Biology:Eoazara
| Eoazara | |
|---|---|
| |
| Holotype cranial remains | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Perissodactyla |
| Family: | Rhinocerotidae |
| Subfamily: | †Elasmotheriinae |
| Genus: | †Eoazara Geraads & Zouhri, 2021 |
| Type species | |
| †Eoazara xerrii Geraads & Zouhri, 2021
| |
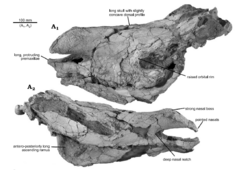
Eoazara xerrii is a species of extinct elasmotheriine rhinoceros from the upper Miocene of Morocco, the first definitive representative of the subfamily in North Africa.[1] It is known from a well preserved skull and postcranial material, preserving the most complete late Miocene rhino skull found in Africa.[1]
Discovery and naming
First descriptions of upper Miocene rhinos from the Skoura regions were published by Zouhri et al. in 2012 including cf. Ceratotherium sp. and aff. Chilotherium sp., the later of which was described on the basis of specimen FSC-Sk-33,then believed to have been a premolar. In 2013 the tooth, now thought to be a molar, was re-identified as belonging to an indetermined species and genus of elasmotheriine. Fossil hunters were also active in the area, uncovering the skulls of other mammals. The holotype skull of Eoazara, specimen FSC-Sk-250, was purchased from such fossil hunters by Serge Xerri in Rabat before being presented to the Aïn Chock Faculty of Sciences, Casablanca. It was subsequently transported to Paris for preparation and returned to the Faculty. Postcranial material has also been referred to this genus, namely Mc II FSC-Sk-45 and Mt II FSC-Sk-53.[1]
The name Eoazara derives from the Greek "eo" meaning early and the Amazigh word for rhino, "azara". The species name honors Serge Xerri for donating the holotype skull.[1]
Description
Eoazara was a large sized elasmotheriine, estimated to have been similar in size to the largest modern rhinos but with a more slender build. The skull is long with a concave profile and relatively complete, missing most of the occiput. Of the dentary part of the left and most of the right side are preserved. Although relatively complete, the skull has been dorsoventrally crushed, however the proportions have not been overly distorted by taphonomy. In life the skull would have been higher than long, most cranial sutures are untraceable, showing that this was a mature specimen. The fused nasal is long and inflated, but tapers to a point at its anterior margin towards the premaxillae. The rugose surface of the nasal would have supported a large keratinous horn with an accordingly deep notch that however does not reach far back as in Hispanotherium. While there is no evidence of a second horn growing from the frontal, its absence cannot be reliably determined due to the fact that these second horns oftentimes only leave faint traces on the skullbone. The premaxillae are long and slender and in close proximity to the nasal bone, separated by a distance of only 40 mm (a distance much smaller than in modern rhinos). The rostrum would have appeared pointed in life and, safe for the lack of a nasal septum, resembled the Pleistocene Coelodonta antiquitatis. The orbits are located about mid-length of the skull, a fair distance from the nasal horn with prominent orbital rims and the zygomatic arch is slender.[1]
While postcranial material was found at the same locality, most of it was rendered hard to identify due to poor preservation and the presence of other species of similarly sized rhinos in the area. However, two specimens representing metapodials, Mc II FSC-Sk-45 and a Mt II FSC-Sk 53, are much straighter and more slender than those of Dicerotini and have subsequently been referred to the elasmotheriine Eoazara.[1]
Eoazara can by differentiated from "Hispanotherium" tungurense by the shallower nasal notch and broader nasal, from Iranotherium through its shorter face, Parelasmotherium via its more anterior orbits, less anterior dental row and larger premaxillae and from Ningxiatherium in its smaller size, complete lack of a nasal septum, longer nasals, more anterior orbits and the molars.[1]
Phylogeny
A section of the majority rule consensus tree of the 16 most parsimonious trees recovered by Geraads & Zouhri can be seen below, focusing on Elasmotheriinae as recovered by the study.[1]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Noticeably, the study presents a monophyletic Elasmotheriinae, with Eoazara being nested deep within the subfamily between Iranotherium and the clade formed by Parelasmotherium, Ningxiatherium and Elasmotherium, while all other African elasmotheriines occupy more basal positions within the phylogenetic tree. The four extant genera of rhinos, alongside Coelodonta, form a sister clade to the Elasmotheriinae.[1]
Paleobiology
The dentition of Eoazara suggests that the animal may have been a grazer while the metapodials suggest a cursorial lifestyle. This denotes that Eoazara likely inhabited wide, open country where it fed mostly on various grasses. This lifestyle would be consistent with the other fauna found near Skoura, which includes giraffes, ostriches, horses such as Hippotherium, antelopes (such as Prostrepsiceros and Skouraia) and the elephantoid Tetralophodon, all fitting of a savannah-like environment. Carnivores are represented through felids and crocodiles.[1]
References
Wikidata ☰ Q108941291 entry
 |

