Biology:Funiculus (neuroanatomy)
From HandWiki
| Funiculus | |
|---|---|
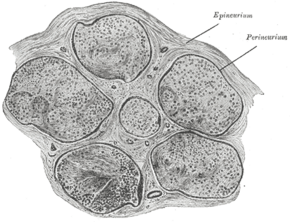 Transverse section of human tibial nerve. | |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy |
A funiculus or column [1] is a small bundle of axons (nerve fibres), enclosed by the perineurium. A small nerve may consist of a single funiculus, but a larger nerve will have several funiculi collected together into larger bundles known as fascicles. Fascicles are bound together in a common membrane, the epineurium.[2][3]
Funiculi in the spinal cord are portions of white matter.[4] Examples include:
- Anterior funiculus of the spinal cord
- Lateral funiculus of the spinal cord
- Posterior funiculus of the spinal cord
- Funiculus separans of the rhomboid fossa
References
- ↑ "Ascending and descending tracts of the spinal cord" (in en). https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/ascending-and-descending-tracts-of-the-spinal-cord.
- ↑ Gray, Henry; Lewis, Warren Harmon (1918). Anatomy of the human body. Harold B. Lee Library. Philadelphia : Lea & Febiger. https://archive.org/details/anatomyofhumanbo1918gray.
- ↑ Siegel, A. & Sapru, H. (2011). Essential neuroscience. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- ↑ "Spinal Cord White Matter". http://vanat.cvm.umn.edu/neurLab2/SpCdWhite.html.
 |
