Biology:Antigone (bird)
| Antigone | |
|---|---|

| |
| Sarus crane (Antigone antigone) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Gruiformes |
| Family: | Gruidae |
| Genus: | Antigone Reichenbach, 1853 |
| Type species | |
| Grus torquata[1] = Ardea antigone Vieillot, 1817
| |
| Species | |
|
See text | |
Antigone is a genus of large birds in the crane family.[2] The species in this genus were formerly placed in the genus Grus.
Taxonomy
The genus was named by Carl Linnaeus to be used for the sarus crane or its old name Grus major Indica because he was confused between Greek princesses Antigone who turned into a stork and Gerana who turned into the crane.[3]
A molecular phylogenetic study published in 2010 found that the genus Grus was polyphyletic.[4] In the subsequent rearrangement, four species were placed in the resurrected genus Antigone.[2] The genus had initially been erected in 1853 by German naturalist Ludwig Reichenbach.[5] The type species is the sarus crane (Antigone antigone).[6]
Species
The genus includes four species:[2]
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sandhill crane | Antigone canadensis (Linnaeus, 1758) Five subspecies
|
North America and extreme northeastern Siberia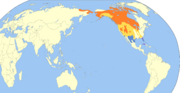
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| White-naped crane | Antigone vipio (Pallas, 1811) |
Northeastern Mongolia, Northeastern China, and adjacent areas of Southeastern Russia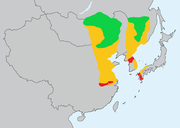
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
VU
|
| Sarus crane | Antigone antigone (Linnaeus, 1758) Four subspecies
|
Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, and Australia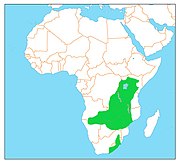
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
VU
|
| Brolga | Antigone rubicunda (Perry, 1810) |
Northern and eastern Australia and New Guinea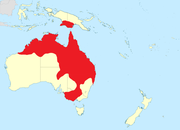
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
References
- ↑ "Gruidae". The Trust for Avian Systematics. https://www.aviansystematics.org/4th-edition-checklist?viewfamilies=45.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Gill, Frank; Donsker, David, eds (2019). "Flufftails, finfoots, rails, trumpeters, cranes, limpkin". World Bird List Version 9.2. International Ornithologists' Union. https://www.worldbirdnames.org/bow/flufftails/. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- ↑ Jobling, James A. (2010). Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London, UK: Christopher Helm. pp. 49–50. ISBN 978-1-4081-3326-2. OCLC 659731768.
- ↑ Krajewski, C.; Sipiorski, J.T.; Anderson, F.E. (2010). "Mitochondrial genome sequences and the phylogeny of cranes (Gruiformes: Gruidae)". Auk 127 (2): 440–452. doi:10.1525/auk.2009.09045. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/277486138.
- ↑ Reichenbach, Ludwig (1853) (in German). Handbuch der speciellen Ornithologie. Leipzig: Friedrich Hofmeister. p. xxiii. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/47618653.
- ↑ The Howard & Moore Complete Checklist of the Birds of the World. 1: Non-passerines (4th ed.). Eastbourne, UK: Aves Press. 2013. p. 164. ISBN 978-0-9568611-0-8.
Wikidata ☰ Q16529427 entry
 |





