Biangular coordinates
From HandWiki
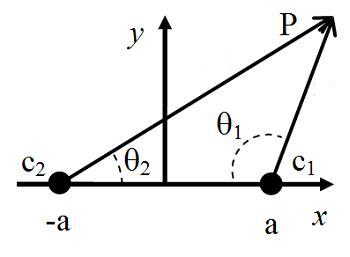
In mathematics, biangular coordinates are a coordinate system for the plane where and are two fixed points, and the position of a point P not on the line is determined by the angles and [1]
The sine rule can be used to convert from biangular coordinates to two-center bipolar coordinates.
Applications
Biangular coordinates can be used in geometric modelling and CAD.[2][3]
See also
References
- ↑ Naylor, Michael; Winkel, Brian (2010), "Biangular Coordinates Redux: Discovering a New Kind of Geometry" (in English), The College Mathematics Journal 41 (1): 29–41, doi:10.4169/074683410X475092
- ↑ Ziatdinov, R.; Kim, T. W.; Nabiyev, R. I. (2015), "Two-point G1 Hermite interpolation in biangular coordinates" (in English), Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 287: 1–11, doi:10.1016/j.cam.2015.02.040, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0377042715001107
- ↑ Ziatdinov, R.; Yoshida, N.; Kim, T. W. (2017), "Visualization and analysis of regions of monotonic curvature for interpolating segments of extended sectrices of Maclaurin" (in English), Computer Aided Geometric Design 56: 35–47, doi:10.1016/j.cagd.2017.06.003, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167839617301206
External links
- G. B. M. Zerr Biangular Coordinates, American Mathematical Monthly 17 (2), February 1910
- J. C. L. Fish, Coordinates Of Elementary Surveying
- George Shoobridge Carr, A synopsis of elementary results in pure mathematics (see page 742)
 |
