Biology:Kanamycin nucleotidyltransferase
From HandWiki
| KNTase C-terminal domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
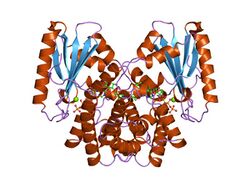 kanamycin nucleotidyltransferase | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | KNTase_C | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF07827 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0291 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR012481 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1kny / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, kanamycin nucleotidyltransferase EC 2.7.7.- (KNTase) is an enzyme which is involved in conferring resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics. It catalyses the transfer of a nucleoside monophosphate group from a nucleotide to kanamycin. This enzyme is dimeric with each subunit being composed of two domains. The C-terminal domain contains five alpha helices, four of which are organised into an up-and-down alpha helical bundle. Residues found in this domain may contribute to this enzyme's active site.[1]
References
- ↑ "Structural investigation of the antibiotic and ATP-binding sites in kanamycin nucleotidyltransferase". Biochemistry 34 (41): 13305–11. October 1995. doi:10.1021/bi00041a005. PMID 7577914.
 |

