Biology:7SK RNA
| 7SK RNA | |
|---|---|
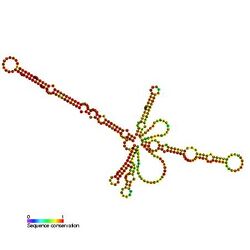 Predicted secondary structure and sequence conservation of 7SK | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | 7SK |
| Rfam | RF00100 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene |
| Domain(s) | Eukaryota |
| SO | 0000274 |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
| RN7SK | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | RN7SK |
| NCBI gene | 125050 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 6 p12.2 |
In molecular biology 7SK is an abundant small nuclear RNA found in metazoans.[1] It plays a role in regulating transcription by controlling the positive transcription elongation factor P-TEFb.[2] 7SK is found in a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex (snRNP) with a number of other proteins that regulate the stability and function of the complex.
Structure
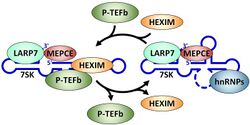
An early study indicated that 7SK in cells is associated with a number of proteins and probing of the secondary structure suggested a model for base pairing between different regions of the RNA.[3] A breakthrough in the function of the 7SK snRNP came with the finding that the positive transcription elongation factor P-TEFb was a component of the complex.[4][5] 7SK associates with and inhibits the cyclin dependent kinase activity of P-TEFb through the action of the RNA binding proteins HEXIM1[6][7] or HEXIM2.[8][9] The gamma phosphate at the 5' end of 7SK is methylated by the methylphosphate capping enzyme MEPCE which is a constitutive component of the 7SK snRNP.[10] A La related protein LARP7 is also found associated with 7SK, presumably in part through its interaction with the 3' end of the RNA.[11][12][13] Reduction of either MEPCE or LARP7 by siRNA mediated knockdown leads to destabilization of 7SK in vivo. A subset of 7SK snRNPs lack P-TEFb and HEXIM, but contains hnRNPs instead.[14]
Function
The major function of the 7SK snRNP is control of the P-TEFb, a factor that regulates the elongation phase of transcription.[2] The kinase activity of P-TEFb is inhibited when the factor is in the 7SK snRNP. P-TEFb can be released from the 7SK snRNP by either the HIV transactivator Tat or the bromodomain containing protein BRD4. This release leads to a conformational change in 7SK RNA and the ejection of HEXIM.[15] hnRNPs stabilize the complex lacking P-TEFb and HEXIM. After P-TEFb functions on specific genes it is re-sequestered in the 7SK snRNP by an unknown mechanism. The 7SK snRNP has been characterized in both human and Drosophila.[16] Detailed review.[14]
References
- ↑ "7SK RNA, a non-coding RNA regulating P-TEFb, a general transcription factor". RNA Biology 6 (2): 122–8. 2009. doi:10.4161/rna.6.2.8115. PMID 19246988.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "7SK snRNA: a noncoding RNA that plays a major role in regulating eukaryotic transcription". Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews. RNA 3 (1): 92–103. 2012. doi:10.1002/wrna.106. PMID 21853533.
- ↑ "Structural analyses of the 7SK ribonucleoprotein (RNP), the most abundant human small RNP of unknown function". Molecular and Cellular Biology 11 (7): 3432–45. July 1991. doi:10.1128/MCB.11.7.3432. PMID 1646389.
- ↑ "7SK small nuclear RNA binds to and inhibits the activity of CDK9/cyclin T complexes". Nature 414 (6861): 322–5. November 2001. doi:10.1038/35104581. PMID 11713533. Bibcode: 2001Natur.414..322N.
- ↑ "The 7SK small nuclear RNA inhibits the CDK9/cyclin T1 kinase to control transcription". Nature 414 (6861): 317–22. November 2001. doi:10.1038/35104575. PMID 11713532. Bibcode: 2001Natur.414..317Y.
- ↑ "MAQ1 and 7SK RNA interact with CDK9/cyclin T complexes in a transcription-dependent manner". Molecular and Cellular Biology 23 (14): 4859–69. July 2003. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.14.4859-4869.2003. PMID 12832472.
- ↑ "Inhibition of P-TEFb (CDK9/Cyclin T) kinase and RNA polymerase II transcription by the coordinated actions of HEXIM1 and 7SK snRNA". Molecular Cell 12 (4): 971–82. October 2003. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(03)00388-5. PMID 14580347.
- ↑ "HEXIM2, a HEXIM1-related protein, regulates positive transcription elongation factor b through association with 7SK". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 280 (16): 16360–7. April 2005. doi:10.1074/jbc.M500424200. PMID 15713662.
- ↑ "Compensatory contributions of HEXIM1 and HEXIM2 in maintaining the balance of active and inactive positive transcription elongation factor b complexes for control of transcription". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 280 (16): 16368–76. April 2005. doi:10.1074/jbc.M500912200. PMID 15713661.
- ↑ "Systematic analysis of the protein interaction network for the human transcription machinery reveals the identity of the 7SK capping enzyme". Molecular Cell 27 (2): 262–74. July 2007. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.06.027. PMID 17643375.
- ↑ "LARP7 is a stable component of the 7SK snRNP while P-TEFb, HEXIM1 and hnRNP A1 are reversibly associated". Nucleic Acids Research 36 (7): 2219–29. April 2008. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn061. PMID 18281698.
- ↑ "The La-related protein LARP7 is a component of the 7SK ribonucleoprotein and affects transcription of cellular and viral polymerase II genes". EMBO Reports 9 (6): 569–75. June 2008. doi:10.1038/embor.2008.72. PMID 18483487.
- ↑ "A La-related protein modulates 7SK snRNP integrity to suppress P-TEFb-dependent transcriptional elongation and tumorigenesis". Molecular Cell 29 (5): 588–99. March 2008. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2008.01.003. PMID 18249148.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 "Cracking the control of RNA polymerase II elongation by 7SK snRNP and P-TEFb". Nucleic Acids Research 44 (16): 7527–39. September 2016. doi:10.1093/nar/gkw585. PMID 27369380.
- ↑ Blagosklonny, Mikhail V., ed (August 2010). "The mechanism of release of P-TEFb and HEXIM1 from the 7SK snRNP by viral and cellular activators includes a conformational change in 7SK". PLOS ONE 5 (8): e12335. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012335. PMID 20808803. Bibcode: 2010PLoSO...512335K.
- ↑ "The Drosophila 7SK snRNP and the essential role of dHEXIM in development". Nucleic Acids Research 40 (12): 5283–97. July 2012. doi:10.1093/nar/gks191. PMID 22379134.
External links
- Human 7SK genome location and 7SK gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
- Human RN7SK genome location and RN7SK gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
 |
