Biology:DFFA
 Generic protein structure example |
| DNA Fragmentation factor 45kDa, C terminal domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
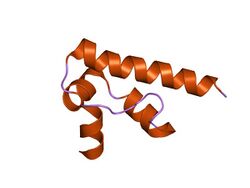 nmr structure of dff-c domain | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | DFF-C | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF09033 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR015121 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
DNA fragmentation factor subunit alpha (DFFA), also known as Inhibitor of caspase-activated DNase (ICAD), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DFFA gene.[1][2][3]
Apoptosis is a cell death process that removes toxic and/or useless cells during mammalian development. The apoptotic process is accompanied by shrinkage and fragmentation of the cells and nuclei and degradation of the chromosomal DNA into nucleosomal units. DNA fragmentation factor (DFF) is a heterodimeric protein of 40-kD (DFFB) and 45-kD (DFFA) subunits. DFFA is the substrate for caspase-3 and triggers DNA fragmentation during apoptosis. DFF becomes activated when DFFA is cleaved by caspase-3. The cleaved fragments of DFFA dissociate from DFFB, the active component of DFF. DFFB has been found to trigger both DNA fragmentation and chromatin condensation during apoptosis. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene.[3]
The C-terminal domain of DFFA (DFF-C) consists of four alpha-helices, which are folded in a helix-packing arrangement, with alpha-2 and alpha-3 packing against a long C-terminal helix (alpha-4). The main function of this domain is the inhibition of DFFB by binding to its C-terminal catalytic domain through ionic interactions, thereby inhibiting the fragmentation of DNA in the apoptotic process. In addition to blocking the DNase activity of DFFB, the C-terminal region of DFFA is also important for the DFFB-specific folding chaperone activity, as demonstrated by the ability of DFFA to refold DFFB.[4]
Interactions
DFFA has been shown to interact with DFFB.[5][6]
References
- ↑ "Assignment of the DNA fragmentation factor gene (DFFA) to human chromosome bands 1p36.3-->p36.2 by in situ hybridization". Cytogenetics and Cell Genetics 79 (3–4): 212–3. Jun 1998. doi:10.1159/000134725. PMID 9605855.
- ↑ "DFF, a heterodimeric protein that functions downstream of caspase-3 to trigger DNA fragmentation during apoptosis". Cell 89 (2): 175–84. April 1997. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80197-X. PMID 9108473.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Entrez Gene: DFFA DNA fragmentation factor, 45kDa, alpha polypeptide". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1676.
- ↑ "Solution structure of the DFF-C domain of DFF45/ICAD. A structural basis for the regulation of apoptotic DNA fragmentation". Journal of Molecular Biology 321 (2): 317–27. August 2002. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00588-0. PMID 12144788.
- ↑ "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Molecular Systems Biology 3 (1): 89. 2007. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMID 17353931.
- ↑ "Study of DFF45 in its role of chaperone and inhibitor: two independent inhibitory domains of DFF40 nuclease activity". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 264 (1): 176–80. October 1999. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1497. PMID 10527860.
Further reading
- "Destruction of bile ducts in primary biliary cirrhosis". Baillière's Best Practice & Research. Clinical Gastroenterology 14 (4): 549–70. August 2000. doi:10.1053/bega.2000.0103. PMID 10976014.
- "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene 138 (1–2): 171–4. January 1994. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene 200 (1–2): 149–56. October 1997. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- "A caspase-activated DNase that degrades DNA during apoptosis, and its inhibitor ICAD". Nature 391 (6662): 43–50. January 1998. doi:10.1038/34112. PMID 9422506. Bibcode: 1998Natur.391...43E.
- "Activation of the apoptotic endonuclease DFF40 (caspase-activated DNase or nuclease). Oligomerization and direct interaction with histone H1". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 274 (20): 13836–40. May 1999. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.20.13836. PMID 10318789.
- "Functional interaction of DFF35 and DFF45 with caspase-activated DNA fragmentation nuclease DFF40". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 274 (30): 20759–62. July 1999. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.30.20759. PMID 10409614.
- "Identification of differentially expressed genes associated with HER-2/neu overexpression in human breast cancer cells". Nucleic Acids Research 27 (20): 4008–17. October 1999. doi:10.1093/nar/27.20.4008. PMID 10497265.
- "Study of DFF45 in its role of chaperone and inhibitor: two independent inhibitory domains of DFF40 nuclease activity". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 264 (1): 176–80. October 1999. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1497. PMID 10527860.
- "Multiple domains of DFF45 bind synergistically to DFF40: roles of caspase cleavage and sequestration of activator domain of DFF40". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 264 (1): 181–5. October 1999. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1498. PMID 10527861.
- "Solution structure of the CIDE-N domain of CIDE-B and a model for CIDE-N/CIDE-N interactions in the DNA fragmentation pathway of apoptosis". Cell 99 (7): 747–55. December 1999. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81672-4. PMID 10619428.
- "Structure of the heterodimeric complex between CAD domains of CAD and ICAD". Nature Structural Biology 7 (8): 658–62. August 2000. doi:10.1038/77957. PMID 10932250.
- "Frequent nuclear localization of ICAD and cytoplasmic co-expression of caspase-8 and caspase-3 in human lymphomas". The Journal of Pathology 192 (2): 194–202. October 2000. doi:10.1002/1096-9896(2000)9999:9999<::AID-PATH685>3.0.CO;2-M. PMID 11004695.
- "Solution structure of DFF40 and DFF45 N-terminal domain complex and mutual chaperone activity of DFF40 and DFF45". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 98 (11): 6051–5. May 2001. doi:10.1073/pnas.111145098. PMID 11371636. Bibcode: 2001PNAS...98.6051Z.
- "Direct cleavage of the human DNA fragmentation factor-45 by granzyme B induces caspase-activated DNase release and DNA fragmentation". The EMBO Journal 20 (12): 3101–13. June 2001. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.12.3101. PMID 11406587.
- "Implications of CAD and DNase II in ischemic neuronal necrosis specific for the primate hippocampus". Journal of Neurochemistry 79 (6): 1196–206. December 2001. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00679.x. PMID 11752060.
- "Analyses of apoptotic regulators CASP9 and DFFA at 1P36.2, reveal rare allele variants in human neuroblastoma tumours". British Journal of Cancer 86 (4): 596–604. February 2002. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6600111. PMID 11870543.
- "Growth phase-dependent expression of ICAD-L/DFF45 modulates the pattern of apoptosis in human colonic cancer cells". Cancer Research 62 (7): 2169–74. April 2002. PMID 11929840.
 |