.In.Deep.Space/NGC%201-7840%20complete.htm.
External links
- NGC 508 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
- SEDS
Coordinates: ![]() 01h 23m 40.6s, +33° 16′ 49″
01h 23m 40.6s, +33° 16′ 49″
 |
