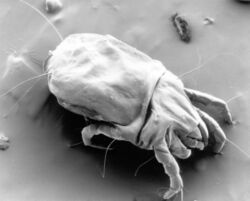
Biology:House dust mite
House dust mites (HDM, or simply dust mites) are various species of acariform mites belonging to the family Pyroglyphidae that are found in association with dust in dwellings.[3] They are known for causing allergies.
Biology
Species
The currently known species are:[4]
- Dermatophagoides farinae (American house dust mite)
- Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (European house dust mite)
- Dermatophagoides evansi
- Dermatophagoides microceras
- Dermatophagoides halterophilus
- Dermatophagoides siboney
- Dermatophagoides neotropicalis
- Dermatophagoides alexfaini
- Dermatophagoides anisopoda
- Dermatophagoides chirovi
- Dermatophagoides deanei
- Dermatophagoides rwandae
- Dermatophagoides scheremeteroskyi
- Dermatophagoides scheremetewskyi
- Dermatophagoides simplex
- Euroglyphus maynei (Mayne's house dust mite)
- Euroglyphus longior
- Hirstia domicola
- Malayoglyphus carmelitus
- Malayoglyphus intermedius
- Pyroglyphus africanus
- Sturnophagoides brasiliensis
- Blomia tropicalis
Taxonomy
The dust mites are cosmopolitan members of the mite family Pyroglyphidae.
Characteristics
House dust mites, due to their very small size and translucent bodies, are barely visible to the unaided eye.[5] A typical house dust mite measures 0.2–0.3 mm in length.[6] The body of the house dust mite has a striated cuticle.
House dust mite faecal pellets range from 10 to 40 µm.[1]
Diet
They feed on skin flakes from humans and other animals, and on some mold. Dermatophagoides farinae fungal food choices in 16 tested species commonly found in homes was observed in vitro to be Alternaria alternata, Cladosporium sphaerospermum, and Wallemia sebi, and they disliked Penicillium chrysogenum, Aspergillus versicolor, and Stachybotrys chartarum.[7]
Predators
The predators of dust mites are other allergenic mites (Cheyletiella), silverfish and pseudoscorpions.[8]
Reproduction
The average life cycle for a house dust mite is 65–100 days.[9] A mated female house dust mite can live up to 70 days, laying 60 to 100 eggs in the last five weeks of her life. In a 10-week life span, a house dust mite will produce approximately 2,000 fecal particles and an even larger number of partially digested enzyme-covered dust particles.
Distribution
Dust mites are found worldwide, but are more common in humid regions.[10] The species Blomia tropicalis is typically found only in tropical or subtropical regions.[11] Detectable dust mite allergen was found in the beds of about 84% of surveyed United States homes.[12] In Europe, detectable Der p 1 or Der f 1 allergen was found in 68% of surveyed homes.[13]
Health issues
Asthma
House dust mite antigens are strongly associated with asthma development and severity; they are estimated to contribute to 60-90% of cases. [14]
Allergies
Tropomyosin, the major allergen in dust mites, is also responsible for shellfish allergy.[15][16]
Oral mite anaphylaxis
Dermatophagoides spp. can cause oral mite anaphylaxis (AKA pancake syndrome) when found in flour.[17][18]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "House dust mite excrements/ faeces HDM excrements". 1 October 2018. https://www.citeqbiologics.com/house-dust-mite-excrements/.
- ↑ "Best Fabrics to Exclude Dust Mites". HouseDustMite.com. http://housedustmite.com/best-fabrics-to-exclude-dust-mites.
- ↑ Denmark, H. A.; Cromroy, H. L. (April 2017). "House dust mites—Dermatophagoides spp.". Featured Creatures. Department of Entomology & Nemotology, University of Florida, and Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services, Division of Plant Industry. http://entnemdept.ufl.edu/creatures/urban/house_dust_mite.htm. Originally published as DPI Entomology Circular 314.
- ↑ "House Dust Mites: Ecology, Biology, Prevalence, Epidemiology and Elimination". https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341258506.
- ↑ "Why study the major cause of allergy, the house dust mite?". HouseDustMite.com. http://housedustmite.com/why-study-the-mite/.
- ↑ "The House Dust Mite: Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus". MicrobiologyBytes. 2007. http://www.microbiologybytes.com/video/mite.html.. Note that the video is gone.
- ↑ Naegele, Alexandre; Reboux, Gabriel; Scherer, Emeline; Roussel, Sandrine; Millon, Laurence (1 April 2013). "Fungal food choices of Dermatophagoides farinae affect indoor fungi selection and dispersal". International Journal of Environmental Health Research 23 (2): 91–95. doi:10.1080/09603123.2012.699029. ISSN 0960-3123. PMID 22774849.
- ↑ "House dust mites: Agents of allergy". acari.be. http://www.acari.be/uk/pest_a.php.
- ↑ Miller, J. D. (23 June 2018). "The Role of Dust Mites in Allergy". Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 57 (3): 312–329. doi:10.1007/s12016-018-8693-0. ISSN 1559-0267. PMID 29936683.
- ↑ Madden, Anne A.; Barberán, Albert; Bertone, Matthew A.; Menninger, Holly L.; Dunn, Robert R.; Fierer, Noah (2016). "The diversity of arthropods in homes across the United States as determined by environmental DNA analyses" (in en). Molecular Ecology 25 (24): 6214–6224. doi:10.1111/mec.13900. ISSN 1365-294X. PMID 27801965.
- Jennifer Frazer (February 16, 2017). "Why Do Dust Mites Seem to Shun the Western U.S.?". Scientific American. https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/artful-amoeba/why-do-dust-mites-seem-to-shun-the-western-u-s/.
- ↑ Dutra, Moisés S; Roncada, Cristian; da Silva, Guilherme L; Ferla, Noeli J; Pitrez, Paulo M (2018-05-04). "Mite Fauna Assessment in Houses of Two distinct Socioeconomic Groups From Southern Brazil" (in en). Journal of Medical Entomology 55 (3): 620–625. doi:10.1093/jme/tjx239. ISSN 0022-2585. PMID 29281052.
- ↑ Arbes, Samuel J.; Cohn, Richard D.; Yin, Ming; Muilenberg, Michael L.; Burge, Harriet A.; Friedman, Warren; Zeldin, Darryl C. (2003-02-01). "House dust mite allergen in US beds: Results from the first national survey of lead and allergens in housing" (in en). Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 111 (2): 408–414. doi:10.1067/mai.2003.16. PMID 12589364.
- ↑ Luczynska, Christina; Svanes, Cecilie; Dahlman-Hoglund, Anna; Ponzio, Michela; Villani, Simona; Soon, Argo; Olivieri, Mario; Chinn, Susan et al. (2006-09-01). "Distribution and determinants of house dust mite allergens in Europe: The European Community Respiratory Health Survey II" (in en). Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 118 (3): 682–690. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2006.04.060. ISSN 0091-6749. PMID 16950288. https://www.jacionline.org/article/S0091-6749(06)01363-7/abstract.
- ↑ "Dust Mites". https://www.lung.org/clean-air/at-home/indoor-air-pollutants/dust-mites.
- ↑ "Allergens and molecular diagnostics of shellfish allergy: Part 22 of the Series Molecular Allergology". Allergo J Int 25 (7): 210–18. November 2016. doi:10.1007/s40629-016-0124-2. PMID 28239537.
- ↑ "Seafood Allergy, Toxicity, and Intolerance: A Review". J Am Coll Nutr 35 (3): 271–83. August 2016. doi:10.1080/07315724.2015.1014120. PMID 26252073.
- ↑ Barrera, OM; Murgas, IL; Bermúdez, S; Miranda, RJ (June 2015). "[Oral anaphylaxis by ingestion of mite contaminated food in Panama City, 2011-2014]". Revista Alergia Mexico 62 (2): 112–7. doi:10.29262/ram.v62i2.71. PMID 25958374.
- ↑ Sánchez-Borges, Mario; Suárez-Chacon, Raúl; Capriles-Hulett, Arnaldo; Caballero-Fonseca, Fernan; Iraola, Victor; Fernández-Caldas, Enrique (1 January 2009). "Pancake Syndrome (Oral Mite Anaphylaxis)". World Allergy Organization Journal 2 (5): 91–6. doi:10.1186/1939-4551-2-5-91. ISSN 1939-4551. PMID 23283016.
External links
- Dust Mite Allergy on the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America website
 |