Astronomy:TOI-4138b
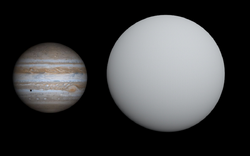 TOI-4138 b compared to Jupiter | |
| Discovery[1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Montalto et al. |
| Discovery site | TESS |
| Discovery date | 13 October 2021 |
| Transit | |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Periastron | 0.049 AU (7,300,000 km) |
| Apoastron | 0.052 AU (7,800,000 km) |
| 0.051 ± 0.002 AU (7,630,000 ± 300,000 km) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.03 ± 0.02 |
| Orbital period | 3.660028 ± 0.000006 d |
| Inclination | 86.0°±0.7° |
| astron|astron|helion}} | 2,458,708.9983 ± 0.0003 JD |
| Semi-amplitude | 74±3 m/s |
| Star | TOI-4138 |
| Physical characteristics[1] | |
| Mean radius | 1.49 ± 0.04 |♃|J}}}}}} |
| Mass | 0.67 ± 0.03 |♃|J}}}}}} |
| Mean density | 250 ± 20 kg/m3 (421 ± 34 lb/cu yd) |
| Physics | 1,762 ± 21 K (2,711.9 ± 37.8 °F; 1,488.8 ± 21.0 °C) |
TOI-4138b is a transiting exoplanet orbiting the G-type subgiant TOI-4138 1,674 light years away in the northern circumpolar constellation Ursa Minor.
Discovery
The planet was recently discovered by TESS using the Transit, which involves measuring light curves during a planet’s eclipse. The paper states that it’s inflated due to heating from its host, which has a high luminosity. [2] Its discovery was announced in October of 2021.
Properties
Orbit and mass
TOI-4138b has an orbital period of 3.6 days, typical for a hot Jupiter. This corresponds to a separation from its host close to one eighth of the distance of Mercury from the Sun. Since the inclination is known, doppler spectroscopy measurements give the planet a mass only 67% that of Jupiter.[1]
Characteristics
TOI-4138b’s transit gives it a radius 149% that of Jupiter; this combined with its low mass gives it a density only 25% that of water. Its separation is comparable with HD 209458 b, but is much larger due to the evolved state of the host star.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Montalto, M.; Malavolta, L.; Gregorio, J.; Mantovan, G.; Desidera, S.; Piotto, G.; Nascimbeni, V.; Granata, V. et al. (January 2022). "TIC 257060897b: An inflated, low-density, hot-Jupiter transiting a rapidly evolving subgiant star". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 509 (2): 2908–2919. doi:10.1093/mnras/stab2923. ISSN 0035-8711. Bibcode: 2022MNRAS.509.2908M.
- ↑ Davis, Margaret (12 October 2021). "NASA Discovered "Hot Jupiter" Exoplanet, Bigger But Less Massive Than Solar System's Largest Planet". https://www.sciencetimes.com/articles/33900/20211012/nasa-discovered-new-inflated-low-density-hot-jupiter-exoplanet-50.htm.

