Biology:Isocitrate epimerase
| Isocitrate epimerase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 5.1.2.6 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 81210-68-6 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
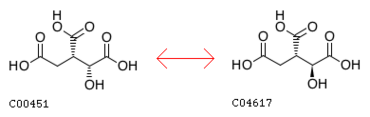
In enzymology, an isocitrate epimerase is classified as follows: EC 5.1.2.6. This number indicates that it is an isomerase, specifically a racemase or epimerase that acts on hydroxy acids and their derivatives, namely isocitrate.[1] Isocitrate epimerase specifically catalyzes the reversible reaction:[2]
- (1R,2S)-1-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate ↔ (1S,2S)-1-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
which can also be described as
- D-threo-isocitrate ↔ D-erythro-isocitrate
History
Isocitrate epimerase was originally isolated from the fungal cell-free extract of Penicillium purpurogenum [3], where it was discovered due to the excess accumulation of L-alloisocitric acid (D-erythro-isocitrate)—a diastereomer of isocitrate previously not seen in nature. In order to accumulate L-alloisocitric acid as a fermentation product, P. purpurogenum needed to be grown on citrate supplemented nutrient agar.[3][4] During this fermentation it was found that the fermentation yield of L-alloisocitric acid was capable of “exceeding 70% without producing any other stereoisomers of isocitiric acid or other metabolites”.[3]
This enzyme has not been heavily studied since first being identified in 1982, as a result of this there is presently not a crystal structure or active site description for isocitrate epimerase. Other isocitrate enzymes, such as isocitrate lyase and isocitrate dehydrogenase have been studied more closely due to their key roles in glycolysis and the TCA cycle.
References
- ↑ "BRENDA - Information on EC 5.1.2.6 - isocitrate epimerase". https://www.brenda-enzymes.org/enzyme.php?ecno=5.1.2.6.
- ↑ "KEGG REACTION: R02318". https://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?rn:R02318.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Mechanism of L-Alloisocitric Acid Fermentation: Isocitrate Epimerase Activity in the Cell-free Extract of Penicillium purpurogenum" (in en). Agricultural and Biological Chemistry 46 (1): 143–151. January 1982. doi:10.1080/00021369.1982.10865025. ISSN 0002-1369. https://academic.oup.com/bbb/article/46/1/143-151/5969606.
- ↑ "Accumulation of allo-isocitric acid by a Penicillium strain". The Journal of General and Applied Microbiology 50 (6): 345–352. December 2004. PMID 15965889. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15965889/.
 |

