Biology:Japanese pygmy seahorse
| Japanese pygmy seahorse | |
|---|---|
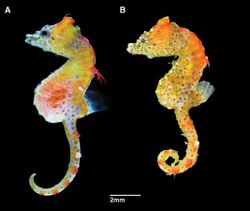
| |
| A is the male; B is the female. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Syngnathiformes |
| Family: | Syngnathidae |
| Genus: | Hippocampus |
| Species: | H. japapigu
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hippocampus japapigu Short, R. Smith, Motomura, Harasti & H. Hamilton, 2018
| |
The Japanese pygmy seahorse (Hippocampus japapigu) is a Japanese species of seahorse in the family Syngnathidae.[2] It is also sometimes known as the Japan pig.[3]
Distribution and habitat
It lives in Northwestern Pacific near Japan , and lives at depths from 5 to 22 meters, but its usually found at 10 to 13 meters,[2] but does not live with any specific species to host, and instead clings onto algal turfs in subtropical reefs.[4]
(As of 2018), H. japapigu is only known to be found in Japan, including Kashiwa-jima Island, Sukumo Bay; Kushimoto, Kii Peninsula; Osezaki, Izu Peninsula; the Izu Islands of Miyake and Hachijo; Sagami Bay; and Chichi-jima, Ogasawara Islands.[5]:44
The type locality was collected off Imasaki, Okago, Hachijo-jima Island, Izu Islands at a depth of 10 m (33 ft).[5]:30
Description and feeding
It reaches a length of 1.6 cm, and contains 28 tail rings, 14 dorsal fin rays, 9 pectoral fin rays, and 4 subdorsal rings.[2] It is the size of a jellybean, and its coloration is made for hiding in algae-covered reefs, clinging to soft corals while feeding on plankton. It has a pair of wing-like protrusions on its neck; unlike other species, it contains only one pair instead of two, and is the only seahorse in the world known to have a bony ridge running down its back.[3]
Taxonomic history
In 2013, after completing his PhD on the biology of the Bargibant's and Denise's pygmy seahorses, Richard Smith went to a fish biology conference in Okinawa in 2013, after which he photographed the Japanese pygmy seahorse on several dives off of Hachijo-jima, one of the Izu Islands about 180 miles from Tokyo. There he found about a dozen specimens.[6]
The species description was published by Short and colleagues in a 2018 issue of ZooKeys; it was based on one female holotype, a male and a female paratype, and two photographs of additional specimens. The holotype and one paratype were deposited at the Burke Museum at the University of Washington; the other paratype was deposited at the Kagoshima University Museum.[5]:30
Short and colleagues proposed Japanese pygmy seahorse as the English and Japanese common names for the species. The specific epithet comes from its colloquial Japanese name: Japan Pig or Japapigu.[5]:45
References
- ↑ "Appendices | CITES". https://cites.org/eng/app/appendices.php.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Capuli, Estelita Emily (2019). "Hippocampus japapigu". in Froese, R.; Pauly, D.. https://www.fishbase.se/summary/68763.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Jewett, Katie (2018). "Academy scientists describe 229 species in 2018" (in en). https://www.calacademy.org/press/releases/academy-scientists-describe-229-species-in-2018.
- ↑ "Japanese Pygmy Seahorse" (in en-US). 2018-08-03. http://oceanrealmimages.com/pygmy-seahorses/japapigu/.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Short, Graham; Smith, Richard; Moromura, Hiroyuki; Harasti, David; Hamilton, Healy (2018). "Hippocampus japapigu, a new species of pygmy seahorse from Japan, with a redescription of H. pontohi (Teleostei, Syngnathidae)". ZooKeys (779): 27–49. doi:10.3897/zookeys.779.24799. PMID 30166895.
- ↑ Smith, Richard (Dec 2018). "The More You See, The More You Know". Wildlife Australia 55 (4): 20–21. https://search.informit.com.au/documentSummary;dn=064773912910090;res=IELHSS.
Wikidata ☰ Q56034064 entry
 |

