Biology:Cyrtopodion scabrum
| Cyrtopodion scabrum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Family: | Gekkonidae |
| Genus: | Cyrtopodion |
| Species: | C. scabrum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cyrtopodion scabrum (Heyden, 1827)
| |
| |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
Cyrtopodion scabrum, also known as the rough-tailed gecko, rough bent-toed gecko, rough-tailed bowfoot gecko, common tuberculate ground gecko, or keeled gecko, is a species of gecko, a lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is endemic to Asia.
Taxonomy
Cyrtopodion basoglui is considered conspecific with Cyrtopodion scabrum. Because Cyrtopodion scabrum was originally described in 1827 and Cyrtodactylus basoglui was described in 1982, Cyrtodactylus basoglui is a junior synonym of Cyrtopodion scabrum.
Geographic range
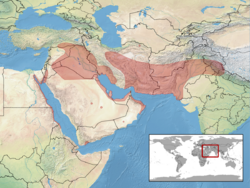
C. scabrum is found in Afghanistan, Djibouti,[3] Egypt[4] (Siwa Oasis: HR 31: 254), Eritrea, Ethiopia, India , Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Oman, Pakistan , Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sinai/Tor, Sudan, Turkey, Greece, United Arab Emirates, and the USA (introduced to Texas and Arizona).[2]
As an introduced species
In the United States, C. scabrum has been introduced in Arizona and Texas . A breeding population has been established in Galveston, Texas, in the area of the commercial shipping docks.[5]
References
- ↑ Els, J.; Al Johany, A.M.H.; Amr, Z.S.S.; Nilson, G.; Sevinç, M.; Tok, C.V.; Werner, Y.L.; Disi, A.M. et al. (2021). "Cyrtopodion scabrum". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2021: e.T164748A1072727. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-3.RLTS.T164748A1072727.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/164748/1072727. Retrieved 21 February 2022.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Cyrtopodion scabrum ". The Reptile Database. www.reptile-database.org.
- ↑ "Keeled Rock Gecko (Cyrtopodion scabrum)". https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/33255-Cyrtopodion-scabrum.
- ↑ Din, Sherif Baha El (2006). A guide to reptiles and amphibians of Egypt. Cairo, Egypt. ISBN 978-1-61797-517-2. OCLC 880445081. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/880445081.
- ↑ Powell R, Conant R, Collins JT (2016). Peterson Field Guide to Reptiles and Amphibians of Eastern and Central North America, Fourth Edition. Boston and New York: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. xiv + 494 pp., 47 plates, 207 figures. ISBN 978-0-544-12997-9. (Cyrtopodion scabrum, p. 259 + Plate 23).
Further reading
- Boulenger GA (1885). Catalogue of the Lizards in the British Museum (Natural History). Second Edition. Volume I. Geckonidæ, Eublepharidæ, Uroplatidæ, Pygopodidæ, Agamidæ. London: Trustees of the British Museum (Natural History). (Taylor and Francis, printers). xii + 436 pp. + Plates I-XXXII. (Gymnodactylus scaber, pp. 27–28).
- Das I (2002). A Photographic Guide to Snakes and other Reptiles of India. Sanibel Island, Florida: Ralph Curtis Books. 144 pp. ISBN 0-88359-056-5. (Cyrtopodion scabrum, p. 92).
- Heyden CHG von (1827). "Reptilien ". pp. 1-24. In: Rüppell E. Atlas zur der Reise im nördlichen Afrika. Erste Abtheilung, Zoologie. Frankfurt am Main: H.L. Brönner. 622 pp. (Stenodactylus scaber, new species, pp. 15-17 + Plate 4, figure 2). (in German and Latin).
- Rösler, Herbert (2000). "Die postanale Beschuppung bei Cyrtodactylus Gray 1827 und Cyrtopodion Fitzinger 1843 - funktionelle und taxonomische Aspekte (Sauria: Gekkonidae)". Gekkota 2: 154–207. (in German).
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q3009475 entry
 |

