Biology:Eremophila dendritica
| Eremophila dendritica | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Scrophulariaceae |
| Genus: | Eremophila |
| Species: | E. dendritica
|
| Binomial name | |
| Eremophila dendritica Chinnock[1]
| |
Eremophila dendritica is a flowering plant in the figwort family, Scrophulariaceae and is endemic to the south of Australia . It is a low, shrub with many tangled branches. Its branches, leaves and flowers are densely covered with hairs giving them a felty texture.
Description
Eremophila dendritica is a small shrub with many tangled branches growing to a height of 0.3–0.5 m (1–2 ft). The branches are covered with a layer of white to yellowish branched hairs. The leaves are arranged in pairs, are almost circular, covered with a dense layer of hairs giving them a felty texture and are mostly 4.5–8.5 mm (0.2–0.3 in) in diameter.[2][3]
The flowers are borne singly in leaf axils and lack a stalk. There are 5 linear to lance-shaped sepals which are densely hairy on both surfaces and 4.5–7.5 mm (0.2–0.3 in) long. The petals are 17–26 mm (0.7–1 in) long and joined at their lower end to form a tube. The petal tube is lilac-coloured on the outside and white with faint spots on the inside. The inside and outside of the tube are both hairy, except for the inner surface of the petal lobes which is glabrous. The 4 stamens are fully enclosed in the petal tube. Flowering occurs from June to September and is followed by fruits which are woolly, oval-shaped and 4.5–7 mm (0.2–0.3 in) long.[2][3]
Taxonomy and naming
The species was first formally described by Robert Chinnock in 2007 and the description was published in Eremophila and Allied Genera: A Monograph of the Plant Family Myoporaceae. The type specimen was collected by Chinnock 2 kilometres (1 mi) south of Rawlinna.[4][2] The specific epithet (dendritica) is a Latin word meaning "tree-like" referring to the branched hairs on the leaves.[2]
Distribution and habitat
This eremophila has been recorded from near Commonwealth Hill Station in South Australia and from Rawlinna to the Plumridge Lakes area in Western Australia.[2] It grows in brown clay soils, sometimes in scattered bluebush shrubland.[2][3]
Conservation status
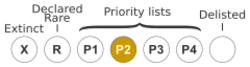
Eremophila dendritica is classified as "Priority Two" by the Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife[5] meaning that is poorly known and from only one or a few locations.[6]
Use in horticulture
The woolly leaves and massed flowers of this eremophila make it useful as a contrast with other small shrubs. It is only known to have been propagated by grafting onto Myoporum species and in this case will grow in most soils. It grows best in full sun, requires little watering in droughts and is only slightly damaged by frosts when young.[7]
References
- ↑ "Eremophila dendritica". Australian Plant Census. https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/apc-format/display/208294. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Chinnock, R.J. (Bob) (2007). Eremophila and allied genera : a monograph of the plant family Myoporaceae (1st ed.). Dural, NSW: Rosenberg. pp. 207–209. ISBN 9781877058165.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Brown, Andrew; Buirchell, Bevan (2011). A field guide to the eremophilas of Western Australia (1st ed.). Hamilton Hill, W.A.: Simon Nevill Publications. p. 79. ISBN 9780980348156.
- ↑ "Eremophila dendritica". APNI. http://id.biodiversity.org.au/name/apni/208294. Retrieved 9 January 2016.
- ↑ "Eremophila dendritica". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/browse/profile/17588.
- ↑ "Conservation codes for Western Australian Flora and Fauna". Government of Western Australia Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://www.dpaw.wa.gov.au/images/documents/plants-animals/threatened-species/Listings/Conservation%20code%20definitions.pdf. Retrieved 9 January 2016.
- ↑ Boschen, Norma; Goods, Maree; Wait, Russell (2008). Australia's eremophilas : changing gardens for a changing climate. Melbourne: Bloomings Books. pp. 196–197. ISBN 9781876473655.
Wikidata ☰ Q15593471 entry
 |