Biology:Epicanthic fold
| Epicanthic fold | |
|---|---|
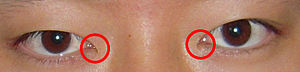
 A Korean girl with the skin fold of the upper eyelid covering the inner angle of the eye | |
| Details | |
| Synonyms | Epicanthal fold, epicanthus, eye fold,[2] Mongoloid fold,[3] palpebronasal fold[4] |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | plica palpebronasalis[1] |
| Anatomical terminology | |
An epicanthic fold or epicanthus[5] is a skin fold of the upper eyelid that covers the inner corner (medial canthus) of the eye.[3] However, variation occurs in the nature of this feature and the possession of "partial epicanthic folds" or "slight epicanthic folds" is noted in the relevant literature.[6][7][8] Various factors influence whether epicanthic folds form, including ancestry, age, and certain medical conditions.
Etymology
Epicanthus means 'above the canthus', with epi-canthus being the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek ἐπί κανθός: 'corner of the eye'.
Classification
Variation in the shape of the epicanthic fold has led to four types being recognised:
- Epicanthus supraciliaris runs from the brow, curving downwards towards the lachrymal sac.
- Epicanthus palpebralis begins above the upper tarsus and extends to the inferior orbital rim.
- Epicanthus tarsalis originates at the upper eyelid crease and merges into the skin near the medial canthus. This is the type most often found in East Asians.
- Epicanthus inversus runs from the lower eyelid skin over the medial canthus and extends to the upper lid.[9]
Ethnogeographic distribution
High-frequency populations
The highest frequency of occurrence of epicanthic folds is found in specific populations or ethnicities: East Asians, Southeast Asians, Central Asians, North Asians, Polynesians, Micronesians, Indigenous peoples of the Americas, and some African peoples (especially among Khoisan and Nilotic peoples). Among South Asians, they occur at very high frequencies among the Nepalis, Bhutanese,[10][better source needed] Northeast Indians,[10] Kirati people and certain Adivasi[10] tribes of Eastern and Southern India. It is also commonly found in Northern India, especially in Kashmir. The Hazara people in Afghanistan and Pakistan commonly have this trait. Some people in Eastern/Northern Pakistan have this trait.
In some of these populations the trait is almost universal, specifically in East Asians and Southeast Asians, where a majority, up to 90% in some estimations, of adults have this feature.[11]
Lower-frequency populations
Epicanthic folds also occur, at a considerably lower frequency, in other populations: Europeans (e.g., Scandinavians, English, Irish,[12] Hungarians, Russians, Poles, Lithuanians, Latvians, Finns, Estonians and Samis),[13][14] Jews, South Asians (Bengalis,[10] Sinhalese,[15] among other groups in eastern and southern South Asia),[10] Nilotes, Cushites, and Amazigh people.[16]
Perception and attribution
The degree of development of the fold between individuals varies greatly, and attribution of its presence or absence is often subjective, being to a degree relative to the occurrence of the trait within the community of the specific observer. Also, its frequency varies clinally across Eurasia. Its use, therefore, as a phenotypic marker to define biological populations is debatable.[8]
Possible evolutionary function
The epicanthic fold is often associated with greater levels of fat deposition around the eyeball. The adipose tissue is thought to provide greater insulation for the eye and sinuses from the effects of cold, especially from freezing winds, and to represent an adaptation to cold climates. It has also been postulated that the fold itself may provide a level of protection from snow blindness. Though its appearance in peoples of Southeast Asia can be linked to possible descent from cold-adapted ancestors, its occurrence in various African peoples is not open to this explanation. The epicanthic fold found in many African people has been tentatively linked to protection for the eye from the high levels of ultraviolet light found in desert and semi-desert areas.[17]
The exact evolutionary function and origin of epicanthic folds remains unknown. Scientific explanations include either random variation and selection (presumably sexual selection), or possible adaption to desert environment and/or high levels of ultraviolet light found in high-altitude environments, such as the Himalayas.
Dr. Frank Poirier, a physical anthropologist at Ohio State University, said that the epicanthic fold among Asian people is often explained as part of an adaptation to severe cold or tropical environments, however he suggests that neither of these explanations are sufficient to explain its presence in East and Southeast Asia, and notes that the fold can also be observed in Irish and African people. He attributes the epicanthic fold to pleiotrophic genes that control for more than one characteristic or function. He also did not offer an explanation for the origin of epicanthic folds.[18]
Other factors
Age
Many fetuses lose their epicanthic folds after three to six months of gestation.[19] Epicanthic folds may be visible in the development stages of young children of any ethnicity, especially before the nose bridge fully develops.[20]
Medical conditions
Epicanthic fold prevalence can sometimes be found as a sign of congenital abnormality, such as in Zellweger syndrome[21] and Noonan syndrome. Medical conditions that cause the nasal bridge not to develop and project are also associated with epicanthic fold. About 60% of individuals with Down syndrome (also known as trisomy 21) have prominent epicanthic folds.[22][23] In 1862, John Langdon Down classified what is now called Down syndrome. He used the term mongoloid for the condition. This was derived from then-prevailing ethnic theory[24] and from his perception that children with Down syndrome shared physical facial similarities (epicanthic folds) with those of Blumenbach's Mongolian race. While the term "mongoloid" (also "mongol" or "mongoloid idiot") continued to be used until the early 1970s, it is now considered pejorative and inaccurate and is no longer in common use since the 1970s about such medical conditions.[25] Other examples are fetal alcohol syndrome, phenylketonuria, and Turner syndrome.[26]
See also
- Blepharitis
- Epicanthoplasty, the surgical modification of epicanthic folds
- Human physical appearance
References
- ↑ "AllRefer Health – Epicanthal Folds (Plica Palpebronasalis)". AllRefer.com. http://health.allrefer.com/health/epicanthal-folds-info.html.
- ↑ "Eye fold". http://www.thefreedictionary.com/eyefold.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Das, Ram Narayan (1997). Sterling Dictionary of Anthropology. Sterling. ISBN 9788173590689. https://books.google.com/books?id=AkH911DbJf4C.
- ↑ "Palpebronasal Fold - Medical Dictionary Search". Palpebronasal Fold - Medical Dictionary Search. 2006. http://www.medilexicon.com/medicaldictionary.php?s=palpebronasal+fold. Retrieved 1 October 2009.
- ↑ "Epicanthus | definition of epicanthus by Medical dictionary". https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/epicanthus.
- ↑ Powell, M. L. (1981) Assessment and management of developmental changes and problems in children, Mosby, Incorporated, p. 38 ISBN:9780801615207
- ↑ U. Schilbach, U. and Rott, H-D. (1988) Ocular Hypotelorism, Submucosal Cleft Palate, and Hypospadias: A New Autosomal Dominant Syndrome, American Journal of Medical Genetics 31, pp. 863–870
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Lang, Berel, ed (2000). Race and Racism in Theory and Practice. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 10. ISBN 9780847696932. https://books.google.com/books?id=VOtU0FzgFPUC&pg=PA10.
- ↑ Nguyen, M.Q., Hsu, P.W. and Dinh, T.A. (2009) Asian Blepharoplasty, Semin Plast Surg. 2009 Aug; 23(3), pp. 185–197 doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1224798, p. 189
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 Coon, Carleton Stevens; Hunt, Edward E. (21 April 1966). "The Living Races of Man". Cape. https://books.google.com/books?id=qepKAAAAYAAJ.
- ↑ Lee, Yoonho; Lee, Euitae; Park, Won Jin (2000). "Anchor Epicanthoplasty Combined with OutFold Type Double Eyelidplasty for Asians: Do We Have to Make an Additional Scar to Correct the Asian Epicanthal Fold?". Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 105 (5): 1866-70; discussion 1871. doi:10.1097/00006534-200004050-00040. PMID 10809118. https://journals.lww.com/plasreconsurg/Abstract/2000/04050/Anchor_Epicanthoplasty_Combined_with_OutFold_Type.40.aspx.

- ↑ "Q&A". The New York Times. 8 October 1985. ISSN 0362-4331. https://www.nytimes.com/1985/10/08/science/q-a-061233.html.
- ↑ "epicanthic fold (anatomy)". Encyclopædia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/189688/epicanthic-fold. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
- ↑ Montagu, A. (1989). Growing Young (2nd ed.). Granby, Mass: Bergin & Garvey. ISBN 978-0-89789-166-0.
- ↑ Angel, J. Lawrence (1963). "The Physical Anthropology of Ceylon. Howard W. Stoudt.". American Anthropologist 65 (3): 694–695. doi:10.1525/aa.1963.65.3.02a00260.
- ↑ Hassan, M. M. (September 1962). "Mongolism in Sudanese children". Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 8 (2): 48–50. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.tropej.a057626. PMID 13905256.
- ↑ Lang, Berel, ed (2000). Race and Racism in Theory and Practice. Rowman & Littlefield. pp. 10–11. ISBN 9780847696932. https://books.google.com/books?id=VOtU0FzgFPUC&pg=PA10.
- ↑ "ORIGIN OF SHAPE OF ASIAN EYES IS STILL A MYSTERY TO SCIENTISTS". Chicago Tribune. https://www.chicagotribune.com/news/ct-xpm-1985-10-13-8503100141-story.html. "Dr. Frank Poirier, a physical anthropologist at Ohio State University, says the classical explanation of epicanthic fold depicts it as an adaptation to the tropical and arctic regions where many Asians live. The fold is described as a sun visor protecting the eyes from overexposure to ultraviolet radiation or as a blanket insulating them from the cold. According to Poirier, the problem with this theory is that a substantial portion of the Asian population evolved in areas outside of the tropical and arctic regions. In addition, he says epicanthic fold is not limited to Asians. John F. Kennedy had a variance of the fold and it is found among Europeans, especially the Irish, he said. It`s just less prevalent. The fold is also found among infants worldwide. Poirier attributes the fold to pleiotropic genes--single genes that control more than one characteristic or function--but he has no explanation for its origin."
- ↑ Park JI (1 January 2000). "Modified Z-Epicanthoplasty in the Asian Eyelid". Archives of Facial Plastic Surgery 2 (1): 43–47. doi:10.1001/archfaci.2.1.43. ISSN 1521-2491. PMID 10925423. http://archfaci.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=479760.
- ↑ "Epicanthal folds". U.S National Library of Medicine. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003030.htm.
- ↑ Kalyanasundaram, S. et al. (2010). "Peroxisomal Disorder-Unusual Presentation as Failure to Thrive in Early Infancy". Indian Journal of Pediatrics 77 (10): 1151–1152. doi:10.1007/s12098-010-0199-6. PMID 20872098.
- ↑ Hammer, Gary, D.; McPhee, Stephen J. (2010). "Pathophysiology of Selected Genetic Diseases". Pathophysiology of Disease: An Introduction to Clinical Medicine (6 ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. ISBN 978-0-07-162167-0.
- ↑ Pham, V. (2010). COMMON OTOLARYNGOLOGICAL CONGENITAL ABNORMALITIES. UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology. [1]
- ↑ Conor, WO (1999). "John Langdon Down: The Man and the Message". Down Syndrome Research and Practice 6 (1): 19–24. doi:10.3104/perspectives.94. PMID 10890244.
- ↑ Howard-Jones, Norman (1979). "On the diagnostic term "Down's disease"". Medical History 23 (1): 102–04. doi:10.1017/s0025727300051048. PMID 153994.
- ↑ Kaneshiro, Neil K.; Zieve, David; Ogilvie, Isla. "Epicanthal folds". MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003030.htm.
External links
 |