Biology:Aciagrion
From HandWiki
Short description: Genus of damselflies
| Aciagrion | |
|---|---|

| |
| Aciagrion occidentale, male | |

| |
| Aciagrion occidentale, female | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Odonata |
| Suborder: | Zygoptera |
| Family: | Coenagrionidae |
| Genus: | Aciagrion Selys, 1891[1] |
| |
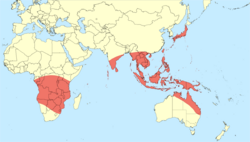
| Likely distribution of Aciagrion | |
Aciagrion is a genus of damselfly in the family Coenagrionidae.[2] Aciagrion are small and slender damselflies with a small head.[1] They are found at still waters including swamps. Aciagrion is widely distributed in the tropics from Africa, through Indonesia to Australia.[3] They are commonly known as Slims.
Species
The genus Aciagrion includes the following species:[4]
- Aciagrion africanum Martin, 1908
- Aciagrion approximans (Selys, 1876)
- Aciagrion azureum Fraser, 1922
- Aciagrion balachowskyi Legrand, 1982 - Gabon Slim[5]
- Aciagrion bapepe Dijkstra, 2015 - Congo Slim[6]
- Aciagrion borneense Ris, 1911
- Aciagrion brosseti Legrand, 1982 - Yellow-winged Slim[7]
- Aciagrion dondoense Dijkstra, 2007 - Opal Slim[8]
- Aciagrion fasciculare Lieftinck, 1934
- Aciagrion feuerborni Schmidt, 1934
- Aciagrion fragile (Tillyard, 1906) - Blue Slim[3]
- Aciagrion gracile (Sjöstedt, 1909) - Graceful Slim[9]
- Aciagrion hamoni Fraser, 1955
- Aciagrion heterostictum Fraser, 1955 - Long Slim[10]
- Aciagrion hisopa (Selys, 1876)
- Aciagrion huaanensis Xu, 2005
- Aciagrion macrootithenae Pinhey, 1972 - Awl-tipped Slim[11]
- Aciagrion migratum (Selys, 1876)
- Aciagrion nodosum (Pinhey, 1964) - Cryptic Slim[12]
- Aciagrion occidentale Laidlaw, 1919
- Aciagrion olympicum Laidlaw, 1919
- Aciagrion pallidum Selys, 1891
- Aciagrion pinheyi Samways, 2001 - Emerald-striped Slim[8]
- Aciagrion rarum (Longfield, 1947) - Tiny Slim[13]
- Aciagrion steeleae Kimmins, 1955 - Swamp Slim[14]
- Aciagrion tillyardi Laidlaw, 1919
- Aciagrion tonsillare Lieftinck, 1937
- Aciagrion walteri Carfi & D'Andrea, 1994
- Aciagrion zambiense Pinhey, 1972
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Aciagrion. |
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Selys-Longchamps, E. (1891). "Viaggio di Leonardo Fea in Birmania e regioni vicine XXXII" (in fr). Annali del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale Genova. 2 10: 433–518 [509]. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/30150020.
- ↑ "Genus Aciagrion Selys, 1891". Australian Biological Resources Study. 2012. https://biodiversity.org.au/afd/taxa/Aciagrion.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Theischinger, Günther; Hawking, John (2006). The Complete Field Guide to Dragonflies of Australia. Collingwood, Victoria, Australia: CSIRO Publishing. pp. 290. ISBN 978 0 64309 073 6.
- ↑ "World Odonata List". University of Puget Sound. http://www.pugetsound.edu/academics/academic-resources/slater-museum/biodiversity-resources/dragonflies/world-odonata-list/.
- ↑ Clausnitzer, V. (2018). "Aciagrion balachowskyi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018: e.T184253A75302044. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T184253A75302044.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/184253/75302044.
- ↑ Clausnitzer, V. (2017). "Aciagrion bapepe". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017: e.T84379236A84382121. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T84379236A84382121.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/84379236/84382121.
- ↑ Clausnitzer, V. (2017). "Aciagrion brosseti". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017: e.T184190A75302561. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T184190A75302561.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/184190/75302561.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Samways, Michael J. (2008). Dragonflies and Damselflies of South Africa. Pensoft. ISBN 954-642-330-0.
- ↑ Clausnitzer, V.; Dijkstra, K.-D.B.; Suhling, F. (2018). "Aciagrion gracile". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018: e.T59781A75303637. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T59781A75303637.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/59781/75303637.
- ↑ Clausnitzer, V.; Suhling, F. (2018). "Aciagrion heterostictum". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018: e.T59783A127507675. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T59783A127507675.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/59783/127507675. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ Clausnitzer, V.; Suhling, F. (2018). "Aciagrion macrootithenae". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018: e.T63181A75305758. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T63181A75305758.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/63181/75305758.
- ↑ Clausnitzer, V.; Suhling, F. (2018). "Aciagrion nodosum". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018: e.T168009A75306252. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T168009A75306252.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/168009/75306252.
- ↑ Clausnitzer, V.; Suhling, F. (2018). "Aciagrion rarum". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018: e.T214A75306973. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T214A75306973.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/214/75306973.
- ↑ Clausnitzer, V.; Suhling, F. (2017). "Aciagrion steeleae". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017: e.T59784A75307602. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T59784A75307602.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/59784/75307602.
Wikidata ☰ Q1305477 entry
 |

