Biology:Geosaurinae
| Geosaurines | |
|---|---|

| |
| Dakosaurus maximus skull, Staatliches Museum für Naturkunde Stuttgart | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Missing taxonomy template (fix): | Archosauria/Reptilia |
| Clade: | Pseudosuchia |
| Clade: | Crocodylomorpha |
| Clade: | Crocodyliformes |
| Suborder: | †Thalattosuchia |
| Family: | †Metriorhynchidae |
| Subfamily: | †Geosaurinae Lydekker, 1889 |
| Genera | |
| |
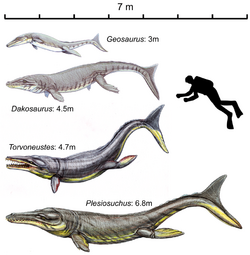
Geosaurinae is a subfamily of metriorhynchid crocodyliforms from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous (Bathonian - Aptian) of Europe, North America and South America.[1][2][3] Named by Richard Lydekker, in 1889, it contains the metriorhynchids Suchodus, Purranisaurus, Neptunidraco, Tyrannoneustes, Torvoneustes, Dakosaurus, Geosaurus and Plesiosuchus. The last four taxa form a tribe within Geosaurinae, the Geosaurini. Geosaurinae is one of two subfamilies of Metriorhynchidae, the other being Metriorhynchinae.[4]
These marine reptiles were widespread during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous, their fossilized remains are being frequently found on various places around the world.[5]
Phylogeny
Geosaurinae is a stem-based taxon defined in 2009 as the most inclusive clade consisting of Geosaurus giganteus, but not Metriorhynchus geoffroyii.[1] Geosaurini was named by Lydekker in 1889, and it is a node-based taxon defined by Andrea Cau and Federico Fanti in 2011 as the least inclusive clade consisting of Geosaurus giganteus, Dakosaurus maximus and Torvoneustes carpenteri. The cladogram below follows the topology from a 2020 analysis by Young et al.[6]
| Geosaurinae |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Mark T. Young; Marco Brandalise de Andrade (2009). "What is Geosaurus? Redescription of Geosaurus giganteus (Thalattosuchia: Metriorhynchidae) from the Upper Jurassic of Bayern, Germany". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 157 (3): 551–585. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2009.00536.x. https://zenodo.org/records/5443313/files/source.pdf.
- ↑ Mark T. Young; Stephen L. Brusatte; Marcello Ruta; Marco Brandalise de Andrade (2010). "The evolution of Metriorhynchoidea (Mesoeucrocodylia, Thalattosuchia): an integrated approach using geometrics morphometrics, analysis of disparity and biomechanics". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 158 (4): 801–859. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2009.00571.x.
- ↑ "The youngest record of metriorhynchid crocodylomorphs, with implications for the extinction of Thalattosuchia". Cretaceous Research 56: 608–616. 2015. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2015.07.001.
- ↑ Andrea Cau; Federico Fanti (2011). "The oldest known metriorhynchid crocodylian from the Middle Jurassic of North-eastern Italy: Neptunidraco ammoniticus gen. et sp. nov.". Gondwana Research 19 (2): 550–565. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2010.07.007. Bibcode: 2011GondR..19..550C.
- ↑ Daniel Madzia, Sven Sachs, Mark T. Young, Alexander Lukeneder and Petr Skupien (2021). Evidence of two lineages of metriorhynchid crocodylomorphs in the Lower Cretaceous of the Czech Republic. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. doi: https://doi.org/10.4202/app.00801.2020
- ↑ "Convergent evolution and possible constraint in the posterodorsal retraction of the external nares in pelagic crocodylomorphs". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 189 (2): 494–520. 2020. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlaa021.
Wikidata ☰ Q5548520 entry
 |