Biology:FtsZ-DE RNA motif
| ftsZ-DE | |
|---|---|
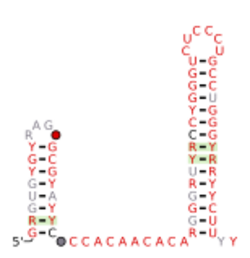 Consensus secondary structure and sequence conservation of ftsZ-DE RNA | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | ftsZ-DE |
| Rfam | RF02985 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene; sRNA |
| SO | 0001263 |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
The ftsZ-DE RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics.[1] ftsZ-DE motifs are found in bacteria belonging to the genus Fibrobacter.
It is ambiguous whether ftsZ-DE RNAs function as cis-regulatory elements or whether they operate in trans as small RNAs. ftsZ-DE RNAs are consistently located immediately downstream of predicted operons, one of whose genes is predicted as ftsZ. ftsZ genes encode a GTPase that is involved in cell division. This genomic arrangement could suggest that ftsZ-DE RNAs function as cis-regulatory elements as part of the 3' untranslated regions of these operons. However, these locations rarely contain cis-regulatory RNAs in bacteria. Another possibility that was proposed[1] is that ftsZ-DE RNAs represent an unusual form of Rho-independent transcription terminators that are specific to the under-studied phylum Fibrobacterota, to which Fibrobacter belongs. However, the ftsZ-DE motif exhibits some features that are not found in many Rho-independent terminators, especially that it consists of two hairpins. The function of ftsZ-DE RNAs has not, as of 2018, been established.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Detection of 224 candidate structured RNAs by comparative analysis of specific subsets of intergenic regions". Nucleic Acids Res. 45 (18): 10811–10823. October 2017. doi:10.1093/nar/gkx699. PMID 28977401.
 |

