Biology:Elacatinus chancei
| Elacatinus chancei | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Gobiiformes |
| Family: | Gobiidae |
| Genus: | Elacatinus |
| Species: | E. chancei
|
| Binomial name | |
| Elacatinus chancei (Beebe & Hollister, 1933)
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
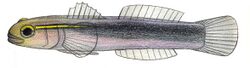
Elacatinus chancei, the shortstripe goby, is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Gobiidae. It lives inside or on the surface of a sponge and occurs in tropical waters in the west central Atlantic Ocean, the Bahamas, the Antilles, and Venezuela.
Description
The shortstripe goby is a small, slender fish growing to about 5 cm (2.0 in) in length. The dorsal fin is divided into two parts with a total of seven spines and 12 soft rays, while the anal fin has no spines and ten soft rays. [2] The general colour is a translucent pale grey. A bright yellow line starts at the eye and runs to near the pectoral fin. It is lined above and below by black lines which converge and continue as a broad stripe to the tail fin. The gill covers and the skin under the eyes are often suffused with pink.[3]
Distribution
The shortstripe goby is found in the tropical western Atlantic Ocean in the Southern Bahamas, Puerto Rico, the Virgin Islands, the Caicos Islands, the Lesser Antilles, Aves Island, and some small islands near Venezuela. It seems to live in areas in which the yellowstripe goby (Elacatinus horsti), a closely related species that also inhabits sponges, does not occur.[4]
Biology
The shortstripe goby lives in association with a tubular sponge such as Verongia aerophoba or a massive sponge such as Neofibularia nolitangere. It feeds on the large number of parasitic worms Haplosyllis spongicola that live on the surface of these sponges.[5][3] It spends most of its time inside the osculi of the sponge, but sometimes rests on the outer surface.[4]
Like other members of its family, the shortstripe goby does not have a lateral line system, relying instead on sensory organs in the head.[3]
Name
The specific name honours Colonel Edwin M. Chance, a businessman who sponsored the expedition during which the type was collected.[6]
References
- ↑ van Tassell, J.; Pezold, F.; Aiken, K.A.; Tornabene, L.; Bouchereau, J.-L. (2015). "Elacatinus chancei". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015: e.T185976A1797646. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T185976A1797646.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/185976/1797646. Retrieved 20 November 2021.
- ↑ "Elacatinus chancei (Beebe & Hollister, 1933)". FishBase. http://www.fishbase.org/summary/speciessummary.php?id=23734.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Alain Feulvarc'h (2010-07-03). "Gobie à lignes courtes" (in French). Sous les Mers. http://fran.cornu.free.fr/affichage/affichage_nom.php?id_espece=1298.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Elacatinus chancei Beebe & Hollister 1933". Gobioid Research Institute. http://gobiidae.com/species_pages/elacatinus_chancei.htm.
- ↑ Colin, Patrick L. (1978). Marine Invertebrates and Plants of the Living Reef. T.F.H. Publications. p. 111. ISBN 978-0-86622-875-6. https://archive.org/details/marineinvertebra00patr_0/page/111.
- ↑ "Order GOBIIFORMES: Family GOBIIDAE (d-h)". The ETYFish Project Fish Name Etymology Database. Christopher Scharpf and Kenneth J. Lazara. 29 May 2018. http://www.etyfish.org/gobiiformes5/.
Wikidata ☰ Q2097483 entry
 |


