Biology:Chromosome 4 open reading frame 54
Chromosome 4 open reading frame 54 is a protein that in humans is coded by the c4orf54 gene.[1][2] This gene is also known as FOPV (Familial Obliterative Portal Venopathy) and LOC285556. This protein is mostly expressed in the nucleus of muscle cells.[1] Orthologs are found in vertebrates but not invertebrates.
Gene
Human chromosome 4 open reading frame 54(c4orf54) is made up of 10451 nucleotides from chromosome 4, map 4q23(chr4:99,636,529-99,657,828), on the complement strand. The mRNA of c4orf54(NM_001354435) is made up of 3 exons.
Gene Expression
Within cells, c4orf54 is primarily expressed in the nucleus with a.[3][4] An analysis of unknown type of human cells treated with an antibody for c4orf54 showed that there is some expression in the nucleus but is primarily in the cytoplasm.[4] C4orf54 is expressed in muscle cells such as biceps and bone, as well as some glands.[1]
Regulation of expression
On the 5'UTR of the c4orf54 gene, there are several transcription factors that have to do with leucine zippers and they bind to the same 11 nucleotides: FOS, BATF::JUN, BATF3, and BATF.
Transcript
Exon 2 is the only exon transcribed. There is also the X1 variant of this gene. The 5' UTR is shorter than the main variant.
Protein
C4orf54 human protein is made up of 1793 amino acids. This unmodified form has a predicted molecular weight of approximately 190 kDal and a predicted isoelectric point of 9.11. This mass is concurrent with results from OMIM. The more enriched protein compared to other human proteins was serine(12.9%) and the pattern of serine then threonine was also highly enriched comparatively at 19.1%. This aligns with the results found from Motif Scan that the amino acid sequence is serine rich from amino acids 237 to 312. There is significant expression in smooth muscle tissue. There is a domain of unknown function.
Post-translational modifications
The c4orf54 protein is myristylated with over 20 predicted sites.[5] There is also significant phosphorylation with 2 experimentally proven sites and over 50 predicted sites.[2] One methylation site was found experimentally.
Structure
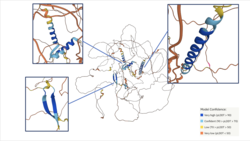
An analysis of the structure using Alpha Fold shows both alpha helices and beta sheets with 70% or more model confidence.[6] The alpha helices have an overall higher higher model confidence.
Function
FOPV has been found to interact with 3 other proteins: BTF3, CUL4A, and KRAS.[7] This protein may have lethal interactions with the Ras Oncogene.[8] There may be an association between mutations in the FOPV gene and Obliterative portal venopathy which is lesions in portal vein branches in the liver.[9]
Orthologs
C4orf54 was found in vertebrates but not invertebrates. The most distant species found using NCBI BLAST with protein c4orf54 was Petromyzon marinus, the sea lamprey, which had the last common ancestor with humans around 600 million years ago with a sequence identity of 26.3%. This is also an estimate of when the c4orf54 gene emerged. The closest non primate relative is from about 87 million years ago with a sequence identity similarity to the human protein of 86.6%.
| c4orf54 | Genus and Species | Common Name | Taxonomic Group | Median Date of Divergence (MYA) | Accession # | Sequence Length (aa) | Query Cover (%) | Sequence Identity to Human Protein (%) | Sequence Similarity to Human Protein (%) | Corrected Divergence |
| Mammal | Homo sapiens | Human | Primates | 0 | NP_001341364.1 | 1793 | 100 | 100 | 100.0 | 0.00 |
| Mus musculus | House Mouse | Rodentia | 87 | NP_001357791.1 | 1786 | 96 | 86.94 | 86.6 | 14.25 | |
| Neosciurus carolinensis | Eastern Grey Squirrel | Rodentia | 87 | XP_047423506.1 | 1786 | 100 | 86.72 | 90.8 | 14.25 | |
| Felis catus | House Cat | Carnivora | 94 | XP_006931007.1 | 1801 | 100 | 84.71 | 89.8 | 16.59 | |
| Reptilia | Trachemys scripta elegans | Red-eared Slider | Testudines | 319 | XP_034627307.1 | 1670 | 79 | 51.47 | 57.9 | 66.42 |
| Terrapene carolina triunguis | Three-toed Box Turtle | Testudines | 319 | XP_024067528.1 | 1553 | 79 | 51.58 | 54.8 | 66.20 | |
| Pantherophis guttatus | Corn Snake | Squamata | 319 | XP_034298051.1 | 1505 | 66 | 51.45 | 49.1 | 66.46 | |
| Chelonia mydas | Green Sea Turtle | Testudines | 319 | XP_037752386.1 | 1553 | 79 | 51.10 | 54.4 | 67.14 | |
| Aves | Catharus ustulatus | Swainson's Thrush | Passeriformes | 319 | XP_032915906.1 | 1472 | 79 | 47.05 | 51.4 | 75.40 |
| Calypte anna | Anna's hummingbird | Apodiformes | 319 | XP_030306184.1 | 1540 | 79 | 46.95 | 51.7 | 75.61 | |
| Gallus gallus | Red Junglefowl | Galliformes | 319 | XP_040527126.1 | 1296 | 62 | 46.35 | 46.5 | 76.89 | |
| Amphibian | Xenopus tropicalis | Western Clawed Frog | Anura | 353 | XP_004911157.2 | 1521 | 74 | 42.92 | 48.0 | 84.58 |
| Rana temporaria | Common Frog | Ranidae | 353 | XP_040184421.1 | 1501 | 79 | 38.75 | 43.0 | 94.80 | |
| Geotrypetes seraphini | Gaboon Caecilian | Gymnophiona | 353 | XP_033813063.1 | 1303 | 58 | 38.15 | 43.0 | 96.36 | |
| Fish | Chanos chanos | Milkfish | Gonorynchiformes | 431 | XP_030635043.1 | 1571 | 74 | 37.92 | 44.0 | 96.97 |
| Megalops cyprinoides | Oxeye Herring | Elopiformes | 431 | XP_036406656.1 | 1612 | 79 | 37.82 | 45.1 | 97.23 | |
| Melanotaenia boesemani | Boeseman's Rainbowfish | Atheriniformes | 431 | XP_041840397.1 | 1505 | 73 | 35.83 | 43.1 | 102.64 | |
| Chiloscyllium plagiosum | Whitespotted Bamboo Shark | Orectolobiformes | 464 | XP_043530392.1 | 1237 | 52 | 48.25 | 37.3 | 72.88 | |
| Carcharodon carcharias | Great White Shark | Lamniformes | 464 | XP_041050558.1 | 1414 | 56 | 34.15 | 37.6 | 107.44 | |
| Petromyzon marinus | Sea Lamprey | Petromyzontiformes | 599 | XP_032825160.1 | 1482 | 27 | 31.20 | 26.3 | 116.48 |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) entry on C4orf54 chromosome 4 open reading frame 54 [ Homo sapiens (human)". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/285556.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) entry on Homo sapiens chromosome 4 open reading frame 54 (C4orf54), mRNA". 8 June 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/NM_001354435.2.
- ↑ "Prediction of Protein sorting Signals and Localization Sites in Amino Acid Sequences(PSORT)". https://psort.hgc.jp/.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "The Human Protein Atlas profile of c4orf54". https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000248713-C4orf54.
- ↑ ExPasy Myristoylator [https://www.expasy.org/resources/myristoylator]
- ↑ "AlphaFold". https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/.
- ↑ "NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) entry on uncharacterized protein C4orf54 [Homo sapiens"]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/1230839365.
- ↑ Luo, J.; Emanuele, M. J.; Li, D.; Creighton, C. J.; Schlabach, M. R.; Westbrook, T. F.; Wong, K. K.; Elledge, S. J. (2009). "A genome-wide RNAi screen identifies multiple synthetic lethal interactions with the Ras oncogene". Cell 137 (5): 835–848. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.006. PMID 19490893. PMC 2768667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.006.
- ↑ Besmond, C; Valla, D; Hubert, L; Poirier, K; Grosse, B; Guettier, C; Bernard, O; Gonzales, E et al. (February 2018). "Mutations in the novel gene FOPV are associated with familial autosomal dominant and non-familial obliterative portal venopathy.". Liver International 38 (2): 358–364. doi:10.1111/liv.13547. PMID 28792652. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.13547.
 |