Biology:Bitis parviocula
| Bitis parviocula | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Viperidae |
| Genus: | Bitis |
| Species: | B. parviocula
|
| Binomial name | |
| Bitis parviocula Böhme, 1977[1]
| |
| |
- Common name: Bale Mountains adder,[2] Ethiopian mountain adder,[3][4] Ethiopian viper,[5] Ethiopian mountain viper.[6]
Bitis parviocula is a venomous viper species found only in Ethiopia.[2] It is large with a broad head and spectacular geometric markings. In 1995, the species was known from only three specimens, but additional information has surfaced since then. Little is known about its natural history or its venom.[7] No subspecies are currently recognized.[2]
The first specimen known to science was a road kill on the east side of the Rift Valley in Ethiopia.[8]
Etymology
The specific name, parviocula, meaning "small-eyed", is derived from the Latin words parvus, meaning "small", and oculus, meaning "eye".[9]
Description
Of the first three specimens, the maximum recorded total length (body + tail) was 75.2 cm (29.6 in),[4] but it is now known to reach a total length of at least 130 cm (51 in).[7] The head is long, flat, triangular and covered with small, strongly keeled scales. The nostrils are large and set well forward. The head is distinct from the thin neck. The body is cylindrical with a slight vertebral ridge, while the tail is short. The dorsal scales are keeled and are arranged in 37–39 rows at midbody.[4]
The color pattern consists of a light brown to dark brown ground color, overlaid with a series of black hexagons or diamonds that run down the center of the back. The black hexagons may have paler crossbars, while being separated from each other by a chain of yellow butterfly shapes. A series of black triangular or subtriangular spots, each with a white center, run down the upper flanks. The lower flanks have a series of greenish-gray triangles, pointing upwards, with yellow edges, especially the tips. The flanks between these triangles are a mottled green color. The head is brown with a dark triangle between the eyes and a dark hammer shape just behind it that extends onto the nape of the neck. The iris is brown. The side of the head is dark, but with a pale stripe that runs from the eye down to the labials. The upper labial scales are white. The chin and throat are white with black speckling. The belly is greenish-gray and may be clear, or with black speckling.[4]
Geographic range
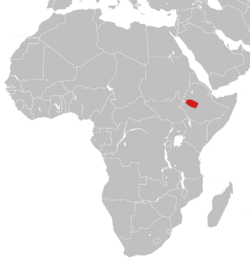
Known from only five localities in Ethiopia, it is found on both sides of the Rift Valley, both in the Bale Mountains[10] to the east and between Bonga and Jimma to the west.[6] It has been collected at altitudes of 1,700–2,800 metres (5,600–9,200 ft).[7]
The type locality is given as "Doki River bridge ( [ ⚑ ] 8°20′N 35°56′E / 8.333°N 35.933°E), bei Yambo (=Yembo), an der Straße von Metu nach Bedelle, Provinz Illubabor, SW-Äthiopien" [Ethiopia].[1][4]
Habitat
Of the three specimens known in 1995, two were found in forested areas west of the Rift Valley and one was found in grassland to the east. Of the two western specimens, one was caught in a forest clearing in an old coffee plantation, while the other was found in a forest town, hiding in grass of the grounds of a brewery. The eastern specimen was found in high grassland near a rocky stream.[3][4]
Behavior
Mostly unknown, its behavior is assumed to be terrestrial and nocturnal. In 1995, the only living specimen known was less irritable than the typical puff adder (B. arietans) and was not inclined to strike. However, it hissed when teased and struggled "furiously" when restrained, suggesting its temperament may be similar to that of the Gaboon viper (B. gabonica).[4] There has been reproduction of these snakes in captivity.[11]
Venom
Until recently, the toxicity and composition of the venom essentially was unknown.[12] It is assumed to cause at least some of the bites reported in the densely populated regions where it occurs. The local people consider it very dangerous.[3] The first US envenomation of a person was in March 2009 when a herpetologist from Texas was bitten in the finger by a young, captive B. parviocula, which he survived. It is the only well-documented bite report of this snake. The venom of this species can be neutralized by SAIMR antivenom.[12]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 McDiarmid RW, Campbell JA, Touré TA (1999). Snake Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, Volume 1. Washington, District of Columbia: Herpetologists' League. 511 pp. ISBN:1-893777-00-6 (series). ISBN:1-893777-01-4 (volume).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Bitis parviocula at the Reptarium.cz Reptile Database. Accessed 1 February 2021.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Mallow D, Ludwig D, Nilson G (2003). True Vipers: Natural History and Toxinology of Old World Vipers. Malabar, Florida: Krieger Publishing Company. 359 pp. ISBN:0-89464-877-2.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 Spawls S, Branch B (1995). The Dangerous Snakes of Africa. Sanibel Island, Florida:Ralph Curtis Books / Dubai: Oriental Press. 192 pp. ISBN:0-88359-029-8.
- ↑ Clinical Toxinology Resources. The University of Adelaide, Australia. http://www.toxinology.com/fusebox.cfm?fuseaction=main.snakes.display&mode=PrintFriendly&1d=SN0208.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Böhme W (2010). "[A review of our knowledge of the rare Ethiopian Mountain Viper, Bitis parviocula Böhme, 1977"]. 3rd Biology of the Vipers Conference – Calci, Pisa, 31 March–2 April 2010. p. 47. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341407465.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Largen MJ, Spawls S (2010). The Amphibians and Reptiles of Ethiopia and Eritrea. Frankfurt am Main: Edition Chimara / Serpents Tale. 694 pp. ISBN:978-3-89973-466-9
- ↑ Böhme W (1977).
- ↑ Ullman, B.L.; Henry, Norman E. (1931). New Elementary Latin. New York: Macmillan. 448 pp. + indices.
- ↑ Gower, David J., Edward OZ Wade, Stephen Spawls, W. O. L. F. G. A. N. G. Böhme, Evan R. Buechley, Daniel Sykes, and Timothy J. Colston. "A new large species of Bitis Gray, 1842 (Serpentes: Viperidae) from the Bale Mountains of Ethiopia." Zootaxa 4093, no. 1 (2016): 41-63.
- ↑ Kane, Daniel, Benjamin Tapley, Kimberley Carter, and Christopher Michaels. "Reproduction of the Ethiopian Mountain Adder, Bitis parviocula Böhme, 1976 (Reptilia: Viperidae), at ZSL London Zoo." Herpetology Notes 15 (2022): 423-429.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Sánchez, Elda E.; Hotle, Doug; Rodríguez-Acosta, Alexis (2011). "Neutralization of Bitis parviocula (Ethiopian mountain adder) venom by the South African Institute of Medical Research (SAIMR) antivenom". Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de São Paulo 53 (4): 213–217. doi:10.1590/S0036-46652011000400007. PMID 21915465.
Further reading
- Böhme W (1977). "Eine neue Art der Gattung Bitis (Serpentes, Viperidae) aus Äthiopien ". Monitore Zoologico Italiano (Nuova Serie), Supplemento 9 (3): 59–68. (Bitis parviocula, new species) (in German).
- Kane, Daniel; Tapley, Benjamin; Carter, Kimberley; Michaels, Christopher (2022). "Reproduction of the Ethiopian mountain adder, Bitis parviocula Böhme, 1976 (Reptilia: Viperidae), at ZSL London Zoo". Herpetology Notes 15: 423–429.
- Largen MJ, Rasmussen JB (1993). "Catalogue of the snakes of Ethiopia (Reptilia: Serpentes), including identification keys". Tropical Zoology 6: 313-434.
- Maritz, Bryan; Wallner, Alfred; Deans, Rob (2013). "Bitis parviocula (Böhme 1977) Reproduction". African Herp News (59): 28-29.
- Spawls S, Mazuch T, Mohammad A (2023). Handbook of Amphibians and Reptiles of North-east Africa. London, Oxford, New York, New Delhi, Sydney: Bloomsbury Wildlife. 640 pp. ISBN:978-1472991447.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bitis parviocula. |
- Bitis parviocula image at Blue Chameleon Ventures. Accessed 6 June 2006.
- The Other Large Bitis on YouTube. Accessed 25 January 2009.
- Bitis parviocula first feeding on YouTube. Accessed 25 January 2009.
- Next Generation Part 1 on YouTube. Accessed 25 January 2009.
Wikidata ☰ Q257576 entry
 |


