Biology:Jonah’s icefish
| Jonah’s icefish | |
|---|---|
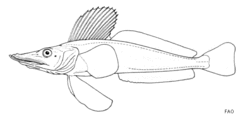
| |
| Drawing by J.C. Hureau | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Perciformes |
| Family: | Channichthyidae |
| Genus: | Neopagetopsis Nybelin, 1947 |
| Species: | N. ionah
|
| Binomial name | |
| Neopagetopsis ionah Nybelin, 1947
| |
Jonah's icefish (Neopagetopsis ionah) is a benthopelagic species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes, it is the only member of the monotypic genus Neopagetopsis. It is found in the Southern Ocean at depths of from 20 to 900 metres (66 to 2,953 ft). It has a circum-Antarctic distribution on the continental slope and continental shelf, with the northernmost records from the South Shetland and the South Orkney Islands.
Taxonomy
Jonah's icefish was first formally described in 1947 by the Swedish ichthyologist Orvar Nybelin (sv) with the type locality given as near the Balleny Islands, Ross Dependency in Antarctica.[1] It is the only species in the genus Neopagetopsis.[2] The genus name is a compound of neo which means "new" and Pagetopsis the name of a related genus which this taxon bears a resemblance to but differs by having long pelvic fins and three lateral lines. The specific name refers to the Biblical prophet Jonah and is an allusion to the type being collected from the stomach of a whale.[3]
Description
Jonah's icefish has a forward curving spine on the snout and there are 3-4 radiating ridges on the operculum each ending at its rear with a spine, none of the other opercular bones have spines. The three lateral lines do not have any bony plates. The first and second dorsal fins are continuous.The dorsal fins hold 14-15 spines and 32-35 soft rays while the anal fin contains 29-32 soft rays. The well-developed first dorsal fins and fan-shaped pelvic fins are blackish while the other fins may be dusky or blackish in color. The overall color is a dark blackish-green or black on the body, althoug the belly is whitish, however, those of juveniles may have irregular dark markings present.[4] This species attain a maximim total length of 56 cm (22 in).[2]
Distribution and habitat
Jonah's icefish is found in the Southern Ocean where it is Circum-Antarctic on the continental shelf and slope with the northernmost reports coming from the South Shetland and South Orkney Islands.[4] It is a benthopelagic species which occurs at depths between 20 and 900 m (66 and 2,953 ft).[2]
Biology
Jonah's icefishes mainly feed on fishes, such as Dacodraco hunteri, Chaenodraco wilsoni, Pleuragramma antarcticum and Chionodraco sp., as well as krill, as adults. Young specimens, however, feed mainly on krill, espacially Euphausia superba, and they are frequently caught along with their prey at 10 cm to 15 cm TL (3.9 to 5.9 inches TL). In the South Shetland Islands, both adults and juveniles show a marked preference for krill (only 3 out of 19 sampled specimens had consumed any kind of fish).[4] This species has a more complete hemoglobin gene than other species of crocodile icefish; however, it is still nonfunctional.[5]
Fisheries
Jonah's icefish of no interest to commercial fisheries.[2]
References
- ↑ Eschmeyer, William N.; Fricke, Ron; van der Laan, Richard, eds. "Species in the genus Neopagetopsis". California Academy of Sciences. http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatget.asp?tbl=species&genus=Neopagetopsis.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2006). Species of Neopagetopsis in FishBase. April 2006 version.
- ↑ Christopher Scharpf; Kenneth J. Lazara, eds (12 April 2021). "Order Perciformes: Suborder Notothenoididei: Families Bovichtidae, Pseaudaphritidae, Elegopinidae, Nototheniidae, Harpagiferidae, Artedidraconidae, Bathydraconidae, Channichthyidae and Percophidae". The ETYFish Project Fish Name Etymology Database. Christopher Scharpf and Kenneth J. Lazara. https://etyfish.org/perciformes7/.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 T. Iwami; K-H Koch (1990). "Channicthyidae Icefishes". Fishes of the Southern Ocean. South African Institute for Aquatic Biodiversity. ISBN 9780868102115. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/240475#page/403/mode/1up.
- ↑ Near, Thomas J.; Parker, Sandra K.; Detrich, H. William (2006-11-01). "A Genomic Fossil Reveals Key Steps in Hemoglobin Loss by the Antarctic Icefishes" (in en). Molecular Biology and Evolution 23 (11): 2008–2016. doi:10.1093/molbev/msl071. ISSN 0737-4038. PMID 16870682. https://academic.oup.com/mbe/article/23/11/2008/1322257.
Wikidata ☰ {{{from}}} entry

