Biology:Eunectes deschauenseei
| Eunectes deschauenseei | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Boidae |
| Genus: | Eunectes |
| Species: | E. deschauenseei
|
| Binomial name | |
| Eunectes deschauenseei | |
| |
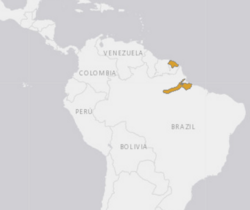
| Dark spotted anaconda natural range | |
Eunectes deschauenseei is a boa species endemic to northeastern South America. No subspecies are currently recognized.[2] Like all boas, it is a non-venomous constrictor.
Taxonomy
The specific name, deschauenseei, is in honor of American ornithologist Rodolphe Meyer de Schauensee,[4] who donated a specimen to the Philadelphia Zoo in 1924.[2] The type locality given is "probably collected on the island of Marajo at the mouth of the Amazon".[5]
Distribution and habitat
Eunectes deschauenseei is found in South America, in north Brazil (Pará and Amapá states) and French Guiana.[1][2] E. deschauenseei is a semi-aquatic species usually found in swampy, seasonally flooded freshwater areas at elevations below 300 m (980 ft).[1]
Description
Adult males measure 130–211 cm (51–83 in) and adult females 120–231 cm (47–91 in) in snout–vent length.[6]
Reproduction
Vitellogenesis in E. deschauenseei probably occurs from autumn to spring (May to December). Gestation may last as long as nine months. Litter size among five gravid females ranged from 3 to 27 (mean 10.6). Newborns measure 29–53 cm (11–21 in) in snout–vent length.[6]
Conservation
The savanna habitat of E. deschauenseei is highly threatened by agricultural expansion, but the threat posed on this species is not known.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Dirksen, Lutz (2010). "Eunectes deschauenseei". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2010: e.T176262A7207195. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-4.RLTS.T176262A7207195.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/176262/7207195.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Eunectes deschauenseei at the Reptarium.cz Reptile Database. Accessed 10 September 2018.
- ↑ Amazon Anaconda, http://www.markoshea.tv/series1/series01-11.html, retrieved 1 December 2008
- ↑ Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 70. ISBN 978-1-4214-0135-5.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedMcD99 - ↑ 6.0 6.1 Pizzatto, Lígia; Marques, Otavio A. V. (2007). "Reproductive ecology of Boinae snakes with emphasis on Brazilian species and a comparison to pythons". South American Journal of Herpetology 2 (2): 107–122. doi:10.2994/1808-9798(2007)2[107:reobsw2.0.co;2].
Further reading
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Eunectes deschauenseei. |
- Dirksen, Lutz; Henderson, Robert W. (2002). Eunectes deschauenseei. Catalogue of American Amphibians and Reptiles. pp. 755.1–755.2. http://hdl.handle.net/2152/44652.
- Dirksen, Lutz (2002) (in German). Anakondas. Monographische Revision der Gattung Eunectes (Wagler, 1830). Münster: Natur und Tier-Verlag. ISBN 3-931587-43-6.
- Dirksen, Lutz (2002). "Zur Kenntnis der Anakonda-Arten (Serpentes: Boidae: Eunectes ). I. Eunectes deschauenseei Dunn & Conant, 1936" (in German). Herpetofauna (Weinstadt) 21 (122): 12–21.
- Dunn, Emmett R.; Conant, Roger (1936). "Notes on Anacondas, with Descriptions of Two New Species". Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia 88: 503–506. (Eunectes deschauenseei, new species).
Wikidata ☰ Q902884 entry