Biology:Outline of New Zealand
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to New Zealand:
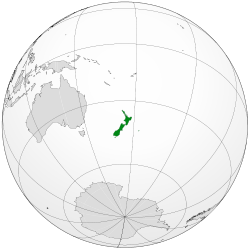
New Zealand is an island nation located in the western South Pacific Ocean comprising two large islands, the North Island and the South Island, and numerous smaller islands, most notably Stewart Island / Rakiura and the Chatham Islands.[1] The indigenous Māori originally called the North Island Aotearoa, commonly translated into English as "The Land of the Long White Cloud"; "Aotearoa" is now used as the Māori language name for the entire country.[2]
New Zealand is situated about 2,000 km (1,200 mi) southeast of Australia across the Tasman Sea, its closest neighbours to the north being New Caledonia, Fiji and Tonga. Because of its remoteness, it was one of the last lands to be settled by humans. During its long period of isolation, New Zealand developed a distinct biodiversity of animal, fungal and plant life. The country's varied topography and its sharp mountain peaks, such as the Southern Alps, owe much to the tectonic uplift of land and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, while its most populous city is Auckland.
The population is mostly of European descent, with the indigenous Māori being the largest minority. Asians and non-Māori Pasifika peoples are also significant minorities, especially in the cities. Charles III, as the King of New Zealand, is the head of state and, in his absence, is represented by a non-partisan governor-general. Political power is held by the democratically elected New Zealand Parliament under the leadership of the Prime Minister, who is the head of government. The Realm of New Zealand also includes the Cook Islands and Niue, which are self-governing but in free association; Tokelau; and the Ross Dependency (New Zealand's territorial claim in Antarctica).
General reference
- Pronunciation: /njuːˈziːlənd/ (
 listen)
listen) - Official English country name: New Zealand
- Official Māori country name: Aotearoa
- Endonym: New Zealand
- Adjectival: New Zealand
- Demonym: New Zealander, "Kiwi"
- Etymology: Name of New Zealand
- International rankings of New Zealand
- ISO country codes: NZ, NZL, 554
- ISO region codes: See NZ
- Internet country code top-level domain: .nz
Geography of New Zealand
Geography of New Zealand
- New Zealand is...
- a group of islands
- a country
- an island country
- a Commonwealth realm
- Location:
- Southern Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere
- Pacific Ocean
- South Pacific Ocean
- Oceania
- South Pacific Ocean
- Pacific Ocean
- Time in New Zealand:
- Chatham Islands – Chatham Standard Time (45), Chatham Daylight Time (45)
- Rest of New Zealand – New Zealand Standard Time (UTC+12), New Zealand Daylight Time (UTC+13) September–April
- Extreme points of New Zealand
- North: Nugent Island, Kermadec Islands
- South: Jacquemart Island, Campbell Islands
- East: Kahuitara Point, Pitt Island, Chatham Islands
- West: Cape Lovitt, Auckland Island
- High: Aoraki / Mount Cook 3,754 m (12,316 ft)
- Low: 45°55'02"S 170°10'58"E; near Momona, Taieri Plain, Otago -2 m[3][citation needed]
- Land boundaries: none
- Coastline: South Pacific Ocean 15,134 km[1] (10th)
- Southern Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere
- Population of New Zealand: 4,982,068 (30 April 2020) – 120th most populous country
- Area of New Zealand: 268,680 km2[1]
- Atlas of New Zealand
- Surveying in New Zealand
Environment of New Zealand
Environment of New Zealand
- Biodiversity of New Zealand
- Flora of New Zealand
- Fauna of New Zealand
- Birds of New Zealand
- Mammals of New Zealand
- Climate of New Zealand
- Climate change in New Zealand
- Ecoregions in New Zealand
- Environmental issues in New Zealand
- Geology of New Zealand
- List of earthquakes in New Zealand
- Natural history of New Zealand
- Stratigraphy of New Zealand
- Volcanism of New Zealand
- Pollution in New Zealand
- Protected areas of New Zealand
- Marine reserves of New Zealand
- National parks of New Zealand
- Renewable energy in New Zealand
Natural geographic features of New Zealand
- Caves of New Zealand
- Fjords of New Zealand
- Glaciers of New Zealand
- Islands of New Zealand
- Lakes of New Zealand
- Mountains of New Zealand
- Volcanoes in New Zealand
- Rivers of New Zealand
- Waterfalls of New Zealand
- List of rock formations of New Zealand
- World Heritage Sites in New Zealand
Political geography of New Zealand
Administrative divisions of New Zealand
Administrative divisions of New Zealand
- Regions of New Zealand
- Territorial authorities of New Zealand
- Districts of New Zealand
- Cities of New Zealand
Demography of New Zealand
Demographics of New Zealand
Government and politics of New Zealand
Politics of New Zealand
- Capital of New Zealand: Wellington
- Form of government:
- Elections in New Zealand
- Electoral system of New Zealand
- Voting in New Zealand
- Political parties in New Zealand
- Taxation in New Zealand
- Types
- Anarchism
- Christian
- Conservatism
- Fascism
- Feminism in New Zealand
- Māori
- Liberalism
- Populism
- Republicanism
- Socialism
- Issues
- Abortion
- Capital punishment
- Electoral reform
- Flag debate
- Gun law
- Nuclear-free zone
- Prostitution
- Same-sex marriage
- Treaty of Waitangi claims and settlements
- Policies
- Think Big
- Rogernomics
- Ruthanasia
- Working for Families
- Principles of the Treaty of Waitangi
Branches of the government of New Zealand
Executive branch of the government of New Zealand
- New Zealand Government
- Head of state: King of New Zealand, Charles III
- Governor-General of New Zealand, Dame Cindy Kiro
- Head of government: Prime Minister of New Zealand, Chris Hipkins
- Ministers in the New Zealand Government
- Cabinet of New Zealand
- Head of state: King of New Zealand, Charles III
Legislative branch of the government of New Zealand
- New Zealand Parliament (unicameral)
- New Zealand House of Representatives
Judicial branch of the government of New Zealand
- Judiciary of New Zealand
- Supreme Court of New Zealand
- Judicial review in New Zealand
Foreign relations of New Zealand
Foreign relations of New Zealand
- Diplomatic missions in New Zealand
- Diplomatic missions of New Zealand
- Australia–New Zealand relations
- New Zealand–United Kingdom relations
International organisation membership
New Zealand is a member of:[1]
|
|
Law and order in New Zealand
Law of New Zealand
- Cannabis in New Zealand
- Capital punishment in New Zealand
- Constitution of New Zealand
- Crime in New Zealand
- Human rights in New Zealand
- Disability rights in New Zealand
- LGBT rights in New Zealand
- Law enforcement in New Zealand
- Terrorism in New Zealand
Military of New Zealand
New Zealand Defence Force
- Ministry of Defence of New Zealand
- Forces
- Army of New Zealand
- Navy of New Zealand
- Air Force of New Zealand
- Special Forces of New Zealand
- Military history of New Zealand
- Military ranks of New Zealand
Local government in New Zealand
Local government in New Zealand
History of New Zealand
History of New Zealand
- Archaeology of New Zealand
- Independence of New Zealand
- Military history of New Zealand
- Political history of New Zealand
- Treaty of Waitangi
- Waihi miners' strike
- 1951 waterfront dispute
- 1981 Springbok Tour
- Rogernomics
- Ruthanasia
- 1993 electoral referendum
- Political scandals in New Zealand
- Corngate
- Foreshore and seabed controversy
- Orewa speech
- Tea tape scandal
- Timeline of New Zealand history
Culture of New Zealand
Culture of New Zealand
- Architecture of New Zealand
- Cuisine of New Zealand
- Festivals in New Zealand
- Housing in New Zealand
- Languages of New Zealand
- New Zealand English
- Māori language
- New Zealand Sign Language
- Māori culture
- Media in New Zealand
- Museums in New Zealand
- National symbols of New Zealand
- Coat of arms of New Zealand
- Flag of New Zealand
- National anthems of New Zealand
- Public holidays in New Zealand
- Religion in New Zealand
- Christianity in New Zealand
- Hinduism in New Zealand
- Islam in New Zealand
- Judaism in New Zealand
- Sikhism in New Zealand
- World Heritage Sites in New Zealand
Art in New Zealand
- Art of New Zealand
- Cinema of New Zealand
- Literature of New Zealand
- Music of New Zealand
- Television in New Zealand
- Theatre in New Zealand
- Kapa haka
Sports in New Zealand
Sports in New Zealand
- Rugby union in New Zealand (national sport)
- Rugby league in New Zealand
- Football in New Zealand
- Horse racing in New Zealand
- New Zealand at the Olympics
- Stadiums in New Zealand
- Horse tracks in New Zealand
Economy and infrastructure of New Zealand
Economy of New Zealand
- Agriculture in New Zealand
- Banks in New Zealand
- Reserve Bank of New Zealand
- Communications in New Zealand
- Internet in New Zealand
- Telecommunications in New Zealand
- Companies of New Zealand
- Currency of New Zealand: Dollar
- ISO 4217: NZD
- Energy in New Zealand
- New Zealand Emissions Trading Scheme
- Oil and gas industry in New Zealand
- Health care in New Zealand
- Hospitals in New Zealand
- Mental health in New Zealand
- Mining in New Zealand
- New Zealand Stock Exchange
- Tourism in New Zealand
- Transport in New Zealand
- Airports in New Zealand
- Rail transport in New Zealand
- Roads in New Zealand
- Water supply and sanitation in New Zealand
Education in New Zealand
- Education in New Zealand
- Secondary education in New Zealand
- Tertiary education in New Zealand
See also
- List of articles about Australia and New Zealand jointly
- List of international rankings
- List of New Zealand-related topics
- Member state of the Commonwealth of Nations
- Member state of the United Nations
- Monarchy of New Zealand
- Outline of geography
- Outline of Oceania
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "New Zealand". The World Factbook. United States Central Intelligence Agency. 2 July 2009. https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/new-zealand/.
- ↑ McLintock, A. H. (24 November 2009). "Aotearoa". An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand. https://teara.govt.nz/en/1966/aotearoa. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ "NZ Topo Map". https://www.topomap.co.nz/NZTopoMap?v=2&ll=-45.91722,170.18278&z=14&pin=1&lbl=45°55′02″S%20170°10′58″E.
External links
- Te Ara, The Encyclopedia of New Zealand
- New Zealand Plant Conservation Network website for information about the indigenous flora and species of introduced weed and animal pest
- Ministry for Culture and Heritage – includes information on flag, anthems and coat of arms
- New Zealand Government portal
- Congressional Research Service (CRS) Reports regarding New Zealand
- New Zealand weather
- NZHistory.net.nz New Zealand history website
- New Zealand in Profile 2007, by Statistics New Zealand
- Tourism New Zealand
 |