Biology:North Island brown kiwi
| North Island brown kiwi | |
|---|---|

| |
| North Island brown kiwi (Apteryx mantelli) | |
| File:Kiwi Male North Island brown kiwi song.ogg | |
| Male song | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Infraclass: | Palaeognathae |
| Order: | Apterygiformes |
| Family: | Apterygidae |
| Genus: | Apteryx |
| Species: | A. mantelli
|
| Binomial name | |
| Apteryx mantelli Bartlett, AD, 1852[2]
| |
| |
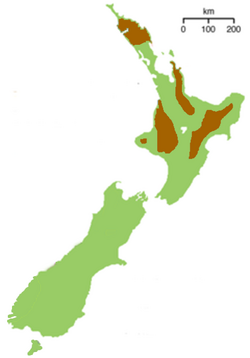
| The distribution of North Island brown kiwi | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The North Island brown kiwi (Apteryx mantelli; Apteryx australis or Apteryx bulleri[5] as before 2000, still used in some sources) is a species of kiwi that is widespread in the northern two-thirds of the North Island of New Zealand and, with about 35,000 remaining,[2] it is the most common kiwi. It holds the world record for laying the largest eggs relative to its body size.[6]
Genetics
The genome of Apteryx mantelli was sequenced in 2015.[7]
Taxonomy

Until 2000, the brown kiwi (then Apteryx australis) was thought to include the rowi and the tokoeka, in addition to the North Island brown kiwi. However using genetic codes from each of the above it was determined that the tokoeka was a separate species, it took the Apteryx australis name, leaving the brown kiwi with its current Apteryx mantelli name. Soon after, in 1998, more genetic tests were done with the rowi and it was determined that it (the rowi) was a separate species (Apteryx rowi). In 2004 an injured bird was found with streaked white around the head and identified by Massey University.[8] The white feathering is likely due to a rarely seen genetic variation sometimes described as a partial albino. Few documented cases exist with only a painting of one found in Ōtorohanga in the 18th century and a specimen in the Canterbury Museum. The injured bird recovered and was introduced into a breeding programme.
The brown kiwi was first described as Apteryx australis by Abraham Dee Bartlett, in 1813, based on a specimen from Dusky Sound, South Island, New Zealand.[9] This is a monotypic species.[10]
| Location | Population | Date | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| North Island[11] | 2500 | 2008 | Decreasing -4% yr |
| Little Barrier Island[2] | 2500 | 1996 | Stable |
| Ponui Island[2] | Stable | ||
| Kapiti Island[11] | Stable | ||
| Kawau Island[2] | Stable | ||
| Total (New Zealand) | 5000[2] | 1996 | Decreasing -2% yr[11] |
Range and habitat
Brown kiwi are found in a number of parts of the North Island, including Northland, Coromandel Peninsula, the eastern North Island, Aroha Island, Little Barrier Island, Kawau Island, Ponui Island, and the Whanganui Region. The North Island brown kiwi has demonstrated a remarkable resilience: it has adapted to live on scrub-like farm land, exotic pine plantations, and native forests, but it prefers dense sub-tropical and temperate forest.[12]
Description

Females stand about 40 cm (16 in) high and weigh about 2.8 kg (6.2 lb) the males about 2.2 kg (4.9 lb). The plumage is streaky red-brown and spiky. The North Island brown kiwi is the only species of kiwi found internationally in zoos.[citation needed]
Behaviour
These kiwi, like all kiwi, feed on invertebrates. They have 2-3 clutches a year with 2 eggs in each clutch. Chicks are fully feathered at hatching and are precocial, being able to leave the nest and fend for themselves within a week.[12]
Conservation
The North Island brown kiwi is Vulnerable, per the IUCN Red List,[1] with the major threat coming from predators, such as dogs, cats, and stoat (Mustela erminea). 94% of chicks die before breeding in areas where mammalian pest control is not carried out.[12] It has an occurrence range of 38,400 km2 (14,800 sq mi), with a population, estimated in 2000, of 35,000.[2]
In 1996 there were around 35,000 North Island Brown Kiwis and in 2006 there were 20,000.[13]
Nationwide studies show that on average only 5 percent of kiwi chicks survive to adulthood. However, in areas under active pest management, survival rates for North Island brown kiwi can be far higher. For example, prior to a joint 1080 poison operation undertaken by DOC and the Animal Health Board in Tongariro Forest in 2006, 32 kiwi chicks were radio-tagged. 57% of the radio-tagged chicks survived to adulthood. Thanks to ongoing pest control, the adult kiwi population at Tongariro has almost doubled since 1998.[citation needed]
In 2022, 11 North Island Brown Kiwi were released on Wellington's South Coast after a 100 year absence.[14] Fifty more kiwi were released into the hills of Wellington in May 2023.[15]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 BirdLife International (2017). "Apteryx mantelli". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017: e.T45353580A119177586. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T45353580A119177586.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/45353580/119177586. Retrieved 18 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 BirdLife International (2008)
- ↑ Gill (2010). "Checklist of the birds of New Zealand, Norfolk and Macquarie Islands, and the Ross Dependency, Antarctica". Te Papa Press. http://nzbirdsonline.org.nz/sites/all/files/checklist/Checklist-of-Birds.pdf.
- ↑ Ümüt Çınar (2015). "01 Pᴀʟᴇᴏɢɴᴀᴛʜᴀᴇ : Sᴛʀᴜᴛʜɪᴏɴɪfᴏʀᴍᴇs, Rʜᴇɪfᴏʀᴍᴇs, Cᴀsᴜᴀʀɪɪfᴏʀᴍᴇs, Aᴘᴛᴇʀʏɢɪfᴏʀᴍᴇs, Aᴇᴘʏᴏʀɴɪᴛʜɪfᴏʀᴍᴇs, Dɪɴᴏʀɴɪᴛʜɪfᴏʀᴍᴇs, Lɪᴛʜᴏʀɴɪᴛʜɪfᴏʀᴍᴇs, Tɪɴᴀᴍɪfᴏʀᴍᴇs & Rᴇfᴇʀᴇɴᴄᴇs". http://kmoksy.com/zobot/birds_English.html.
- ↑ A History of the Birds of New Zealand
- ↑ Guinness World Records 2013, Page 050, Hardcover Edition. ISBN:9781904994879
- ↑ Le Duc, Diana; Renaud, Gabriel; Krishnan, Arunkumar; Almén, Markus Sällman; Huynen, Leon; Prohaska, Sonja J.; Ongyerth, Matthias; Bitarello, Bárbara D. et al. (2015-07-23). "Kiwi genome provides insights into evolution of a nocturnal lifestyle". Genome Biology 16 (1): 147. doi:10.1186/s13059-015-0711-4. ISSN 1465-6906. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-015-0711-4.
- ↑ "Massey News Article - do ya think I'm sexy?". http://masseynews.massey.ac.nz/2004/Press_Releases/11_09_04.html.
- ↑ Davies, S. J. J. F. (2003)
- ↑ Clements, J (2007)
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Save the Kiwi (2008)
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 BirdLife International
- ↑ Sales, James (1 May 2005). "The endangered kiwi: a review". Folia Zool: 20. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242117254. Retrieved 9 July 2021.
- ↑ "Brown kiwi released on Wellington's southwest coast" (in en-nz). 2022-11-22. https://www.rnz.co.nz/national/programmes/afternoons/audio/2018868095/brown-kiwi-released-on-wellington-s-southwest-coast.
- ↑ "Fifty kiwi set to be released into the hills of Wellington" (in en-nz). 2023-05-09. https://www.rnz.co.nz/news/national/489547/fifty-kiwi-set-to-be-released-into-the-hills-of-wellington.
Further reading
- Davies, S.J.J.F. (2003). "Kiwis". in Hutchins, Michael. Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia. 8 Birds I Tinamous and Ratites to Hoatzins (2nd ed.). Farmington Hills, MI: Gale Group. pp. 89–92. ISBN 978-0-7876-5784-0.
External links
- ARKive - images and movies of the North Island Brown Kiwi (Apteryx mantelli)
- Save the Kiwi (2008). "Population status of the North Island Brown Kiwi". Save the Kiwi. http://www.savethekiwi.org.nz/about-the-bird/brown-kiwi.html.
- BirdLife Species Factsheet
- Video of North Island Brown Kiwi feeding in full daylight
- Taranaki Kiwi Trust
Wikidata ☰ Q734829 entry
 |


