Biography:Lew Mander
Lew Mander | |
|---|---|
| Born | Lewis Norman Mander 8 September 1939 |
| Died | 8 February 2020 (aged 80) |
| Awards | AC (2018) |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Organic chemistry |
| Institutions | Australian National University |
| Doctoral students | Jacqueline Whalley |
Lewis Norman Mander, AC, FAA, FRS (8 September 1939 – 8 February 2020) was a New Zealand-born Australian organic chemist. He has widely explored the synthesis and chemistry of the gibberellin class of diterpenes over a 20-year period at the Australian National University (ANU).[1][2] In particular, he studied the effect of these hormones on stem growth and on the reasons why plant undergo bolting during plant development. The July 2004 edition of the Australian Journal of Chemistry was dedicated to Mander on the occasion of his 65th birthday. He retired in 2002 but remained active at the ANU until 2014. In 2018 Mander was made a Companion in the General Division in the Order of Australia which "...is awarded for eminent achievement and merit of the highest degree in service to Australia or humanity at large".[3] In an interview he gave after winning his award, Mander said that his goal was to improve the efficiency of extracting food from plants with the possibility of reducing food shortages in the future.[4]
Education

Mander completed a BSc degree at the University of Auckland, New Zealand in 1960, followed by an MSc degree in 1961 from the same institution. He then moved to Australia in 1962 to undertake a PhD degree at the University of Sydney before committing to an initial postdoctoral fellowship at the University of Michigan. Mander then moved to Caltech in 1965 (after his PhD had been conferred) for an additional two years.
Career
Mander returned to Australia in 1966 to become a lecturer in organic chemistry at the University of Adelaide. He was promoted to Senior Lecturer in organic chemistry in 1970, where he remained until 1975. During this time Mander visited the University of Cambridge to research "...pathways to the pigments of life".[5] In 1977, he served as a Fulbright Senior Scholar at the California Institute of Technology. He was a distinguished Alumnus Professor at the University of Auckland in 1992 and an Eminent Scientist of RIKEN at Wako, in Saitama Prefecture, Japan from 1995 to 1996.
In Australia, he relocated to the Australian National University Research School of Chemistry as a Senior Fellow. He retired in 2002 but retained the title of Professor Emeritus at the Australian National University.
Notable students of Mander's include Jacqueline Whalley, professor at Auckland University of Technology.[6]
Death
Mander died at home in Canberra, Australia on 8 February 2020, at age 80.[7]
Research interests
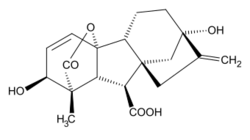
In the early days, Mander was involved in extracting chemicals in plants that might help fight against cancer.[4] Eventually, he turned his research skills to “...the gibberellin family of plant bioregulators".[8] He further developed his interest in this chemical group to include an understanding of their role in plant development. Professor Sir Alan R. Battersby said that Mander's “...synthesis of gibberellic acid was a brilliant landmark achievement. This molecule is of daunting complexity and he developed two flexible routes to it, both depending on many ingenious and novel synthetic procedures".[9]
Amongst his many scholarly activities, Mander contributed a chapter on 'Stereoselective Synthesis' to the classic text 'Stereochemistry of Organic Compounds' by Professors Ernest L. Eliel and Samuel H. Wilen.
Other interests include:
- Synthesis and preparation of semi-synthetic derivatives of gibberellins.
- Molecular basis of plant growth regulation with gibberellins.
- Synthesis of diterpenoid natural products with high bioactivity.
- Dissolving metal-mediated reductive alkylation of benzenoid synthons.
- C-selective acylation of enolates using methyl cyanoformate (Mander's reagent).
Fellowships and awards
- Nuffield Commonwealth Fellow 1971–1972 (Cambridge)[10]
- Fulbright Senior Scholar (California Institute of Technology, 1977, and Harvard University, 1986)
- H.G. Smith Memorial Medal 1981 (RACI)[11]
- Member of the Australian Academy of Science 1983
- Flintoff Medal and Prize (RSC) 1990[12]
- Fellow of the Royal Society of London 1990
- Hon. Fellow of the Royal Society of New Zealand 1991 (FRSNZ Hon)[13]
- Made a Companion of the Order of Australia "for eminent service to science through pioneering contributions to organic chemistry in the field of plant growth hormones, to higher education as an academic, researcher and author, and to national and international scientific societies".[14]
Representative Publications
- King G.R., Mander L.N., Monck N.J.T., Morris J.C. and Zhang H. A New and Efficient Strategy for the Total Synthesis of Polycyclic Diterpenoids: The Preparation of Gibberellins (±)-GA103 and (±)-GA73. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 3828–3829.
- Frey, B., Wells, A. P., Rogers, D. R. and Mander, L. N. Synthesis of the Unusual Diterpenoid Tropones, Hainanolidol and Harringtonolide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 1914–1915.
- Mander, L. N. Twenty years of gibberellin research. Natural Product Reports, 2003, 20, 49–69.
- Mander, L. N. and McLachlan, M. M. Total synthesis of the Galbulimima alkaloid GB 13. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 2400–2401.
- Mander, L. N. and Thomson, R. J. Total synthesis of Sordaricin. Org. Lett., 2003, 5, 1321–1324.
References
- ↑ "Professor Lewis N. Mander". Archived from the original on 16 June 2005. https://web.archive.org/web/20050616004927/http://rsc.anu.edu.au/RSC/ChemResearch/Chemists/mander.html. Retrieved 2007-03-26.
- ↑ Centre, The University of Melbourne eScholarship Research. "Mander, Lewis Norman (Lew) - Biographical entry - Encyclopedia of Australian Science". http://www.eoas.info/biogs/P004075b.htm.
- ↑ "COMPANION OF THE ORDER OF AUSTRALIA". Australian Government. https://www.pmc.gov.au/government/its-honour/companion-order-australia. Retrieved 21 January 2019.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Shirley, Adam (26 January 2018). "ANU Professor Lewis Mander awarded a Companion of the Order (AC) in the 2018 Australia Day Honours". ABC Canberra Breakfast Show (Australian Broadcasting Commission). https://www.abc.net.au/radio/canberra/programs/breakfast/anu-professor-lewis-mander-awarded-ac/9364182. Retrieved 21 January 2019.
- ↑ Battersby, Alan (July 2004). "Lewis N. Mander". Australian Journal of Chemistry 57 (7): 611–617. doi:10.1071/ch04134.
- ↑ Whalley, Jacqueline Louise (1995). Synthetic studies towards the total synthesis of sordaricin (PhD thesis). Australian National University.
- ↑ "Lewis MANDER Death Notice - Belconnen, Australian Capital Territory | The Canberra Times". https://tributes.canberratimes.com.au/obituaries/canberratimes-au/obituary.aspx?n=lewis-mander&pid=195407598&fhid=15591.
- ↑ Mander, Lewis N. (28 November 2002). "Twenty years of gibberellin research". Natural Product Reports 20 (1): 49–69. doi:10.1039/b007744p. PMID 12636083. https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2003/np/b007744p?page=search.
- ↑ Battersby, Alan (2004). "Lewis N. Mander". Australian Journal of Chemistry 57 (7): 611–617. doi:10.1071/ch04134.
- ↑ "Mander, Lewis Norman (Lew) (1939–)". http://www.eoas.info/biogs/P004075b.htm. Retrieved 28 February 2018.
- ↑ "Information on RACIs Past Award Recipients". RACI. https://www.raci.org.au/document/item/239. Retrieved 21 January 2019.
- ↑ "Flintoff Medal Winners". Royal Society of Chemistry. http://www.rsc.org/ScienceAndTechnology/Awards/Archive/FlintoffMedal/Index.asp. Retrieved 21 January 2019.
- ↑ "View our current Honorary Fellows". Royal Society of New Zealand. https://royalsociety.org.nz/who-we-are/our-people/our-fellows/view-our-honorary-fellows/. Retrieved 21 January 2019.
- ↑ "Australia Day Honours 2018: The full list" (in en-US). The Sydney Morning Herald. 2018-01-26. http://www.smh.com.au/national/australia-day-honours-2018-the-full-list-20180125-h0o20j.html.
 |
