Biology:Aphaneramma
| Aphaneramma | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | †Temnospondyli |
| Suborder: | †Stereospondyli |
| Family: | †Trematosauridae |
| Subfamily: | †Lonchorhynchinae |
| Genus: | †Aphaneramma Woodward, 1904 |
| Type species | |
| †Aphaneramma rostratum Woodward, 1904
| |
| Other species | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Halobatrachus Hammer, 1987 | |
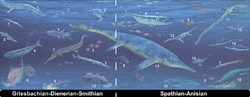
Aphaneramma is an extinct genus of marine temnospondyl amphibian. It lived during the Early Triassic epoch, approximately 252–247 Ma ago, and had a global distribution.
Fossils have been found in the Mianwali Formation of Pakistan ,[2] Madagascar ,[3] the Zhitkov Formation of Russia,[4] and the Vikinghøgda Formation (Kongressfjellet Formation) of Svalbard (Norway ).[5]
Aphaneramma had a skull about 40 centimetres (16 in) in length.[3] Its jaws were very long, similar to the extant gharial's, and lined with small teeth. This adaptation suggests that it may have preyed on fish. A marine lifestyle for this animal was proposed.[1]
Aphaneramma is closely related to Cosgriffius from North America.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Scheyer, Torsten M.; Romano, Carlo; Jenks, Jim; Bucher, Hugo (19 March 2014). "Early Triassic Marine Biotic Recovery: The Predators' Perspective". PLOS ONE 9 (3): e88987. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0088987. PMID 24647136. Bibcode: 2014PLoSO...988987S.
- ↑ Maisch, Michael W. (31 March 2020). "Aphaneramma kokeni (von Huene, 1920), a lonchorhynchine trematosaurid (Amphibia: Temnospondyli) from the Lower Triassic of Pakistan". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen 295 (3): 211–241. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2020/0879.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Fortuny, Josep; Gastou, Stéphanie; Esquillié, François; Ranivoharimanana, Lovasoa; Steyer, Sébastien (29 June 2017). "A new extreme longirostrine temnospondyl from the Triassic of Madagascar: phylogenetic and palaeobiogeographical implications for trematosaurids". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology 16 (8): 675–688. doi:10.1080/14772019.2017.1335805. https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/A_new_extreme_longirostrine_temnospondyl_from_the_Triassic_of_Madagascar_phylogenetic_and_palaeobiogeographical_implications_for_trematosaurids/5155366.
- ↑ Zhitkov Formation at Fossilworks.org
- ↑ Woodward, Arthur Smith (1904). "On two new labyrinthodont skulls of the genera Capitosaurus and Aphaneramma". Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London 1904 (3): 170–176. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1904.tb08328.x.
Wikidata ☰ Q2544680 entry
 |

