Biology:Body size and species richness
The body size-species richness distribution is a pattern observed in the way taxa are distributed over large spatial scales. The number of species that exhibit small body size generally far exceed the number of species that are large-bodied. Macroecology has long sought to understand the mechanisms that underlie the patterns of biodiversity, such as the body size-species richness pattern. This pattern was first observed by Hutchinson and MacArthur (1959),[1] and it appears to apply equally well to a broad range of taxa: from birds and mammals to insects, bacteria (May, 1978;[2] Brown and Nicoletto, 1991[3]) and deep sea gastropods (McClain, 2004[4]). Nonetheless, its ubiquity remains undecided. Most studies focus on the distribution of taxonomic fractions of largely non-interacting species such as birds or mammals; this article is primarily based on those data.

Introduction
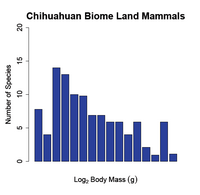
The body size-species richness pattern (see fig. 1) has been documented for land mammals across numerous continents such as North America, South America, Eurasia and Africa (Brown and Maurer, 1989;[5] Bakker and Kelt, 2000;[6] Maurer et al. 1992[7]). Traditionally the pattern has been explored by plotting the number of species on the y-axis and the logarithm to the base two of the species body mass (g) on the x-axis. This yields a highly right skewed body size distribution with a mode centered near species with a mass ranging from 50-100 grams. Although this relationship is very distinct at large spatial scales, the pattern breaks down when the sampling area is small (Hutchinson and MacArthur, 1959;[1] Brown and Maurer 1989;[5] Brown and Nicoletto 1991;[3] Bakker and Kelt 2000[6]).
Scale dependence of the pattern
At small spatial scales (e.g. a dozen hectares or a local community) the body size-species richness pattern dissolves and the number of species per body size class is almost uniform (i.e. there is an equal number of small and large bodied species in the community (see fig. 2 b)). Researchers have documented this transition by sampling species at different spatial scales; at intermediate spatial scales (e.g. a thousand hectares or a biome) the body size-species richness distribution begins to shift from being right skewed (from fewer large-bodied species) towards a normal distribution. Finally, when macroecologists compare the body size-species richness distributions of continents to those of communities the distributions are significantly different (Hutchinson and MacArthur, 1959;[1] Brown and Maurer, 1989;[5] Brown and Nicoletto, 1991;[3] Bakker and Kelt, 2000[6]) (see fig. 1 vs. fig. 2 b)).
Figure 2. The Frequency distribution of land mammals at two different spatial scales. The figure shows a shift from a slightly right skewed distribution at the biome scale (a) to a normal distribution at the community level (b). The x-axis ranges from 0 to 20 on a log-scale in both graphs. Redrawn from Brown and Nicoletto (1991).[3]
Counter examples
Not all geographic subsets of taxonomic groups follow this broad pattern, in contrast, Northwest European land snails exhibit a normal distribution (Hausdorf, 2006[8]). Additionally, the terrestrial mammals of the islands of Madagascar, New Guinea and Australia do not show a right skewed body size-species richness distribution (Maurer et al. 1992[7]). Given the limited amount of non-conforming data it is not possible to determine if this phenomenon is universal or is simply novel in certain environments. Underreporting of taxonomic and geographic subsets that do not conform to this pattern may be partially responsible for this unresolve.
Possible mechanisms
If it were possible to randomly sample a subset of the known continental species pool for mammals, one would expect the body size-species richness distribution of this sample to roughly mirror that of the entire continent. Since it does not, and if it is assumed that the observed distribution of species among body sizes is not a sampling bias, then some ecological interactions must underlie this pattern. Explanations in the literature suggest the rates of speciation and/or dispersal ability vary with size and could lead to more small bodied organisms (May, 1978[2]). Additionally, extinction risk, competition and energetic restraints have also been proposed as critical mechanisms that may drive this pattern (Brown and Maurer, 1989;[5] Brown and Nicoletto, 1991[3]). Finally, the metabolic theory of ecology explains how there is a negative relationship between number of individuals (N) and size (M) ([math]\displaystyle{ N = M ^ {-3/4} }[/math]), but it is silent on species richness. Remember, while there are fewer individuals in the largest size classes, energy availability is equal across all classes of interacting organisms (i.e. they share the same energy pool and are thus part of the same ecosystem) (energetic equivalence) (May, 1988[9]). It is important to note that the 3 sub-mechanisms: dispersal, competition and energetic restraints must in some manner feed back into either speciation or extinction rates as these are the only ultimate processes (see Tinbergen's four questions) governing the number of species on earth and hence the body size-species richness pattern.
Speciation rates
Small organisms generally have shorter generation times and are quick to mature and reproduce (May, 1978;[2] Denney et al. 2002;[10] Savage et al. 2004[11]). These traits may promote speciation through increased mutation and selection events as molecular evolution scales with metabolic rate (Gillooly et al. 2005[12]) and thus with body size. For example, bacteria can evolve a degree of antibiotic resistance in a very short time period. This evolution is facilitated by a short generation time and presumably would not be possible for species with slower life histories. Thus, one can think of it as if the "evolutionary clock ticks faster" (May, 1978[2]) for small organisms. If this were true then a simple explanation of why there are more small species on earth would be because they speciate faster. However, an analysis by Cardillo and colleagues (2003)[13] revealed that body size did not influence the speciation rates of Australia's mammals. Similarly, a study using birds failed to demonstrate that body size and speciation rates were negatively correlated (Nee et al. 1992[14]).
Differential extinction rates
It is known that extinction risk is directly correlated to the size of a species population. Small populations tend to go extinct more frequently than large ones (MacArthur and Wilson, 1967[15]). As large species require more daily resources they are forced to have low population densities, thereby lowering the size of the population in a given area and allowing each individual to have access to enough resources to survive. In order to increase the population size and avoid extinction, large organisms are constrained to have large ranges (see Range (biology)). Thus, the extinction of large species with small ranges becomes inevitable (MacArthur and Wilson, 1967;[15] Brown and Maurer, 1989;[5] Brown and Nicoletto, 1991[3]). This results in the amount of space limiting the overall number of large animals that can be present on a continent, while range size (and risk of extinction) prevents large animals from inhabiting only a small area. These constraints undoubtedly have implications for the species richness patterns for both large and small-bodied organisms, however the specifics have yet to be elucidated.
Dispersal rate
Understanding dispersal is an important mechanism that may underlie the body size-species richness pattern. Mainly, dispersal ability can affect speciation rates in various ways: if an organism is capable of dispersing across great distances which span variable habitat, it will be more likely that individuals that settle in these new areas will be subject to different selection regimes, leading to new species through natural selection. Alternatively, great dispersal ability can act against the efforts of natural selection by facilitating geneflow. Thus, species with greater dispersal ability may in fact have lower speciation rates. Then again, if a species disperses long distances and has a large range, it may also be more likely to have its range bisected by natural barriers which could promote allopatric speciation over evolutionary time.
Researchers have shown that body size and dispersal ability do not correlate (Jenkins et al. 2007[16]). However, this finding rests heavily on the fact that active and passive dispersers have been grouped together in the analyses. When the same data are separated into two categories (active and passive dispersers) a pattern emerges. Jenkins and others (2007[16]) have found that for active dispersers larger organisms will disperse greater distances. Regardless of this correlation its effects on speciation rates remain unclear.
Interspecific competition
Could similar sized species be mitigating the effects of competition by avoiding each other? Interspecific competition is in fact strong among species that are the same size (Bowers and Brown, 1982[17]). Researchers have proposed that in order to lessen the burden of competition among animals within the same guild (see Guild (ecology)), they must vary in size (Brown and Maurer, 1989;[5] Brown and Nicoletto, 1991[3]). For example, Bowers and Brown (1982)[17] found that the number of similar sized species in a community of granivorous rodents was fewer than expected. They believe that these results suggest that competition between same-sized species is prohibiting co-existence in this community.
Energetic constraints
A small bodied animal has a greater capacity to be more abundant than a large bodied one. Purely as a function of geometry many more small things can be packed into a given space than can large things into the same area. However, these limits are generally never reached in ecological systems as other resources become limiting long before the packing limits are reached. Additionally, smaller species may have many more ecological niches available to them and thus facilitating the diversification of life (Hutchinson and MacArthur, 1959[1]).
Larger organisms require more food overall (Blackburn and Gaston, 1997[18]), however they require less energy per unit of body mass. As a result, larger species are able to survive on a lower quality diet than smaller species. For example, grazing animals make up for their poor quality diet by digesting food longer and are able to extract more energy from it (Maurer et al. 1992[7]). Smaller species tend to specialize in a habitat that can provide them with a high quality diet.
Habitat quality is highly variable and as a result smaller species tend to be present in less of their range. Instead, they are only found in patches of their range where there is good habitat. A correlate to this argument is that the opposite is true for larger species. Larger species have lower beta diversity and are replaced less frequently across landscapes and as a result tend to occupy more of their range (see Occupancy-abundance relationship relationships) (Brown and Maurer, 1989;[5] Brown and Nicoletto, 1991[3]). This mechanism likely contributes to the shift in body size-species richness distribution observed between continental and local scales.
Recently, the metabolic theory of ecology has been used to explain macroecological patterns. According to May (1978[9]) there is equal energy flow through all size classes of interacting organisms. This has implications for the number of individuals in each size class and potentially the number of species as well. May (1978[2]) was the first to describe a mathematical equation that could be used to explain the right hand side of the body size-species richness pattern . His equation states that the number of species (S) is proportional to the length (L) of the species raised to the exponent of negative two ([math]\displaystyle{ S = L ^ {-2} }[/math]). This theory is based on data from many different terrestrial animals (mammals, birds, beetles, and butterflies) and has garnered further support from a more recent study by Rice and Gislason (1996).[19] These new results also demonstrate a slope of negative two with respect to the right side of the body size-species richness pattern in the fish assemblage of the North Sea. Whether a slope of -2 is universal and what the mechanisms are that underlie this theory remain unclear.

See also
- Macroecology
- Metabolic theory of ecology
- Niche apportionment models
- Occupancy-abundance relationship
- Range (biology)
- Relative species abundance
- Species richness
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Hutchinson GE & MacArthur RH (1959) A theoretical ecological model of size distributions among species of animals. American Naturalist 93(869):117-125.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 May, R. Diversity of insect faunas. Blackwell scientific publications:London. 1978. 188-203.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 Brown JH & Nicoletto PF (1991) Spatial scaling of the species composition - body masses of North-American land mammals. American Naturalist 138(6):1478-1512.
- ↑ McClain CR (2004) Connecting species richness, abundance and body size in deep-sea gastropods. Global Ecology and Biogeography 13(4):327-334.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 Brown JH & Maurer BA (1989) Macroecology – the division of food and space among species on the continents. Science 243(4895):1145-1150.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Bakker VJ & Kelt DA (2000) Scale-dependent patterns in body size distributions of neotropical mammals. Ecology 81(12):3530-3547.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Maurer BA, Brown JH, & Rusler RD (1992) The micro and macro in body size evolution. Evolution 46(4):939-953.
- ↑ Hausdorf B (2006) Is the interspecific variation of body size of land snails correlated with rainfall in Israel and Palestine? Acta Oecologica-International Journal of Ecology 30(3):374-379.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 May, R (1988) How many species are there on earth? Science 241(4872):1441-1449.
- ↑ Denney NH, Jennings S & Reynolds JD (2002) Life history correlates of maximum population growth rates in marine fishes. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, 269(1506):2229-2237.
- ↑ Savage VM, Gillooly JF, Brown JH, West GB & Charnov EL (2004) Effects of body size and temperature on population growth. American Naturalist. 163:429-441.
- ↑ Gillooly JF, Allen AP, West GB, & Brown JH (2005) The rate of DNA evolution: Effects of body size and temperature on the molecular clock. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 102(1):140-145.
- ↑ Cardillo M, Huxtable JS, & Bromham L (2003) Geographic range size, life history and rates of diversification in Australian mammals. Journal of Evolutionary Biology 16(2):282-288.
- ↑ Nee S, Mooers A & Harvey P (1992) Tempo and mode of evolution revealed from molecular phylogenies. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 89(17):8322-8326.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 MacArthur, RH & Wilson, EO (1967) The theory of island biogeography. Princeton, New Jersey. Princeton Universal Press.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Jenkins DG, Brescacin CR, Duxbury CV, Elliott JA, Evans JA, Grablow KR, Hillegass M, Lyon BN, Metzger GA, Olandese ML, Pepe D, Silvers GA, Suresch HN, Thompson TN, Trexler CM, Williams GE, Williams NC & Williams SE (2007) Does size matter for dispersal distance? Global Ecology and Biogeography 16(4):415-425.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Bowers MA & Brown JH (1982) Body size and coexistence in desert rodents – chance or community structure. Ecology 63(2):391-400.
- ↑ Gaston, KJ, TM Blackburn, & JH Lawton (1997) Interspecific abundance-range size relationships: an appraisal of mechanisms. Journal of Animal Ecology 66:579–601.
- ↑ Rice J & Gislason H (1996) Patterns of change in the size spectra of numbers and diversity of the North Sea fish assemblage, as reflected in surveys and models. 53:1214-1225.
 |