Biology:Arbutus unedo
| Arbutus unedo | |
|---|---|

| |
| Arbutus berries | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Ericaceae |
| Genus: | Arbutus |
| Species: | A. unedo
|
| Binomial name | |
| Arbutus unedo L. 1753
| |
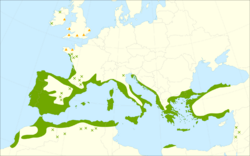
| |
Distribution map. Explanation:
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Synonymy
| |
Arbutus unedo, commonly known as strawberry tree, or chorleywood in the United Kingdom, is an evergreen shrub or small tree in the family Ericaceae, native to the Mediterranean Basin and Western Europe. The tree is well known for its fruits, the arbutus berry, which bear some resemblance to the strawberry, hence the common name strawberry tree.[2][3][4] However, it is not closely related to true strawberries of the genus Fragaria.
Its presence in Ireland also lends it the name "Irish strawberry tree", or cain, or cane apple (from the Irish name for the tree, caithne[5]), or sometimes "Killarney strawberry tree". The strawberry tree is the national tree of Italy because of its green leaves, its white flowers and its red berries, colors that recall the Italian flag.[6]
Taxonomy
Arbutus unedo was one of the many species described by Carl Linnaeus in Volume One of his landmark 1753 work Species Plantarum, giving it the name it still bears today.[7]
A study published in 2001 which analyzed ribosomal DNA from Arbutus and related genera found Arbutus to be paraphyletic, and A. unedo to be closely related to the other Mediterranean Basin species such as A. andrachne and A. canariensis and not to the western North American members of the genus.[8]
Arbutus unedo and A. andrachne hybridise naturally where their ranges overlap; the hybrid has been named Arbutus × andrachnoides (syn. A. × hybrida, or A. andrachne × unedo),[9] inheriting traits of both parent species, though fruits are not usually borne freely, and as a hybrid is unlikely to breed true from seed. It is sold in California as Arbutus x Marina named for a district in San Francisco where it was hybridized.[citation needed]
Description
Arbutus unedo grows to 4–7 m (13–23 ft) tall,[10] rarely up to 15 m (50 ft), with a trunk diameter of up to 80 cm (31 in).[citation needed] It grows in hardiness zones 7–10.[citation needed]
The leaves are green and glossy on the upper side, dull on the underside, 8–10 cm (3–4 in) long and 3–4 cm (1–1 1⁄2 in) broad, laurel-like and with a serrated or serrulated margin.[10]
The hermaphrodite[citation needed] flowers are white (yellow when desiccated), bell-shaped, 7–8 mm (1⁄4–5⁄16 in) in diameter, and flower from a reddish hanging panicle in autumn.[10] They are pollinated by bees, and have a mild sweet scent.[citation needed]
Twigs are reddish-brown and abundantly foliose, and often have small hairs.[10]
The fruit is a red berry, 7–20 mm (1⁄4–13⁄16 in) diameter, spherical in shape with a rough surface.[10] It matures in about 12 months, in autumn, at the same time as the next flowering. It is edible; the fruit is sweet when reddish. Seeds are small, brown and angular[10] and are often dispersed by frugivorous birds.[11]
The name unedo is attributed to Pliny the Elder, who allegedly claimed that "unum tantum edo", meaning "I eat only one".[12] It is not known whether he meant that the fruit was so good he could eat only one, or whether he meant that the fruit was uninteresting so he ate only one.[13]
Distribution
Arbutus unedo is widespread in the Mediterranean region: in Portugal, Spain and southeastern France ; southward in Algeria, Morocco, Libya, and Tunisia, and eastward in Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, Montenegro, Greece, Turkey, Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon and Syria. It is also found in western France, Albania, Bulgaria and southwestern Ireland.[14]
Its disjunct distribution, with an isolated relict population in southwestern and northwestern Ireland, notably in Killarney and around Lough Gill in County Sligo, which is its most northerly stand in the world, is a remnant of former broader distribution during the milder climate of the Atlantic period, the warmest and moistest Blytt–Sernander period, when the climate was generally warmer than today. The red-flowered variant, named A. unedo rubra by William Aiton in 1785, was discovered growing wild in Ireland in 1835.[citation needed]
Cultivation
Arbutus unedo is quite an easy plant to cultivate, and is adaptable to many climates. Once established it is fairly drought resistant, frost resistant, shade tolerant and salt tolerant.[15]
Lower production of fruit mass has however been reported in case of summer droughts, and frosts in flowering time were seen to decrease the numbers of fruits.[16]
Arbutus unedo is naturally adapted to dry summer climates, and has become a very popular ornamental plant in California and the rest of the west coast of North America. It can grow easily in USDA hardiness zone 7 or warmer.[17]
It also grows well in the cool, wet summers of western Ireland and England, and temperate regions of Europe and Asia. Pests include scales and thrips, and diseases include anthracnose, Phytophthora, root rot, and rust.[citation needed]
Unlike most of the Ericaceae, A. unedo grows well in basic (limy) pH soils, even though it does better in more acidic soils.
The fruit production is not very high and is highly variable on the weather, and that may be part of the reason this plant is not frequently cultivated. The average yield in a two years study is around 46 kg per hectare, and 180 grams per cubic metre of crown.[18] However, very little work has so far been done in terms of genotype selection.[19]
Arbutus unedo has been seen to form a mycorrhizal relationship. Inoculation with Pisolithus tinctorius has shown to greatly improve the plant's root mass, size, tolerance to drought and nutritional status.[20][21]
In cultivation in the UK, the form A. unedo f. rubra[22] and the cultivar ‘Atlantic’[23] have gained the Royal Horticultural Society’s Award of Garden Merit
Propagation
Propagation can be done via seed,[24] layering, or cutting.
The seed should undergo a one-month cold stratification period,[25] then soaked for 5 to 6 days in warm water to improve germination success. Seedlings are prone to damp, and should be cared for in the first year.
Germination rate is low, rarely over 20%.[26]
Layering can take up to two years, but has a good success rate, while cutting is done with a 15–20 cm (6–8 in) long mature wood, preferably with a heel in November to December. The success rate however is not very high.[27]
Uses
Culinary uses
Arbutus berries have a high content of sugars (40%), and antioxidant vitamins[28] such as vitamin C, beta-carotene, niacin, tocopherols, and organic acids that are precursors to omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids (nearly 9%).[29][30] They are edible fresh, but that is an uncommon consumption, especially because the mature fruit tends to bruise very easily, making transportation difficult.
They are used mostly for jam, marmalades, yogurt and alcoholic beverages,[31][29] such as the Portuguese medronho, a type of strong brandy. Many regions of Albania prepare the traditional drink rakia from the fruits of the plant (mare or kocimare in Albanian), whence comes the name of the drink, which is raki kocimarje.
The flowers are pollinated by bees, and the resulting honey is bitter tasting but still considered a delicacy.[32]
Herbal medicine
Arbutus unedo's leaves have been employed in traditional and folk medicine in the form of a decoction said to have the following properties: astringent, diuretic, urinary anti-septic, antiseptic, intoxicant, rheumatism, tonic, and more recently, in the therapy of hypertension and diabetes.[31][33][34]
The leaves are reported to have a high concentration of flavonol antioxidants, especially quercitin, best extracted with a decoction, and together with the fruits are a source of antioxidants.[35][36]
The leaves also have anti-inflammatory properties[37][non-primary source needed]
The nectar contains the isoprenoid unedone (2-(1,2-dihydroxypropyl)-4,4,8-trimethyl-1-oxaspiro[2.5]oct-7-en-6-one) which is biologically active against a common and debilitating parasite of bumble bees, Crithidia bombi, so could provide a naturally occurring way for bees to withstand the burden of disease which has been reported to be a contributing factor in pollinator declines. The compound is glycosylated to an inactive form unedone-8-O-glycoside once consumed by the bee (perhaps to reduce any toxic effects against the bee herself) then transformed back to the active aglycone by the bee's microbiome in the hindgut where the parasite is most prevalent and damaging - suggesting that the microbiome assists in the anti-parasitic process.[38]
Ecological design
In landscape design, ecosystem restoration or permaculture based designs, A. unedo can have many purposes. While the ornamental one is the most common, this can be a valuable plant also for restoring degraded ecosystems and preventing desertification. Being a pioneer plant and growing well also in poor soils, it can be used in a wide array of situations.
- The flowers are a significant source of nectar and pollen for bees, while the fruits are food for the birds.
- Its salt tolerance, coupled with it being an evergreen, make it a good choice for wind barriers in lands close to the sea.
- A. unedo is fire resistant (can regrow after a fire), and being a pioneer plant can contribute to the discontinuity of fire-prone pines and eucalyptus monocultures;[39] for the same reasons it is a good candidate for reforestation in Mediterranean areas.[40]
- The dense foliage throughout the year can be a shelter for insects and small animals during the winter.
- Its extensive root system can help in the soil stabilization process.[41]
Other uses
- The wood is quite hard and well suited for a various uses such as fire wood and to make pipes. Since it does not usually grow straight, it is not well suited for construction or similar uses.
- The tree is also grown as an ornamental plant, because of its nice-looking and -smelling flowers and fruit and their interesting presence on the plant at the same time, and because it is an evergreen. It is used as a single or multi-trunked ornamental tree, and as a specimen or hedge shrub in gardens and public landscapes.
History
Its Mediterranean habitat, elegant details of leaf and habit and dramatic show of fruit with flowers made Arbutus unedo notable in Classical Antiquity, when it was called Andrachne, and for which Theophrastos (4th c. BCE) wrote about it, as well as the ancient army medical herbalist Pedanios Dioscorides [De Materia Medica, Book II-150]; in addition, Pliny thought it should not be planted where bees are kept, for the bitterness it imparts to honey.[citation needed]
The first evidence of its importation into northern European gardens was to 16th-century England from Ireland. In 1586 a correspondent in Ireland sent plants to the Elizabethan courtiers Lord Leicester and Sir Francis Walsingham.[42] An earlier description by Rev. William Turner (The Names of Herbes, 1548) was probably based on hearsay. The Irish association of Arbutus in English gardens is reflected in the inventory taken in 1649 of Henrietta Maria's Wimbledon: "one very fayre tree, called the Irish arbutis standing in the midle parte of the sayd kitchin garden, very lovely to look upon"[42] By the 18th century Arbutus unedo was well known enough in English gardens for Batty Langley to make the bold and impractical suggestion that it might be used for hedges, though it "will not admit of being clipped as other evergreens are".[42]
In the United States, Thomas Jefferson lists the plant in his Monticello gardens in 1778.[43]
The form A. unedo f. rubra[44] and the hybrid A. × andrachnoides,[45] have gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit.
Symbolic uses
Ancient history
The tree is mentioned by Roman poet Ovid, in Book I: 89–112 "The Golden Age" of his Metamorphoses: "Contented with food that grew without cultivation, they collected mountain strawberries and the fruit of the strawberry tree, wild cherries, blackberries clinging to the tough brambles, and acorns fallen from Jupiter's spreading oak-tree."[46]
The name of the Italian promontory Mount Conero, situated directly south of the port of Ancona on the Adriatic Sea, derives from the Greek name κόμαρος (komaròs) indicating the strawberry tree which is common on the slopes of the mountain.[47] Mount Conero, the only coastal high point on the Adriatic sea between Trieste and the Gargano massif in the region of Apulia, assists navigators to sail across the Adriatic sea since ancient times.[48]
Spain
The Garden of Earthly Delights, a painting by Hieronymus Bosch, was originally listed by José de Sigüenza, in the inventory of the Spanish Crown as La Pintura del Madroño – "The Painting of the Strawberry Tree".[49]
The tree makes up part of the Coat of arms of Madrid (El oso y el madroño, The Bear and the Strawberry Tree) of the city of Madrid, Spain . In the center of the city (Puerta del Sol) there is a statue of a bear eating the fruit of the Madroño tree. The image appears on city crests, taxi cabs, man-hole covers, and other city infrastructure. The fruit of the Madroño tree ferments on the tree if left to ripen, so some of the bears become drunk from eating the fruits. [citation needed]
Italy
The strawberry tree (Italian: corbezzolo) began to be considered one of the national symbols of Italy in the 19th century, during the Italian unification, because with its autumn colors is reminiscent of the flag of Italy (green for its leaves, white for its flowers and red for its berries).[50][6]
For this reason the poet Giovanni Pascoli dedicated a poem to the strawberry tree. He refers to the Aeneid passage in which Pallas, killed by Turnus, was posed on branches of a strawberry tree. He saw in the colours of that plant a prefiguration of the flag of Italy and considered Pallas the first national cause martyr.[51] Pascoli's ode says:
(in Italian)
O verde albero italico, il tuo maggio
è nella bruma: s'anche tutto muora,
tu il giovanile gonfalon selvaggio
spieghi alla bora
Oh green Italian tree, your May month
is in the mist: if everything die,
you, the youthful wild banner
unfold to the northern wind
See also
References
- ↑ Khela, S.; Rivers, M.C. (2017). "Arbutus unedo". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017: e.T202930A68076133. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T202930A68076133.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/202930/68076133. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ↑ Rydelek, Jared (2014). "Fruits & Vegetables: Strawberry Tree Fruit". https://www.atlasobscura.com/foods/strawberry-tree-fruit.
- ↑ "Arbutus unedo | strawberry tree". The Royal Horticultural Society. http://www.rhs.org.uk/plants/1473/Arbutus-unedo/Details.
- ↑ "Arbutus unedo". Missouri Botanical Garden. http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?taxonid=279932.
- ↑ "cane apple". http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/cane+apple.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Il corbezzolo simbolo dell'Unità d'Italia. Una specie che resiste agli incendi" (in it). 3 October 2011. http://www.altovastese.it/cultura/il-corbezzolo-simbolo-unita-italia-specie-che-resiste-agli-incendi/.
- ↑ Linnaeus, Carl (1753) (in la). Species Plantarum. Tomus I. Holmiae (Stockholm), Sweden: Laurentii Salvii. p. 395. http://www.botanicus.org/title/b12069590. "caule erecto, foliis glabris serratis, baccis polyspermis"
- ↑ Hileman, Lena C.; Vasey, Michael C.; Parker, V. Thomas (2001). "Phylogeny and Biogeography of the Arbutoideae (Ericaceae): Implications for the Madrean-Tethyan Hypothesis". Systematic Botany 26 (1): 131–143. doi:10.1043/0363-6445-26.1.131. http://userwww.sfsu.edu/parker/pages/respubs/HilemanEtAl2001.pdf.
- ↑ Bertsouklis, Konstantinos Fotios; Papafotiou, Maria (2016-12-14). "Morphometric and Molecular Analysis of the Three Arbutus Species of Greece". Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca 44 (2): 423–430. doi:10.15835/nbha44210572. ISSN 1842-4309. https://www.notulaebotanicae.ro/index.php/nbha/article/view/10572.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 "A. unedo". Flora Iberica. http://www.floraiberica.es/floraiberica/texto/pdfs/04_074_07_Arbutus.pdf.
- ↑ Molina, M.; Pardo-De-Santayana, M.; Aceituno, L.; Morales, R.; Tardio, J. (1 October 2011). "Fruit production of strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo L.) in two Spanish forests". Forestry 84 (4): 419–429. doi:10.1093/forestry/cpr031. ISSN 0015-752X. "Many frugivorous birds and several mammals feed on its fleshy fruits".
- ↑ Gaius Plinius Secundus (in la), Naturalis Historia, Liber XV. XXVIII, 99
Pliny The Elder, Natural History, XV, XXVIII, 99 - ↑ "Strawberry Tree Curse". 31 August 2011. http://www.eattheweeds.com/the-strawberry-tree-curse-2/.
- ↑ {{citation | mode = cs1 | title = Arbutus unedo | work = Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN) | url = | publisher = [[Organization:Agricultural Research ServAgricultural Research Service (ARS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) | access-date = 11 December 2017 }}
- ↑ Richins Myers, Vanessa. "Strawberry tree-Arbutus unedo". https://www.thespruce.com/strawberry-tree-arbutus-unedo-3269240. "As long as you have made sure that it has regular watering for the first year so that the tree can form a strong root, it will be drought resistant. It can also grow in salty areas."
- ↑ Molina, María; Pardo-De-Santayana, Manuel; Aceituno, Laura; Morales, Ramón; Tardío, Javier (1 October 2011). "Fruit production of strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo L.) in two Spanish forests". Forestry 84 (4): 419–429. doi:10.1093/forestry/cpr031. ISSN 0015-752X. "The number of fruits per branch appeared to be affected by frost risk at flowering time. [...] The number of fruits per branch appeared to be affected by frost risk at flowering time.".
- ↑ "Arbutus unedo - L.". Plants For a Future. http://pfaf.org/user/plant.aspx?latinname=Arbutus+unedo.
- ↑ Molina, María; Pardo-De-Santayana, Manuel; Aceituno, Laura; Morales, Ramón; Tardío, Javier (1 October 2011). "Fruit production of strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo L.) in two Spanish forests". Forestry 84 (4): 419–429, tables 1–4. doi:10.1093/forestry/cpr031. ISSN 0015-752X.
- ↑ Celikel, Gulay; Demirsoy, Leyla; Demirsoy, Husnu (16 September 2008). "The strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo L.) selection in Turkey". Scientia Horticulturae 118 (2): 115–119. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2008.05.028.
- ↑ Navarro, A.; Sánchez-Blanco, M. J.; Morte, A.; Bañón, S. (1 September 2009). "The influence of mycorrhizal inoculation and paclobutrazol on water and nutritional status of Arbutus unedo L.". Environmental and Experimental Botany 66 (3): 362–371. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2009.04.005.
- ↑ Navarro García, Alejandra; Del Pilar Bañón Árias, Sebastián; Morte, Asunción; Sánchez-Blanco, María Jesús (2010). "Effects of nursery preconditioning through mycorrhizal inoculation and drought in Arbutus unedo L. plants". Mycorrhiza 21 (1): 53–64. doi:10.1007/s00572-010-0310-x. ISSN 1432-1890. PMID 20405149.
- ↑ "Arbutus unedo f. rubra". Royal Horticultural Society. https://www.rhs.org.uk/Plants/94930/i-Arbutus-unedo-i-f-i-rubra-i/Details.
- ↑ "RHS Plantfinder - Arbutus unedo 'Atlantic'". Royal Horticultural Society. https://www.rhs.org.uk/Plants/153810/i-Arbutus-unedo-i-Atlantic/Details.
- ↑ Bertsouklis, Konstantinos F.; Papafotiou, Maria (2013-03-01). "Seed Germination of Arbutus unedo, A. andrachne and Their Natural Hybrid A. andrachnoides in Relation to Temperature and Period of Storage". HortScience 48 (3): 347–351. doi:10.21273/HORTSCI.48.3.347. ISSN 0018-5345. https://journals.ashs.org/hortsci/view/journals/hortsci/48/3/article-p347.xml.
- ↑ Pipinis, Elias; Stampoulidis, Athanasios; Milios, Elias; Kitikidou, Kyriaki; Radoglou, Kalliopi (2017). "Effects of Cold Stratification and Ga3 on Germination Ofarbutus Unedoseeds of Three Provenances". African Journal of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines 14 (1): 318–323. doi:10.21010/ajtcam.v14i1.34. ISSN 2505-0044. PMID 28480410. "in all three provenances seed germinability was significantly improved by a one-month period of CS or treatment".
- ↑ Hammami, I.; Jellal, M.; Ksontini, M.; Rejeb, M.N. (2005). "Propagation of the Strawberry Tree Through Seed (Arbutus unedo)". International Journal of Agriculture & Biology 7: 457–459. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229694726. Retrieved 17 September 2017. "In the case of A. unedo, most prior studies found very low germination percentages, varying between 0 and 5 % (Smiris et al. 2006: 0 %; Demirsoy et al. 2010:1–3 %; Tilki 2004: 4 %; Ertekın and Kırdar 2010: 5 %). Hammami et al. (2005), however, obtained a considerably better result (19 %).".
- ↑ "Arbutus unedo, The Strawberry Tree". Plants For a Future. http://pfaf.org/user/cmspage.aspx?pageid=55.
- ↑ Bertsouklis, Konstantinos F.; Daskalakis, Ioannis; Biniari, Katerina; Papafotiou, Maria (2021-02-15). "Comparative study of polyphenolic content and antioxidant capacity in fruits of Arbutus unedo, A. andrachne and their natural hybrid A.× andrachnoides". Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca 49 (1): 12165. doi:10.15835/nbha49112165. ISSN 1842-4309. https://www.notulaebotanicae.ro/index.php/nbha/article/view/12165.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 Alarcão-E-Silva, M. L. C. M. M.; Leitão, A. E. B.; Azinheira, H. G.; Leitão, M. C. A. (1 February 2001). "The Arbutus Berry: Studies on its Color and Chemical Characteristics at Two Mature Stages". Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 14 (1): 27–35. doi:10.1006/jfca.2000.0962. "Arbutus berry appears to be a good source of vitamins, namely niacin, ascorbic acid and β -carotene (content of 9.1, 346.3 and 70.9 mg/100 g, respectively), organic acids (nearly 9%), total sugars (c. 42%) and tannins (1.75 mg g−1).".
- ↑ Barros, Lillian; Carvalho, Ana Maria; Morais, Jorge Sá; Ferreira, Isabel C. F. R. (1 May 2010). "Strawberry-tree, blackthorn and rose fruits: Detailed characterisation in nutrients and phytochemicals with antioxidant properties". Food Chemistry 120 (1): 247–254. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.10.016. "The analysed fruits contain very useful bioactive phytochemicals such as phenolics, vitamins (ascorbic acid and tocopherols) and carotenoids [..] The combination of bioactive compounds and rich nutritional composition (high contents in carbohydrates, low contents in fat with the precious contribution of polyunsaturated fatty acids, precursors of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids) of the studied wild fruits make them a very special food.".
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 Bonet, M. Angels; Vallès, Joan (2002). "Use of non-crop food vascular plants in Montseny biosphere reserve (Catalonia, Iberian Peninsula)". International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition 53 (3): 225–248. doi:10.1080/09637480220132841. ISSN 0963-7486. PMID 11951586.
- ↑ Tuberoso, CI; Bifulco, E; Caboni, P; Cottiglia, F; Cabras, P; Floris, I (2010). "Floral markers of strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo L.) honey". J Agric Food Chem 58 (1): 384–9. doi:10.1021/jf9024147. PMID 19919097.
- ↑ Mariotto, S.; Ciampa, A. R.; de Prati, A. Carcereri; Darra, E.; Vincenzi, S.; Sega, M.; Cavalieri, E.; Shoji, K. et al. (2008). "Aqueous extract of Arbutus unedo inhibits STAT1 activation in human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 and human fibroblasts through SHP2 activation". Medicinal Chemistry 4 (3): 219–228. doi:10.2174/157340608784325179. ISSN 1573-4064. PMID 18473914.
- ↑ Dr. Duke's Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases: Ethnobotanical uses of Arbutus unedo.
- ↑ Ioannis Erkekoglou; Nikolaos Nenadis; Efrosini Samara; Fani Th. Mantzouridou (June 2017). "Functional Teas from the Leaves of Arbutus unedo: Phenolic Content, Antioxidant Activity, and Detection of Efficient Radical Scavengers". Plant Foods for Human Nutrition 72 (2): 176–183. doi:10.1007/s11130-017-0607-4. PMID 28421300.
- ↑ Mendes, Lídia; de Freitas, Victor; Baptista, Paula; Carvalho, Márcia (2011). "Comparative antihemolytic and radical scavenging activities of strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo L.) leaf and fruit". Food and Chemical Toxicology 49 (9): 2285–2291. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2011.06.028. ISSN 1873-6351. PMID 21703325.
- ↑ Navarro García, Alejandra; Del Pilar Bañón Árias, Sebastián; Morte, Asunción; Sánchez-Blanco, María Jesús (2010). "Effects of nursery preconditioning through mycorrhizal inoculation and drought in Arbutus unedo L. plants". Mycorrhiza 21 (1): 53–64. doi:10.1007/s00572-010-0310-x. ISSN 1432-1890. PMID 20405149. "aqueous extract is promising, at least, as an auxiliary anti-inflammatory treatment of diseases in which STAT1 plays a critical role.".
- ↑ Koch, H; Welcome, V; Kendal-Smith, A; Thursfield, L; Farrell, IW; Langat, MK; Brown, MJF; Stevenson, PC (2022). "Host and gut microbiome modulate the antiparasitic activity of nectar metabolites in a bumblebee pollinator". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B 377 (1853): 20210164. doi:10.1098/rstb.2021.0162. PMID 35491601.
- ↑ Maria Filomena Figueiredo Nazaré Gomes (2011). Strategies for the improvement of Arbutus unedo L. (strawberry tree): in vitro propagation, mycorrhization and diversity analysis. Departamento de Ciências da Vida Universidade de Coimbra. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/278004210. Retrieved July 30, 2020. "A. unedo may contribute to the discontinuity of the forest biomass due to monocultures of pines and eucalyptus, particularly in the centre and north regions of Portugal, a situation responsible for the high number of fires and high fire intensity that all summers occur in these areas of the country"
- ↑ Maria Filomena Figueiredo Nazaré Gomes (2011). Strategies for the improvement of Arbutus unedo L. (strawberry tree): in vitro propagation, mycorrhization and diversity analysis. Departamento de Ciências da Vida Universidade de Coimbra. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/278004210. Retrieved July 30, 2020. "The species is drought tolerant and able to regenerate following forestry fires making it quite interesting for forestation programs in Mediterranean regions."
- ↑ Maria Filomena Figueiredo Nazaré Gomes (2011). Strategies for the improvement of Arbutus unedo L. (strawberry tree): in vitro propagation, mycorrhization and diversity analysis. Departamento de Ciências da Vida Universidade de Coimbra. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/19131968.pdf. Retrieved 19 September 2017. "[A. unedo] contributes to maintain biodiversity, helps to stabilize soils and survives well in marginal lands"
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 42.2 Quoted in Alice M. Coats, Garden Shrubs and Their Histories (1964) 1992, s.v. "Arbutus".
- ↑ Ann Leighton, American Gardens in the Eighteenth Century: 'For Use or Delight' , 1976:395.
- ↑ "RHS Plant Selector - Arbutus unedo f. rubra". http://apps.rhs.org.uk/plantselector/plant?plantid=159.
- ↑ "RHS Plant Selector - Arbutus x andrachnoides". http://apps.rhs.org.uk/plantselector/plant?plantid=160.
- ↑ Ovid. The Metamorphoses. Book I. http://www.poetryintranslation.com/PITBR/Latin/Metamorph.htm. Retrieved 7 December 2022.
- ↑ S. Pignatti, Flora d'Italia, volume II, p. 261, Edagricole, 1982. ISBN:9788820623128
- ↑ Braccesi L., & Luni M. (Eds.). I greci in Adriatico, 2 (Hesperìa, Vol. 18). L'Erma Di Bretschneider, 2004, p.54 ISBN:8882652661.
- ↑ Warner, Marion. Fantastic metamorphoses, other worlds: ways of telling the self. Oxford University Press, 2002. 70.
- ↑ (in Italian) various authors - Guida pratica agli alberi e arbusti in Italia; Biblioteca per chi ama la natura - Selezione dal Reader's Digest Milano 1983, 1991.
- ↑ Giovanni Pascoli, in the autograph note to his poem "Il corbezzolo" ("The strawberry tree"), compared the virgilian, deposed after death on branches of a strawberry tree, to the Italian martyrs wrapped up, during the burial ceremonies, in the Italian flag.
External links
- Arbutus unedo — Calphotos Photo gallery, University of California
- House Shadow Drake's page about uses of this tree in Welsh and Irish witchcraft
- Very wide-spacing article with many reference published on Forestry
- Plants for a Future website
Wikidata ☰ Q329046 entry
az:Çiyələk ağacı
 |












